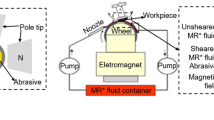
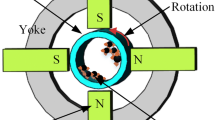
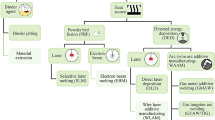
Abstract
Magnetic field-assisted finishing (MFAF) technology, as a non-traditional surface finishing technology, has a unique advantage in machining components composed of complex shapes and difficult-to-process materials and has been widely concerned. To date, more than thirty MFAF technologies have been developed; however, there has not been a detailed study to classify these technologies and compare and contrast the advantages and limitations of these technologies. Therefore, in order to promote the development of MFAF technology, MFAF technology is reviewed in detail in this study. This paper introduces the origin and development of MFAF technology and proposes a classification method based on media. On this basis, the differences of wear mechanisms and the action mechanism of composite processing are discussed, the representative MFAF techniques are overviewed, and the commonly used material removal models of MFAF techniques are summarized. Finally, the possible research directions of MFAF process in the future are described. This paper has important reference value for researchers in the field of ultra-precision machining.



































Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
Abbreviations
- MFAF:
-
Magnetic field-assisted finishing
- MAF:
-
Magnetic abrasive finishing
- MAFF:
-
Magnetic abrasive flow finishing
- MAJ:
-
Magnetic abrasive jet finishing
- V-MAF:
-
Vibration-magnetic abrasive composite finishing
- E-MAF:
-
Electrolytic-magnetic abrasive composite finishing
- C-MAF:
-
Chemical-magnetic abrasive composite finishing
- V-C-MAF:
-
Vibration chemical-magnetic abrasive composite finishing
- V-E-MAF:
-
Vibration electrolytic-magnetic abrasive composite finishing
- MNF:
-
Magnetic needle finishing
- V-MNF:
-
Vibration-magnetic needle finishing
- C-MNF:
-
Chemical-magnetic needle finishing
- AFM:
-
Abrasive flow machining
- ECM:
-
Electrochemical machining
- MFG:
-
Magnetic fluid grinding
- MFP:
-
Magnetic fluid floating polishing
- MFAP:
-
Magnetic field-assisted uniform pressure polishing
- MRF:
-
Magnetorheological finishing
- MRFPF:
-
Magnetorheological foam plane finishing
- MJP:
-
Magnetorheological jet polishing
- MRAFF:
-
Magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing
- MCFF:
-
Magnetic composite fluid finishing
- MSTF:
-
Magnetic shear thickening finishing
- EMRF:
-
Electromagnetic rheological finishing
- ERF:
-
Electrorheological finishing
- MAGIC:
-
Magnetic intelligent composite polishing
- MHF:
-
Magnetic honing finishing
- MRR :
-
Material removal rate
- MR :
-
Material removal
References
Ciambriello L, Cavaliere E, Gavioli L (2022) Influence of roughness, porosity and grain morphology on the optical properties of ultrathin Ag films. Appl Surface Sci 576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151885
Alves H P, Castro de Barros T H, Silva Nascimento D L et al (2022) Influence of surface roughness on the sensitivity of a D-shaped optical fiber-based refractive index sensor. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.113702
Oh SH, Cho SU, Kim CS et al (2011) Fabrication of nickel stamp with improved sidewall roughness for optical devices. Microelectron Eng 88(9):2900–2907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2011.03.021
Yianni S A, Creedon D L, Schenk A K et al (2021) Correlation between electronic micro-roughness and surface topography in two-dimensional surface conducting hydrogen-terminated diamond. Diam Relat Mater 116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108377
Liu X-l, Cai Z-b, Liu S-b et al (2017) Effect of roughness on electrical contact performance of electronic components. Microelectron Reliab 74:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2017.05.024
Logunov AV, Zavodov SA, Danilov DV (2019) The challenges in development of nickel-based heat-resistant superalloys for gas turbine disks and creation of a new superalloy with increased operational characteristics. Mater Today: Proceedings 11:459–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.01.013
Zhao Q, Sun Q, Xin S et al (2022) High-strength titanium alloys for aerospace engineering applications: a review on melting-forging process. Mater Sci Eng: A 845:143260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.143260
Ramesh S, Karunamoorthy L, Palanikumar K (2012) Measurement and analysis of surface roughness in turning of aerospace titanium alloy (gr5). Measurement 45(5):1266–1276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2012.01.010
Catalucci S, Senin N, Sims-Waterhouse D et al (2020) Measurement of complex freeform additively manufactured parts by structured light and photogrammetry. Measurement 164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108081
Hu X, Park SH, Gil ES et al (2011) The influence of elasticity and surface roughness on myogenic and osteogenic-differentiation of cells on silk-elastin biomaterials. Biomaterials 32(34):8979–8989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.037
Xia Z, Fang F, Ahearne E et al (2020) Advances in polishing of optical freeform surfaces: a review. J Mater Process Technol 286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116828
Ronoh K, Mwema F, Dabees S et al (2022) Advances in sustainable grinding of different types of the titanium biomaterials for medical applications: a review. Biomed Eng Adv 4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bea.2022.100047
Zhu W-L, Beaucamp A (2020) Compliant grinding and polishing: a review. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2020.103634
Li G, Bao Y, Wang H et al (2023) An online monitoring methodology for grinding state identification based on real-time signal of CNC grinding machine. Mech Syst Signal Process 200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2023.110540
Yu S, Yao P, Xu J et al (2023) Profile error compensation in ultra-precision grinding of aspherical-cylindrical lens array based on the real-time profile of wheel and normal residual error. J Mater Process Technol 312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117849
Singh A K, Kumar A, Sharma V et al (2020) Sustainable techniques in grinding: state of the art review. J Clean Prod 269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121876
Deng T, Li J, Zheng Z (2020) Fundamental aspects and recent developments in metal surface polishing with energy beam irradiation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.103472
Xiao H, Dai Y, Duan J et al (2021) Material removal and surface evolution of single crystal silicon during ion beam polishing. Appl Surface Sci 544 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.148954
