Abstract
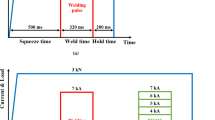
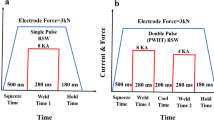
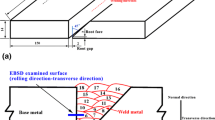
The present study aims to investigate the effect of in situ postweld heat treatment (PWHT) on microstructure, tensile shear properties, failure mode, and hardness distribution of resistance spot weld of dual-phase (DP590) steel. Tensile shear properties were evaluated in terms of peak load and failure energy. Results showed that welds subjected to high heat input in situ PWHT via double-pulse RSW process exhibit higher peak load and failure energy compared with conventional single-pulse weld. The improvement in mechanical performance is attributed to increased weld nugget size and the transition of failure mode from interfacial fracture mode to pullout fracture mode. Moreover, it was also found that increasing the tensile shear test velocity from 1.6 × 10−4 ms−1 (quasi-static) to 8.3 × 10−3 ms−1 for low-dynamic increased the peak load and failure energy of the weld.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kundu J, Ray T, Kundu A, Shome M (2019) Effect of the laser power on the mechanical performance of the laser spot welds in dual phase steels. J Mater Process Technol 267:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.12.014
Zhao J, Jiang Z (2015) Thermomechanical processing of advanced high strength steels. Prog Mater Sci 94:174–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.01.006
Tasan CC, Diehl M, Yan D, Bechtold M, Roters F, Schemmann L, Zheng C, Peranio N, Ponge D, Koyama M, Tsuzaki K, Raabe D (2015) An overview of dual-phase steels: advances in microstructure-oriented processing and micromechanically guided design. Annu Rev Mater Res 45(1):391–431. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-matsci-070214-021103
Zhang J, Di H, Deng Y, Misra RDK (2015) Effect of martensite morphology and volume fraction on strain hardening and fracture behavior of martensite–ferrite dual phase steel. Mater Sci Eng A 627:230–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.01.006
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2013) Key factors influencing mechanical performance of dual phase steel resistance spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 15(2):149–155. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217109x12590746472535
Pouranvari M (2012) Susceptibility to interfacial failure mode in similar and dissimilar resistance spot welds of DP600 dual phase steel and low carbon steel during cross-tension and tensile-shear loading conditions. Mater Sci Eng A 546:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.03.040
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH, Jaber HL (2015) DP780 dual-phase-steel spot welds: critical fusion-zone size ensuring the pull-out failure mode. Materiali in tehnologije 49(4):579–585. https://doi.org/10.17222/mit.2014.184
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2013) Factors affecting mechanical properties of resistance spot welds. Mater Sci Technol 26(9):1137–1144. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328409x459301
Pouranvari M, Ranjbarnoodeh E (2013) Failure mode of HSLA/DQSK dissimilar steel resistance spot welds. Ironmak Steelmak 40(4):76–281. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743281212y.0000000044
Abadi MMH, Pouranvari M (2014) Failure-mode transition in resistance spot welded DP780 advanced high-strength steel: effect of loading conditions. Materiali in tehnologije 48(1):67–71
Eftekharimilani P, van der Aa EM, Hermans MJM, Richardson IM (2017) Microstructural characterisation of double pulse resistance spot welded advanced high strength steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 22(7):545–554. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2016.1274848
Soomro IA, Pedapati SR, Awang M (2021) Optimization of postweld tempering pulse parameters for maximum load bearing and failure energy absorption in dual phase (DP590) steel resistance spot welds. Mater Sci Eng A 803:140–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140713
Chabok A, van der Aa E, Basu I, De Hosson J, Pei Y (2018) Effect of pulse scheme on the microstructural evolution, residual stress state and mechanical performance of resistance spot welded DP1000-GI steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 23(8):649–658. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2018.1452875
Chabok A, van der Aa E, De Hosson JTM, Pei YT (2017) Mechanical behavior and failure mechanism of resistance spot welded DP1000 dual phase steel. Mater Des 124:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.070
Soomro IA, Pedapati SR (2019) Application of in situ post weld heat treatment using double pulse technology and its effect on microstructure and mechanical performance of resistance spot welded HSLA350 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:3249–3260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04569-2
