Abstract
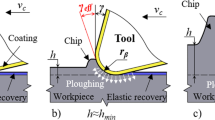
With the development of science and technology, the surgical blade cutting soft tissue continuously improves the design of blade to meet the higher technical requirements of clinical treatment in material properties, blade structure, and cutting performance. The purpose of this article is to review the research advance of surgical blades for soft cutting biological tissues, including cutting mechanisms of cutting soft tissue with blades, optimization of cutting parameters, the advance of surgical blade, the damage of biological tissue, and blades after cutting. Finally, the conclusions and perspective are put forward.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Rezaian J, Forouzanfar F (2012) Consideration on Trephinated skull in the Ŝahre-e Sukte (Burnt City) in Sistan. J Res Hist Med 1(4):157–167
Brill JB, Harrison EK, Sise MJ, Romeo C, Ignacio J (2017) The history of the scalpel: From flint to zirconium-coated steel. The American College of Surgeons (ACS) Clinical Congress, pp 157–167
Shan L, Xiaoyue H, Chengyong W, Lijuan Z, Danna Z (2018) Diamond application in medical field. Diam Abras Eng 38(02):1–7. https://doi.org/10.13394/j.cnki.jgszz.2018.2.0001
Fatiny FI, Sunbol HM, Alhazzazi TY (2019) Dental restoration scalpel. U. S. Patent
Hao YC, Wang QL, Liu ZA, Liu X, Sun J, Song JL (2020) Preparation of scalpel with stable anti-blood property. Materials Science Forum. Trans Tech Publ. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.996.70
Martini FHTM, Tallitsch RB (2012) Human Anatomy, 7th edn. Pearson Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco
Skinner HB (2006) Current diagnosis & treatment in orthopedics, Stamford, Conn: Lange Medical Books/McGraw Hill, p 346
Hu Z, Sun W, Zhang B (2013) Characterization of aortic tissue cutting process: experimental investigation using porcine ascending aorta. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 18:81–89
Chanthasopeephan T, Desai JP, Lau ACW (2003) Measuring forces in liver cutting: new equipment and experimental results. Ann Biomed Eng 31(11):1372–1382
Chanthasopeephan T, Desai JP, Lau AC (2006) Determining fracture characteristics in scalpel cutting of soft tissue. The First IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics:899–904. https://doi.org/10.1109/BIOROB.2006.1639205
Zhang Z, Song X, Sahn DJ (2011) Cardiac motion estimation from 3D echocardiography with spatiotemporal regularization. International Conference on Functional Imaging and Modeling of the Heart, pp 350–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21028-0_45
Kim C, Lee DY (2016) An empirical nonlinear viscoelastic model of reflective force by a layer of soft tissue. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), pp 003556–003560. https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC.2016.7844784
Peña J, Martínez M, Peña E (2011) A formulation to model the nonlinear viscoelastic properties of the vascular tissue. Acta Mech 217(1–2):63–74
Dong Y, Liu X, Li H, Wang ZA (2016) Nonlinear viscoelastic meshless model for soft tissue deformation. International Conference on Virtual Reality and Visualization (ICVRV), pp 204–211. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICVRV.2016.42
Panda SK, Buist ML (2018) A finite nonlinear hyper-viscoelastic model for soft biological tissues. J Biomech 69:121–128
Liu H, Noonan DP, Zweiri YH, Althoefer KA, Seneviratne LD (2007) The development of nonlinear viscoelastic model for the application of soft tissue identification. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems: 208–213. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2007.4399336
Chabiniok R, Wong J, Giese D, Nordsletten D, Shi W, Greil G, Rueckert D, Razavi R, Schaeffter T, Smith N (2013) Flow analysis in cardiac chambers combining phase contrast, 3D tagged and cine MRI. International Conference on Functional Imaging and Modeling of the Heart, pp 360–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-38899-6_43
Ouzir N, Basarab A, Liebgott H, Harbaoui B, Tourneret J-Y (2017) Motion estimation in echocardiography using sparse representation and dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(1):64–77
Zhang W, Chen HY, Kassab GS (2007) A rate-insensitive linear viscoelastic model for soft tissues. Biomaterials 28(24):3579–3586