Wang J, Chen J, Jin T et al (2020) Preparation of nanotwinned cBN cutting edge by combining mechanical lapping and ion beam polishing. Diam Relat Mater 105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2020.107801
Fang N, Birch R, Britton T B (2022) Optimizing broad ion beam polishing of zircaloy-4 for electron backscatter diffraction analysis. Micron 159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2022.103268
Meng F, Yu T, Wiercigroch M et al (2023) Profile prediction for ultrasonic vibration polishing of alumina ceramics. Int J Mech Sci 252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108360
Yuan Z, Xiang D, Peng P et al (2023) A comprehensive review of advances in ultrasonic vibration machining on SiCp/Al composites. J Mater Res Technol 24:6665–6698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.04.245
Deng H, Zhong M, Xu W (2023) Effects and mechanisms of different types of surfactants on sapphire ultrasonic polishing. Tribol Int 187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2023.108734
Kumar AS, Deb S, Paul S (2021) Ultrasonic-assisted abrasive micro-deburring of micromachined metallic alloys. J Manuf Process 66:595–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.04.019
Liu S, Li C, Jin X et al (2023) Quantitative-regulated material removal rate in solid dielectric electrochemical polishing (QRR-SDEP) for smoothing high roughness surface of additively manufactured 316L stainless steel components. Addit Manuf 73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2023.103689
Cheng J, Kang R, Dong Z et al (2023) A new polishing method for complex structural parts: moist particle electrolyte electrochemical mechanical polishing (MPE-ECMP). Electrochem Commun 150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2023.107475
Wu W, Wang J, Liu Q et al (2022) Electrochemical polishing assisted selective laser melting of biomimetic superhydrophobic metallic parts. Appl Surface Sci 596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153601
Chen X, Liang Y, Cui Z et al (2022) Study on material removal mechanism in ultrasonic chemical assisted polishing of silicon carbide. J Manuf Process 84:1463–1477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.11.014
Liu H, Ye M, Ye Z et al (2022) High-quality surface smoothening of laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing AlSi10Mg via intermittent electrochemical polishing. Surface Coat Technol 443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128608
Mu J, Sun T, Leung CLA et al (2023) Application of electrochemical polishing in surface treatment of additively manufactured structures: a review. Progress Mater Sci 136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2023.101109
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Ming W et al (2021) A review on magnetic field assisted electrical discharge machining. J Manuf Process 64:694–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.01.054
Peruri S R, Chaganti P K (2019) A review of magnetic-assisted machining processes. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41(10). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1944-z
Bains PS, Sidhu SS, Payal HS (2017) Magnetic field assisted EDM: new horizons for improved surface properties. SILICON 10(4):1275–1282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9600-7
Ahmad S, Singari RM, Mishra RS (2021) Development of Al2O3-SiO2 based magnetic abrasive by sintering method and its performance on Ti-6Al-4V during magnetic abrasive finishing. Trans IMF 99(2):94–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/00202967.2021.1865644
Xie H, Zou Y (2021) Study on the magnetic abrasive finishing process using alternating magnetic field—discussion on the influence of current waveform variation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114(7–8):2471–2483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07048-9
Singh M, Singh AK (2019) Performance investigation of magnetorheological finishing of rolls surface in cold rolling process. J Manuf Process 41:315–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.04.007
Amir M, Mishra V, Sharma R et al (2022) Development of magnetic nanoparticle based nanoabrasives for magnetorheological finishing process and all their variants. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.11.033
Ghosh G, Sidpara A, Bandyopadhyay P P (2021) Magnetorheological finishing of WC-Co coating using iron-B4C-CNT composite abrasives. Tribol Int 155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106807
Wang Y, Wu Y, Nomura M (2016) Feasibility study on surface finishing of miniature V-grooves with magnetic compound fluid slurry. Precis Eng 45:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.01.010
Wan S, Wei C, Hu C et al (2021) Novel magic angle-step state and mechanism for restraining the path ripple of magnetorheological finishing. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2020.103673
Bae JT, Kim HJ (2021) Finishing characteristics of Inconel alloy 625 bars in ultra-precision magnetic abrasive finishing using CNC machine center. J Mech Sci Technol 35(7):2851–2859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-021-0608-y
Kumar M, Das M (2022) Impact of different magnetorheological fluid compositions on poppet valve profile polishing. Precis Eng 76:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2022.03.002
Gupta M K, Dinakar D, Chhabra I M et al (2021) Experimental investigation and machine parameter optimization for nano finishing of fused silica using magnetorheological finishing process. Optik 226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165908
Bedi TS, Kant R (2021) Comparative performance of magnetorheological external finishing tools using different magnetic structures. Mater Today: Proceedings 41:908–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.485
Zhang Z, Geng K, Qiao G et al (2021) The heat flow coupling effect of laser-assisted magnetorheological polishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114(1–2):591–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06880-3
Wang C, Cheung C F, Ho L T et al (2020) A novel magnetic field-assisted mass polishing of freeform surfaces. J Mater Process Technol 279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116552
Bedi TS, Singh AK (2015) Magnetorheological methods for nanofinishing – a review. Part Sci Technol 34(4):412–422. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2015.1081657
Yadav PK, Jayswal SC, Saxena KK (2020) Magnetic abrasive flow finishing: a review. Mater Today: Proceedings 26:3257–3264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.909