Aghajani H, Pouranvari M (2019) Influence of in situ thermal processing strategies on the weldability of martensitic stainless steel resistance spot welds: effect of second pulse current on the weld microstructure and mechanical properties. Metall Mater Trans A 50(11):5191–5209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05443-2
Lee HT, Chang YC (2020) Effect of double pulse resistance spot welding process on 15B22 hot stamped boron steel. Metals 10(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10101279
Pouranvari M, Aghajani H, Ghasemi A (2019) Enhanced mechanical properties of martensitic stainless steels resistance spot welds enabled by in situ rapid tempering. Sci Technol Weld Join 25(2):119–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2019.1641962
Yurioka N (2004) Comparison of preheat predictive methods. Welding in the World 48(1–2):21–27
AWS standard D8.9M (2012) Test Methods for Evaluating the Resistance Spot Welding Behavior of Automotive Sheet Steel Materials. https://pubs.aws.org/p/1067/d89m2012-test-methods-for-evaluating-the-resistance-spot-welding-behavior-of-automotive-sheet-steel-materials. https://pubs.aws.org/Download_PDFS/D8.9M-2012PV.pdf
Pak JH, Bhadeshia HKDH, Karlsson L (2013) Mechanism of misorientation development within coalesced martensite. Mater Sci Technol 28(8):918–923. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743284712y.0000000023
Jaber HL, Pouranvari M, Salim RK, Hashim FA, Marashi SPH (2016) Peak load and energy absorption of DP600 advanced steel resistance spot welds. Ironmak Steelmak 44(9):699–706. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2016.1229880
Pouranvari M, Sobhani S, Goodarzi F (2018) Resistance spot welding of MS1200 martensitic advanced high strength steel: microstructure-properties relationship. J Manuf Process 31:867–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.01.009
Tamizi M, Pouranvari M, Movahedi M (2021) The role of HAZ softening on cross-tension mechanical performance of martensitic advanced high strength steel resistance spot welds. Metall Mater Trans A 52(2):55–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-06104-5
Soomro IA, Pedapati SR, Awang M (2021) Double pulse resistance spot welding of dual phase steel: parametric study on microstructure, failure mode and low dynamic tensile shear properties. Materials (Basel) 14(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040802
Pouranvari M, Mousavizadeh SM, Marashi SPH, Goodarzi M, Ghorbani M (2011) Influence of fusion zone size and failure mode on mechanical performance of dissimilar resistance spot welds of AISI 1008 low carbon steel and DP600 advanced high strength steel. Mater Des 32(3):1390–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2010.09.010
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2013) Critical review of automotive steels spot welding: process, structure and properties. Sci Technol Weld Join 18(5):361–403. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171813y.0000000120
Bayraktar E, Kaplan D, Grumbach M (2004) Application of impact tensile testing to spot welded sheets. J Mater Process Technol 153-154:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.04.020
Chao YJ, Wang K, Miller KW, Zhu XK (2009) Dynamic separation of resistance spot welded joints: part 1-experiments. Exp Mech 50(7):889–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-009-9276-z
Khan MI, Kuntz ML, Zhou Y (2013) Effects of weld microstructure on static and impact performance of resistance spot welded joints in advanced high strength steels. Sci Technol Weld Join 13(3):294–304. https://doi.org/10.1179/174329308x271733
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH (2011) Failure mode transition in AHSS resistance spot welds. Part I. Controlling factors. Mater Sci Eng A 528(29-300):8337–8343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.08.017
Pouranvari M, Marashi SPH, Safanama DS (2011) Failure mode transition in AHSS resistance spot welds. Part II: experimental investigation and model validation. Mater Sci Eng A 528(29-30):8344–8352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.08.016
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Bloxwich Sdn Bhd Malaysia for providing resistance spot welding facility. The authors are thankful to Peoples Steel Mill Karachi Pakistan for providing scanning electron microscope facility.
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soomro, I.A., Pedapati, S.R. & Awang, M. Influence of in situ postweld heat treatment on microstructure and failure behavior of dual-phase steel resistance spot weld. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 114, 3739–3750 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07134-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07134-y