De Geeter N, Ionescu C, De Keyser R (2009) A mechanical model of soft biological tissue—an application to lung parenchyma. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society:2863–2866. https://doi.org/10.1109/iembs.2009.5333606
Selyutina N, Argatov I, Mishuris G (2015) On application of Fung's quasi-linear viscoelastic model to modeling of impact experiment for articular cartilage. Mech Res Commun 67:24–30
Pelkie GJ (2011) Characterization of viscoelastic behaviors in bovine pulmonary arterial tissue. University of Colorado at Boulder. https://scholar.colorado.edu/concern/graduate_thesis_or_dissertations/cf95jb826
Chung CW, Buist ML (2012) A novel nonlinear viscoelastic solid model. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 13(3):1480–1488
Wang X, Schoen JA, Rentschler ME (2013) A quantitative comparison of soft tissue compressive viscoelastic model accuracy. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 20:126–136
Yang W, Fung T, Chian K, Chong C (2006) Investigations of the viscoelasticity of esophageal tissue using incremental stress-relaxation test and cyclic extension test. J Mech Med Biol 6(03):261–272
Labus KM, Puttlitz CM (2016) Viscoelasticity of brain corpus callosum in biaxial tension. J Mech Phys Solids 96:591–604
Chagnon G, Rebouah M, Favier D (2015) Hyperelastic energy densities for soft biological tissues: a review. J Elast 120(2):129–160
Wex C, Arndt S, Stoll A, Bruns C, Kupriyanova Y (2015) Isotropic incompressible hyperelastic models for modelling the mechanical behaviour of biological tissues: a review. Biomed Eng-Biomed Te 60(6):577–592
McCarthy CT, Hussey M, Gilchrist MD (2007) On the sharpness of straight edge blades in cutting soft solids: part I–indentation experiments. Eng Fract Mech 74(14):2205–2224
Hu Z, Zhang B, Sun W (2012) Cutting characteristics of biological soft tissues. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61(1):135–138
Comley K, Fleck NA (2010) The toughness of adipose tissue: measurements and physical basis. J Biomech 43(9):1823–1826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.02.029
Zhang B, Shiang CS, Yang SJ, Hutchens SB (2019) Y-shaped cutting for the systematic characterization of cutting and tearing. Exp Mech 59(4):517–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-019-00479-2
Barnett AC, Lee Y-S, Moore JZ (2015) Fracture mechanics model of needle cutting tissue. J Manuf Sci Eng 138(1). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4030374
Liu W, Yang Z, Li P, Zhang J, Jiang S (2019) Mechanics of tissue rupture during needle insertion in transverse isotropic soft tissue. Med Biol Eng Comput 57(6):1353–1366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-01955-6
Triki E, Gauvin C (2019) Stress state analysis and tensile-shear fracture criterion in combined puncture and cutting of soft materials. Eng Fail Anal 106:104140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2019.08.006
Wang D, Song Q, Liu Z, Wan Y (2018) Cutting characteristics of porcine tenderloin tissue along tangential direction of surface. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 98(1–4):17–27
Gao LY, Zhang QH, Liu M (2012) Orthogonal cutting of biological soft tissue with single cutting edge. Applied Mechanics and Materials. Trans Tech Publ. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.121-126.283
Pereira BP, Lucas PW, Swee-Hin T (1997) Ranking the fracture toughness of thin mammalian soft tissues using the scissors cutting test. J Biomech 30(1):91–94
Zhongwei H (2011) Experiment and theory research on cutting mechanism of biological soft tissue. Hunan University. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFD1214&filename=1013171246.nh
Gokgol C, Basdogan C, Canadinc D (2012) Estimation of fracture toughness of liver tissue: experiments and validation. Med Eng Phys 34(7):882–891
Azar T, Hayward V (2008) Estimation of the fracture toughness of soft tissue from needle insertion. International Symposium on Biomedical Simulation:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-70521-5_18
Shergold OA, Fleck NA (2005) Experimental investigation into the deep penetration of soft solids by sharp and blunt punches, with application to the piercing of skin. J Biomech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1992528