Malpotra A, Singh B, Singh L (2023) Electrolytic magnetic abrasive finishing process – a review. Mater Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.03.237
Han R, Yang G, Zhao G et al (2023) Strengthening mechanism and three-body impact abrasive wear behavior of the hot-rolled air-cooling martensitic wear resistant steel. J Mater Res Technol 24:3023–3032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.03.216
Zhu P, Zhang G, Du J et al (2021) Removal mechanism of magnetic abrasive finishing on aluminum and magnesium alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114(5–6):1717–1729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06952-4
Pandiyan V, Shevchik S, Wasmer K et al (2020) Modelling and monitoring of abrasive finishing processes using artificial intelligence techniques: a review. J Manuf Process 57:114–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.06.013
Moore MA (1974) A review of two-body abrasive wear. Wear 27:1–17
Sun J, Fang L, Han J et al (2014) Phase transformations of mono-crystal silicon induced by two-body and three-body abrasion in nanoscale. Comput Mater Sci 82:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.09.055
Song D, Du H, Lin J et al (2022) A review on magnetorheological jet polishing technique for microstructured functional surfaces. Lubricants 10(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10100237
Luo Q, Lu J, Xu X (2016) Study on the processing characteristics of SiC and sapphire substrates polished by semi-fixed and fixed abrasive tools. Tribol Int 104:191–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.09.003
Kang M, Gu Y, Lin J et al (2023) Material removal mechanism of non-resonant vibration-assisted magnetorheological finishing of silicon carbide ceramics. Int J Mech Sci 242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107986
Yin SH, Wang Y, Shinmura T et al (2008) Material removal mechanism in vibration-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing. Adv Mater Res 53–54:57–63. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.53-54.57
Guo J, Feng W, Jong HJH et al (2020) Finishing of rectangular microfeatures by localized vibration-assisted magnetic abrasive polishing method. J Manuf Process 49:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.11.026
Misra A, Pandey PM, Dixit US et al (2017) Modeling of finishing force and torque in ultrasonic-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part B: J Eng Manuf 233(2):411–425. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405417737579
Misra A, Pandey PM, Dixit US et al (2018) Multi-objective optimization of ultrasonic-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 101(5–8):1661–1670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3060-0
Gu Y, Fu B, Lin J et al (2023) A novel wheel-type vibration-magnetorheological compound finishing method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 125(9–10):4213–4235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11034-8
Yun H, Han B, Chen Y et al (2015) Internal finishing process of alumina ceramic tubes by ultrasonic-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85(1–4):727–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7927-z
Judal KB, Yadava V, Pathak D (2013) Experimental investigation of vibration assisted cylindrical–magnetic abrasive finishing of aluminum workpiece. Mater Manuf Process 28(11):1196–1202. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2013.811725
Zheng J, Guo Y, Zhu L et al (2021) Cavitation effect in two-dimensional ultrasonic rolling process. Ultrasonics 115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2021.106456
Fu Y, Zhu X, Wang J et al (2022) Numerical study of the synergistic effect of cavitation and micro-abrasive particles. Ultrason Sonochem 89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106119
Tian J, Liu H, Cheng J et al (2022) Improving the small ball-end magnetorheological polishing efficiency of fused silica workpiece by the promoting effect of water-bath heating and sodium hydroxide addition on polishing velocity and chemical reaction. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 123(1–2):645–656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10180-9
Rajput AS, Das M, Kapil S (2022) Investigations on a hybrid chemo-magnetorheological finishing process for freeform surface quality enhancement. J Manuf Process 81:522–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.07.015
Liu G, Zhao Y, Meng J et al (2022) Preparation of Al2O3 magnetic abrasives by combining plasma molten metal powder with sprayed abrasive powder. Ceram Int 48(15):21571–21578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.04.129
Li W, Li J, Cheng B et al (2021) Achieving in-situ alloy-hardening core-shell structured carbonyl iron powders for magnetic abrasive finishing. Mater Des 212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110198
Qin P, Zhang G, Zhao Y et al (2020) Study of CBN/Fe-based spherical magnetic abrasive bonding interfacial microstructure prepared by gas atomization with rapid solidification. Adv Powder Technol 31(4):1597–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.01.036
Pandey K, Pandey PM (2019) An integrated application of chemo-ultrasonic approach for improving surface finish of Si (100) using double disk magnetic abrasive finishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103(9–12):3871–3886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03829-5
Singh Farwaha H, Deepak D, Singh Brar G (2020) Design and performance of ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process set up for machining and finishing of 316L stainless steel. Mater Today: Proceedings 33:1626–1631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.143
Chen HL, Zhang YX, Yan WL (2004) The technology of finishing process of die space based upon magnetic abrasive finishing. Key Eng Mater 259–260:657–661. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.259-260.657
Wang Y, Hu DJ (2004) Mechanical cutting model of magnetic abrasive particles and analysis of experimental results. Key Eng Mater 274–276:451–456. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.274-276.451
Ahmad S, Singari RM, Mishra RS (2021) Tri-objective constrained optimization of pulsating DC sourced magnetic abrasive finishing process parameters using artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Mater Manuf Process 36(7):843–857. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1866196
Jiang L, Zhang G, Du J et al (2021) Processing performance of Al2O3/Fe-based composite spherical magnetic abrasive particles. J Magn Magn Mater 528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.167811.
Lin C-T, Yang L-D, Chow H-M (2006) Study of magnetic abrasive finishing in free-form surface operations using the Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(1–2):122–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0573-8
Kang J, Yamaguchi H (2012) Internal finishing of capillary tubes by magnetic abrasive finishing using a multiple pole-tip system. Precis Eng 36(3):510–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2012.01.006
Heng L, Kim JS, Song JH et al (2021) Application of Al2O3/iron-based composite abrasives on MAF process for inner surface finishing of oval-shaped tube: predicting results of MAF process using artificial neural network model. J Mater Res Technol 15:3268–3282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.09.146
Kang J, George A, Yamaguchi H (2012) High-speed internal finishing of capillary tubes by magnetic abrasive finishing. Procedia CIRP 1:414–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2012.04.074
Patil MG, Chandra K, Misra PS (2011) Magnetic abrasive finishing – a review. Adv Mater Res 418–420:1577–1581. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.418-420.1577
Tan KL, Yeo S-H, Ong CH (2016) Nontraditional finishing processes for internal surfaces and passages: a review. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part B: J Eng Manuf 231(13):2302–2316. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405415626087
Qian C, Fan Z, Tian Y et al (2020) A review on magnetic abrasive finishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 112(3–4):619–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06363-x
Singh B, Chaudhary S, Bhardwaj S et al (2023) A review on micro finishing by magnetic abrasive finishing: challenges and opportunities. Mater Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.02.070
Singh S, Shan HS (2002) Development of magneto abrasive flow machining process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:953–959
Sehijpal Singh HSS, Kumar P (2002) Wear behavior of materials in magnetically assisted abrasive flow machining. J Mater Process Technol 128:155–161
Singh P, Singh L, Singh S (2020) Manufacturing and performance analysis of mechanically alloyed magnetic abrasives for magneto abrasive flow finishing. J Manuf Process 50:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.12.033
Jeong-Du Kim Y-H K, Young-Han Bae, Su-Won Lee (1997) Development of a magnetic abrasive jet machining system for precision internal polishing of circular tubes. J Mater Process Technol 71:384-393
Singh A, Ghosh S, Aravindan S (2019) Influence of dry micro abrasive blasting on the physical and mechanical characteristics of hybrid PVD-AlTiN coated tools. J Manuf Process 37:446–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.11.024
Mulik RS, Pandey PM (2010) Mechanism of surface finishing in ultrasonic-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. Mater Manuf Process 25(12):1418–1427. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2010.499580
Heng L, Kim JS, Tu J-F et al (2020) Fabrication of precision meso-scale diameter ZrO2 ceramic bars using new magnetic pole designs in ultra-precision magnetic abrasive finishing. Ceram Int 46(11):17335–17346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.022
Wang L, Sun Y, Chen F et al (2022) Experimental study on vibration-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing for internal blind cavity by bias external rotating magnetic pole. Precis Eng 74:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2021.11.007
Mulik RS, Pandey PM (2011) Ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing of hardened AISI 52100 steel using unbonded SiC abrasives. Int J Refract Metals Hard Mater 29(1):68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2010.08.002
Guo C, Zhang D, Li X et al (2022) A permanent magnet tool in ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing for 30CrMnSi grooves part. Precis Eng 75:180–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2022.02.010
Guo J, Kum CW, Au KH et al (2016) New vibration-assisted magnetic abrasive polishing (VAMAP) method for microstructured surface finishing. Opt Expr 24(12):13542–13554. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.013542
Liu GY, Guo ZN, Li YB et al (2011) Composite tools design for electrolytic magnetic abrasive finishing process with FEM. Adv Mater Res 325:536–541. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.325.536
Muhamad MR, Jamaludin MF, Karim MSA et al (2018) Effects of electrolysis on magnetic abrasive finishing of AA6063-T1 tube internal surface using combination machining tool. Materialwiss Werkstofftech 49(4):442–452. https://doi.org/10.1002/mawe.201700266
Sun X, Zou Y (2017) Development of magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process for finishing SUS304 stainless steel plane. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92(9–12):3373–3384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0408-9
Zou Y, Xing B, Sun X (2020) Study on the magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process—investigation of machining mechanism. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 108(5–6):1675–1689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05442-3
Xing B, Zou Y (2020) Investigation of finishing aluminum alloy A5052 using the magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolytic process. Machines 8(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8040078.