Atkins AG, Xu X, Jeronimidis G (2004) Cutting, by ‘pressing and slicing,‘of thin floppy slices of materials illustrated by experiments on cheddar cheese and salami. J Mater Sci 39(8):2761–2766. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000021451.17182.86
Taylor D, O’Mara N, Ryan E, Takaza M, Simms C (2012) The fracture toughness of soft tissues. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 6:139–147
Gao LY, Zhang QH, Liu M (2011) Orthogonal cutting of biological soft tissue with single cutting edge. Appl Mech Mater 121-126:283–287. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.121-126.283
Moore JZ, Malukhin K, Shih AJ, Ehmann KF (2011) Hollow needle tissue insertion force model. CIRP Ann 60(1):157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2011.03.101
van Gerwen DJ, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ (2012) Needle–tissue interaction forces – a survey of experimental data. Med Eng Phys 34(6):665–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2012.04.007
de Jong TL, Pluymen LH, van Gerwen DJ, Kleinrensink G-J, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ (2017) PVA matches human liver in needle-tissue interaction. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 69:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.01.014
Spagnoli A, Terzano M, Brighenti R, Artoni F, Ståhle P (2018) The fracture mechanics in cutting: a comparative study on hard and soft polymeric materials. Int J Mech Sci 148:554–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.09.013
Tholey G, Chanthasopeephan T, Hu T, Desai JP, Lau ACW (2003) Measuring grasping and cutting forces for reality-based haptic modeling. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0531-5131(03)00492-8
Shetty PP, Hatton RW, Barnett AC, Homich AJ, Moore JZ (2015) Modeling the cutting edge geometry of scalpel blades. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 231(1):65–72. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405414567928
Giovannini M, Ehmann K (2016) Vibrational cutting of soft tissue with micro-serrated surgical scalpels. Procedia CIRP 45:199–202
Oldfield MJ, Dini D, Jaiswal T, Rodriguez y Baena F (2013) The significance of rate dependency in blade insertions into a gelatin soft tissue phantom. Tribol Int 63:226–234
McGorry RW, Dowd PC, Dempsey PG (2005) The effect of blade finish and blade edge angle on forces used in meat cutting operations. Appl Ergon 36(1):71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2004.08.002
Marsot J, Claudon L, Jacqmin M (2007) Assessment of knife sharpness by means of a cutting force measuring system. Appl Ergon 38(1):83–89
Jang JS-C, Tsai P-H, Shiao A-Z, Li T-H, Chen C-Y, Chu JP, Duh J-G, Chen M-J, Chang S-H, Huang W-C (2015) Enhanced cutting durability of surgical blade by coating with Fe-based metallic glass thin film. Intermetallics 65:56–60
Tsai P, Li T, Hsu K, Chiou J, Jang J, Chu J (2016) Effect of coating thickness on the cutting sharpness and durability of Zr-based metallic glass thin film coated surgical blades. Thin Solid Films 618:36–41
Sorouri K, Podolsky DJ, Wang AM, Fisher DM, Wong KW, Looi T, Drake JM, Forrest CR (2018) Utilization of a robotic mount to determine the force required to cut palatal tissue. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 86:433–439
Zhongwei H, Wangyuan L, Xipeng X (2016) Experimental study on the cutting characteristics of three typical biological soft tissues. J Mech Eng 52(11):186
Y L (2016) Research on biomechanics of soft tissue in minimally invasive surgery. Dissertation, Jilin University
Dong W (2018) Cutting experiment and simulation of muscle tissue. Dissertation, Shangdong University
Kirkup J (1995) The history and evolution of surgical instruments. VI The surgical blade: from finger nail to ultrasound. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 77(5):380–388
Kaliaraj GS, Vishwakarma V, Kirubaharan AK (2018) Biocompatible zirconia-coated 316 stainless steel with anticorrosive behavior for biomedical application. Ceram Int 44(8):9780–9786
Huacho PMM, Nogueira MNM, Basso FG, Jafelicci Junior M, Francisconi RS, Spolidorio DM (2017) Analyses of biofilm on implant abutment surfaces coating with diamond-like carbon and biocompatibility. Braz Dent J 28(3):317–323
Yang K-H, Narayan RJ (2019) Biocompatibility and functionalization of diamond for neural applications. Curr Opin Biomed Eng 10:60–68