Du ZW, Chen Y, Zhou K et al (2015) Research on the electrolytic-magnetic abrasive finishing of nickel-based superalloy GH4169. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 81(5–8):897–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7270-4
Muhamad MR, Zou Y, Sugiyama H (2016) Investigation of the finishing characteristics in an internal tube finishing process by magnetic abrasive finishing combined with electrolysis. Trans IMF 94(3):159–165. https://doi.org/10.1080/00202967.2016.1162400
Pandey N, Singh R, Pant P et al (2018) Development of mathematical model for material removal and surface roughness in electrolytic magnetic abrasive finishing process. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 404. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/404/1/012053
Singh G, Kumar H (2021) Influence of chemically assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process parameters on external roundness of Inconel 625 tubes. Mater Today: Proceedings 37:3283–3288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.114
Kumar H, Singh G (2021) Parametric studies on finishing of inconel 718 flat surfaces with chemically assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. Mater Today: Proceedings 37:3262–3269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.110
Singh G, Kumar H, Kansal HK (2020) Investigations into internal roundness of Inconel 625 tubes with chemically assisted magnetic abrasive finishing. Mater Today: Proceedings 33:1579–1585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.002
Pandey K, Pandey U, Pandey PM (2018) Statistical modeling and surface texture study of polished silicon wafer Si (100) using chemically assisted double disk magnetic abrasive finishing. SILICON 11(3):1461–1479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9961-6
Pandey K, Pandey PM (2017) Chemically assisted polishing of monocrystalline silicon wafer Si (100) by DDMAF. Proc Eng 184:178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.04.083
CHENG Hai-dong, MA Xiao-gang, HAN Bing et al (2022). Removal of oxide scale on weld surface of pipe fittings by vibration assisted magnetic needle magnetic Grindina. Surf Technol. 51(08):400–407+459. https://doi.org/10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2022.08.036
Chen Yan, Yugang H, Yini L et al (2019) A magnetic needle magnetic grinding method and device for complex shape workpieces [p].Chinese patent: CN110000688A. 2019.07.12
Xu H, Kang R, Zhu X et al (2020) Study and analysis of removing the carbon deposition on the inner surface of a turbo-shaft by chemically assisted magnetic grinding. Front Mater 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2020.00232
Li X, Yu Q, Zhou X et al (2023) Magnetic sensing technology of fiber optic interferometer based on magnetic fluid: a review. Measurement 216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2023.112929
Umehara N, Hayashi T, Kato K (1995) In situ observation of the behavior of abrasives in magnetic fluid grinding. J Magn Magn Mater 149:181–184
Umehara N, Kalpakjian S (1994) Magnetic fluid grinding – a new technique for finishing advanced ceramics. CIRP Ann 43(1):185–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-8506(07)62192-1
Lee R-T, Hwang Y-C, Chiou Y-C (2009) Dynamic analysis and grinding tracks in the magnetic fluid grinding system. Precis Eng 33(1):81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2008.04.001
Lee R-T, Hwang Y-C, Chiou Y-C (2009) Dynamic analysis and grinding tracks in the magnetic fluid grinding system. Precis Eng 33(1):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2008.04.004
Umehara N, Kirtane T, Gerlick R et al (2006) A new apparatus for finishing large size/large batch silicon nitride (Si3N4) balls for hybrid bearing applications by magnetic float polishing (MFP). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46(2):151–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.04.015
Jiang M, Komanduri R (1997) Application of Taguchi method for optimization of finishing conditions in magnetic float polishing (MFP). Wear 213:59–71
.H.C. Childs D J M (2001) Wear and cost issues in magnetic fluid grinding. Wear 249(2001):509–516
Umehara N, Komanduri R (1996) Magnetic fluid grinding of HIP-Si3N4 rollers. Wear 192:85–93
Zhang B, Nakajima A (2003) Dynamics of magnetic fluid support grinding of Si3N4 ceramic balls for ultraprecision bearings and its importance in spherical surface generation. Precis Eng 27:1–8
Suzuki H, Kodera S, Hara S et al (1989) Magnetic field-assisted polishing——application to a curved surface. Precis Eng:197–202
Suzuki H, Okada M, Lin W et al (2014) Fine finishing of ground DOE lens of synthetic silica by magnetic field-assisted polishing. CIRP Ann 63(1):313–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2014.03.027
Kumar S, Sehgal R, Wani M F et al (2021) Stabilization and tribological properties of magnetorheological (MR) fluids: a review. J Magn Magn Mater 538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168295
Shlyago Y I, Bibik E E, V.S.Evstishenkov et al (1978) Use of magnetorheological liquids with an abrasive filler for the finishing of glass. Glass Ceram 35(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00695095
Zhao F, Zhang Z, Yang J et al (2023) Advanced nonlinear rheology magnetorheological finishing: a review. Chin J Aeronaut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2023.06.006
Liu S, Wang H, Hou J et al (2022) Morphology characterization of polishing spot and process parameters optimization in magnetorheological finishing. J Manuf Process 80:259–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.06.008
Liu H, Cheng J, Wang T et al (2019) Magnetorheological finishing of an irregular-shaped small-bore complex component using a small ball-end permanent-magnet polishing head. Nanotechnol Precis Eng 2(3):125–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npe.2019.10.001
Ghosh G, Sidpara A, Bandyopadhyay PP (2021) Experimental and theoretical investigation into surface roughness and residual stress in magnetorheological finishing of OFHC copper. J Mater Process Technol 288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116899
Arora K, Singh AK (2021) Theoretical and experimental investigation on surface roughness of straight bevel gears using a novel magnetorheological finishing process. Wear 476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2021.203693
Yadav RD, Singh AK, Arora K (2020) Parametric analysis of magnetorheological finishing process for improved performance of gear profile. J Manuf Process 57:254–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.06.024
Luo H, Guo M, Yin S et al (2018) An atomic-scale and high efficiency finishing method of zirconia ceramics by using magnetorheological finishing. Appl Surface Sci 444:569–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.091
Wang W, Ji S, Zhao J (2023) Review of magnetorheological finishing on components with complex surfaces. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11611-x
Gu Y, Kang M, Lin J et al (2021) Non-resonant vibration-assisted magnetorheological finishing. Precis Eng 71:263–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2021.03.016
Liang H, Yan Q, Lu J et al (2019) Material removal mechanisms in chemical-magnetorheological compound finishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103(1–4):1337–1348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03594-5
Ghasemi SH, Hantehzadeh MR, Sabbaghzadeh J et al (2012) Designing a plano-convex aspheric lens for fiber optics collimator. Opt Lasers Eng 50(2):293–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2011.07.014
Fu X, Duan F, Jiang J et al (2022) Optical design of a broadband spectrometer with compact structure based on echelle and concave gratings. Opt Lasers Eng 151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2021.106926
Beaucamp A, Simon P, Charlton P et al (2017) Brittle-ductile transition in shape adaptive grinding (SAG) of SiC aspheric optics. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 115:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.11.006
Natarajan Y, Murugesan PK, Mohan M et al (2020) Abrasive water jet machining process: a state of art of review. J Manuf Process 49:271–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.11.030
Yang L, Zhang X, Chen Y et al (2007) Optimization of removal function for magnetorheological jet polishing, 3rd international symposium on advanced optical manufacturing and testing technologies: advanced optical manufacturing technologies. 6722(6722). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.783038
Yang H, Cheng H, Wu H et al (2017) Electromagnetic optimization of the integrated magnetorheological jet polishing tool and its application in millimeter-scale discontinuous structure processing. Appl Opt 56(11):3162–3170. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.56.003162
Kordonski W, Shorey A, Sekeres A (2003) New magnetically assisted finishing method: material removal with magnetorheological fluid jet. Opt Manuf Test V:107–114
Kordonski W I, Shorey A B, Tricard M (2006) Magnetorheological Jet „MR JetTM… finishing technology. JANUARY 128:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2140802
Kordonski W, Shorey A (2016) Magnetorheological (MR) jet finishing technology. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 18(12):1127–1130. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389x07083139
Tricard M, Kordonski WI, Shorey AB et al (2006) Magnetorheological jet finishing of conformal, freeform and steep concave optics. CIRP Ann 55(1):309–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-8506(07)60423-5
Kordonski, Webster WI (2001) Apparatus and method for abrasive jet finishing of deeply concave surfaces using magnetorheological fluid [p]. European Patent: 01127843.9.2001.11.22
Kordonski, Webster WI (1999) System for abrasive jet shaping and polishing of a surface using magnetorheological fluid [p]. International patent: WO 99/48643.1999.9.30
Li P-y A, Cheung M-f M, Tong H et al (2014) Design and implementation of a technique for iterative magnetorheological jet polishing. Int J Optomechatronics 8(3):195–205. https://doi.org/10.1080/15599612.2014.915603
Kim W-B, Lee S-H, Min B-K (2004) Surface finishing and evaluation of three-dimensional silicon microchannel using magnetorheological fluid. Trans ASME 126:772–778. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1811113
Yang H, Cheng H, Feng Y et al (2018) Removal of millimeter-scale rolled edges using bevel-cut-like tool influence function in magnetorheological jet polishing. Appl Opt 57(13):3377–3384. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.003377
Jha S, Jain VK (2004) Design and development of the magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (MRAFF) process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44(10):1019–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.03.007
Jha S, Jain VK, Komanduri R (2006) Effect of extrusion pressure and number of finishing cycles on surface roughness in magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (MRAFF) process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 33(7–8):725–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0502-x
Jha S, Jain VK (2006) Nanofinishing of silicon nitride workpieces using magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing. Nano Manuf 1:17–25
Jha S, Jain VK (2008) Rheological characterization of magnetorheological polishing fluid for MRAFF. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42(7–8):656–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1637-8
Nagdeve L, Jain VK, Ramkumar J (2017) Preliminary investigations into nano-finishing of freeform surface (femoral) using inverse replica fixture. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100(5–8):1081–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1459-7
Sharma VK (2021) Modeling and analysis of a novel rotational magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing process. Int J Lightweight Mat Manuf 4(3):290–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlmm.2021.02.001
Das M, Jain VK, Ghoshdastidar PS (2011) Nanofinishing of flat workpieces using rotational–magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (R-MRAFF) process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(1–4):405–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3808-2
Kheradmand S, Esmailian M, Fatahy A (2016) A novel approach of magnetorheological abrasive fluid finishing with swirling-assisted inlet flow. Results Phys 6:568–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2016.08.014
Das M, Jain VK, Ghoshdastidar PS (2011) The out-of-roundness of the internal surfaces of stainless steel tubes finished by the rotational–magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing process. Mater Manuf Process 26(8):1073–1084. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2010.537141
Kumar S, Jain VK, Sidpara A (2015) Nanofinishing of freeform surfaces (knee joint implant) by rotational-magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (R-MRAFF) process. Precis Eng 42:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.04.014
Choopani Y, Razfar MR, Khajehzadeh M et al (2022) Design and development of ultrasonic assisted-rotational magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (UA-RMRAFF) process. Appl Acoustics 197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2022.108950
Mohseni-Mofidi S, Pastewka L, Teschner M et al (2022) Magnetic-assisted soft abrasive flow machining studied with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Appl Math Modell 101:38–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2021.07.015
Shimada K, Wu Y, Wong YC (2003) Effect of magnetic cluster and magnetic field on polishing using magnetic compound fluid (MCF). J Magn Magn Mater 262(2):242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-8853(02)01497-x
Shimada K, Shuchi S, Shibayama A et al (2004) Effect of a magnetic cluster on the magnetic pressure of a magnetic compound fluid. Fluid Dyn Res 34(1):21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluiddyn.2003.09.002
Sato T, Wu YB, Lin WM et al (2009) Study of three-dimensional polishing using magnetic compound fluid (MCF). Adv Mater Res 76–78:288–293. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.76-78.288
Sato T, Wu YB, Lin WM et al (2010) Study of dynamic magnetic field assisted finishing for metal mold using magnetic compound fluid (MCF). Key Eng Mater 447–448:258–262. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.447-448.258
Jiao L, Wu Y, Wang X et al (2013) Fundamental performance of magnetic compound fluid (MCF) wheel in ultra-fine surface finishing of optical glass. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 75:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2013.09.003
Feng M, Wu Y, Wang Y et al (2020) Investigation on the polishing of aspheric surfaces with a doughnut-shaped magnetic compound fluid (MCF) tool using an industrial robot. Precis Eng 61:182–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2019.09.018
Feng M, Wu Y, Wang Y et al (2020) Effect of the components of magnetic compound fluid (MCF) slurry on polishing characteristics in aspheric-surface finishing with the doughnut-shaped MCF tool. Precis Eng 65:216–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2020.04.021
Feng M, Wu YB, Bitoh T et al (2018) Fundamental Investigation on the polishing aspheric elements with doughnut-shaped MCF slurry. Key Eng Mater 792:179–184. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.792.179
Nomura M, Ozasa K, Fujii T et al (2022) Development of ultrasonic vibration-assisted magnetic compound fluid (MCF) polishing technology. Int J Autom Technol 16(1):71–77. https://doi.org/10.20965/ijat.2022.p0071
Qian C, Tian Y, Fan Z et al (2022) Investigation on rheological characteristics of magnetorheological shear thickening fluids mixed with micro CBN abrasive particles. Smart Mater Struct 31(9). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/ac7bbd
Ren Y, Yang S, Huang X et al (2021) Research on the rheological characteristic of magnetorheological shear thickening fluid for polishing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 117(1–2):413–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07706-y
Zhou D, Huang X, Ming Y et al (2021) Material removal characteristics of magnetic-field enhanced shear thickening polishing technology. J Market Res 15:2697–2710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.09.092
Ming Y, Huang XM, Zhou DD et al (2022) Rheological properties of magnetic field-assisted thickening fluid and high-efficiency spherical polishing of ZrO2 ceramics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121(1–2):1049–1061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09344-4
Li J, Fan Z, Yang Z et al (2023) Simulation and modeling of magnetorheological shear thickening polishing processes for slender tube. J Mater Res ogy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.05.226
Gao WQ, Yan QS, Liu Y et al (2010) Parametric study of micro machining three dimensional microstructure with the tiny-grinding wheel based on the EMR effect. Key Eng Mater 447–448:193–197. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.447-448.193
Lu JB, Yan QS, Tian H et al (2010) Effect of abrasive on the machining performance the EMR-effect-based tiny-grinding wheel. Adv Mater Res 135:24–29. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.135.24
Hong T,Qiusheng Y,Jiabin L, et al. (2007) Foundational study on micro machining with instantaneous tiny grinding wheel based on electro-magneto-rheological effect[J]. Guangdong Univ. of Technology (China); Veeco Instruments, Inc. (United States); Institute of Optics and Electronics, CAS (China);Institute of Electrical Engineering (China);Rutherford Appleton Lab. (United Kingdom) 6724. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.782682
Zhu Y, Umehara N, Ido Y et al (2006) Computer simulation of structures and distributions of particles in MAGIC fluid. J Magn Magn Mater 302(1):96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.08.015
Hagiwara S, Kawashima N, Umehara N et al (2003) Proposal for die polishing using a new bonding abrasive type grinding stone: development of MAGIC grinding stone. Mach Sci Technol 7(2):267–279. https://doi.org/10.1081/mst-120022781
Umehara N, Shibata I, Edamura K (1999) New polishing method with magnetic congelation liquid. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 10:620–624
Xingai Y, gang Y, Shiying W et al (2013) The utility model relates to a surface processing equipment and process for a long circular inner tube [p]. Chinese patent: CN101982299B.2013.02.27
Zhaokun Y, Xingai Y, Ruipeng G et al (2022) Magnetic honing process of long diameter stainless steel inner surface [J]. Mech Electr Eng. 39(05):705–712
Ping Y, Xingai Y, Hui Y (2016) Experimental study on polishing inner wall of stainless steel pipe with permanent magnet rotor abrasives. Modern Manuf Eng (01):100–104. https://doi.org/10.16731/j.cnki.1671-3133.2016.01.019
Singh Gill J, Singh L, Singh P (2022) Analyses of rate of material removal during magnetic abrasive finishing of stainless steel SS304 using RSM method. Mater Today: Proceedings 60:2117–2123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.02.039
Seok J, Kim Y-J, Jang K-I et al (2007) A study on the fabrication of curved surfaces using magnetorheological fluid finishing. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(14):2077–2090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2007.05.007
Jiao A, Zhang G, Liu B et al (2020) Study on improving hole quality of 7075 aluminum alloy based on magnetic abrasive finishing. Adv Mech Eng 12(6). https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814020932006
Wang C, Loh YM, Cheung CF et al (2022) Shape-adaptive magnetic field-assisted batch polishing of three-dimensional surfaces. Precis Eng 76:261–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2022.04.003
Ghosh G, Sidpara A, Bandyopadhyay PP (2021) Theoretical analysis of magnetorheological finishing of HVOF sprayed WC-Co coating. Int J Mech Sci 207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106629
He X, Jin H, Zhou C et al (2022) Modeling of material removal in magnetic finishing based on Maxwell’s stress tensor theory and its experimental validation. J Mater Process Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117808
Kordonski W, Golini D (1999) Progress update in magnetorheological finishing. Int J Modern Phys B 13:205–2212
Guo H, Wu Y, Lu D et al (2014) Effects of pressure and shear stress on material removal rate in ultra-fine polishing of optical glass with magnetic compound fluid slurry. J Mater Process Technol 214(11):2759–2769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.06.014
Liu J, Li X, Zhang Y et al (2020) Predicting the material removal rate (MRR) in surface magnetorheological finishing (MRF) based on the synergistic effect of pressure and shear stress. Appl Surface Sci 504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144492
Wang T, Cheng H-B, Dong Z-C et al (2013) Removal character of vertical jet polishing with eccentric rotation motion using magnetorheological fluid. J Mater Process Technol 213(9):1532–1537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.03.017
Wang C, Loh YM, Cheung CF et al (2022) Magnetic field-assisted batch superfinishing on thin-walled components. Int J Mech Sci 223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107279
Liu S, Wang H, Zhang Q et al (2020) Regionalized modeling approach of tool influence function in magnetorheological finishing process for aspherical optics. Optik 206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164368
Gao Y, Zhao Y, Zhang G et al (2020) Modeling of material removal in magnetic abrasive finishing process with spherical magnetic abrasive powder. Int J Mech Sci 177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105601
Li C, Zhang F, Meng B et al (2017) Material removal mechanism and grinding force modelling of ultrasonic vibration assisted grinding for SiC ceramics. Ceram Int 43(3):2981–2993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.11.066
Kum CW, Sato T, Guo J et al (2018) A novel media properties-based material removal rate model for magnetic field-assisted finishing. Int J Mech Sci 141:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.04.006
Li W, Li X, Yang S et al (2018) A newly developed media for magnetic abrasive finishing process: material removal behavior and finishing performance. J Mater Process Technol 260:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.05.007
Misra A, Pandey PM, Dixit US (2017) Modeling of material removal in ultrasonic assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process. Int J Mech Sci 131–132:853–867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.07.023
Prakash C, Singh S, Pramanik A et al (2021) Experimental investigation into nano-finishing of β-TNTZ alloy using magnetorheological fluid magnetic abrasive finishing process for orthopedic applications. J Mater Res Technol 11:600–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.01.046
Zhang J, Chaudhari A, Wang H (2019) Surface quality and material removal in magnetic abrasive finishing of selective laser melted 316L stainless steel. J Manuf Process 45:710–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.07.044
Qin D, Wu J, Ye M et al (2022) Sulfuric acid modified magnetorheological finishing of polycrystalline magnesium aluminate spinel. Mater Sci Semiconduct Process 152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.107098
Funding
The work was co-supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 52075362) and the Central Government Guides Local Foundation for Science and Technology Development (grant no. YDZJSX2022B004 and YDZJSX2022A020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhaokun Yan designed and performed the manuscript, analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. Shengqiang Yang conceived and supervised the study, and edited the manuscript. Yonggang Li analyzed the data. Wenhui Li and Xiuhong Li Provide fund support. Xingai Yao performed the experiments. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have consent for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Yang, S., Li, Y. et al. Magnetic field-assisted finishing: mechanism, application, and outlook. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 131, 2719–2758 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12283-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12283-3