Patel B, Duran-Martinez AC, Gurman P, Auciello O, Barao V, Campbell S, Sukotjo C, Mathew MT (2017) Ultrananocrystalline diamond coatings for the dental implant: electrochemical nature. Surf Innov 5(2):106–117
Auciello O (2017) Novel biocompatible ultrananocrystalline diamond coating technology for a new generation of medical implants devices and scaffolds for developmental biology. Biomater Med Appl 1(1):1–11
Nistor P, May P (2017) Diamond thin films: giving biomedical applications a new shine. J R Soc Interface 14(134):20170382
Goldar K, Chaubey KK, Agarwal S, Agarwal T (2020) Gingival depigmentation by gingival ceramic trimmer. Univ J Dent Sci 6(1):43–48
Liu C, Lei AN, Wei D, Zhu Y, Neurosurgery DO (2015) Exploration on the biological features and clinical application of disposable ceramic scalpel. Clin Med Eng
Spellman G, Werne R (2018) MR-compatible surgical instruments final report CRADA no. TSB-0847-94, United States. https://doi.org/10.2172/1424645
KERATOTOMY R (2018) Astigmatic keratotomy: the transition from diamond blades. Ophthalmology E-Book:131
Dawson C, Naranjo C, Sanchez-Maldonado B, Fricker GV, Linn-Pearl RN, Escanilla N, Kafarnik C, Gould DJ, Sanchez RF, Matas-Riera M (2017) Immediate effects of diamond burr debridement in patients with spontaneous chronic corneal epithelial defects, light and electron microscopic evaluation. Vet Ophthalmol 20(1):11–15
Chang C-H, Li C-L, Yu C-C, Chen Y-L, Chyntara S, Chu JP, Chen M-J, Chang S-H (2018) Beneficial effects of thin film metallic glass coating in reducing adhesion of platelet and cancer cells: clinical testing. Surf Coat Technol 344:312–321
Chu JP, Bönninghoff N, Yu C-C, Liu Y-K, Chiang G-H (2019) Coating needles with metallic glass to overcome fracture toughness and trauma: analysis on porcine tissue and polyurethane rubber. Thin Solid Films 688:137320
Chu JP, Diyatmika W, Tseng Y-J, Liu Y-K, Liao W-C, Chang S-H, Chen M-J, Lee J-W, Jang JS (2019) Coating cutting blades with thin-film metallic glass to enhance sharpness. Sci Rep 9(1):1–11
Giovannini M, Moser N, Ehmann K (2015) Experimental and analytical study of micro-serrations on surgical blades. International Electronic Packaging Technical Conference and Exhibition, p V003T003A004. https://doi.org/10.1115/IPACK2015-48046
Reilly G, McCormack B, Taylor D (2004) Cutting sharpness measurement: a critical review. J Mater Process Technol 153:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.04.297
Li Y (2016) Research on biomechanics of soft tissue in minimally invasive surgery. Jilin University https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202001&filename=1019922418.nh
Lu J, Wang X, Huang Y, Zhou C, Xu B, Fu Q (2020) Fabrication and cutting performance of bionic micro-serrated scalpels based on the miscanthus leaves. Tribol Int 145:106162
McCarthy CT, Annaidh AN, Gilchrist MD (2010) On the sharpness of straight edge blades in cutting soft solids: part II–analysis of blade geometry. Eng Fract Mech 77(3):437–451
Luttrull JK (2016) Microvitreoretinal surgery blades
Ahmed IK, Schlenker MB (2017) Canaloplasty. Operative Dictations in Ophthalmology. Springer, In, pp 247–249
Szabo RL, Radwin RG, Henderson CJ (2001) The influence of knife dullness on poultry processing operator exertions and the effectiveness of periodic knife steeling. AIHAJ Am Ind Hyg Assoc 62(4):428–433
Bishu R, Calkins C, Lei X, Chin A (1996) Effect of knife type and sharpness on cutting forces. Adv Occup Ergon Saf 2:479–483
Arcona C, Dow T (1996) The role of knife sharpness in the slitting of plastic films. J Mater Sci 31(5):1327–1334
McGorry RW, Dowd PC, Dempsey PG (2005) A technique for field measurement of knife sharpness. Appl Ergon 36(5):635–640
Zhou D, McMurray G (2010) Modeling of blade sharpness and compression cut of biomaterials. Robotica 28(2):311
Zahara AT (2018) Clinical evaluation of scalpel Er: YAG laser 2940nm and conventional surgery incisions wound after Oral soft tissue biopsy. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 43(3)
Sinha UK, Gallagher LA (2010) Effects of steel scalpel, ultrasonic scalpel, CO2 laser, and monopolar and bipolar electrosurgery on wound healing in guinea pig oral mucosa. Laryngoscope 113(2):228–236. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200302000-00007
Karimi A, Sobouti F, Torabi S, Bakhshandehfard A, Amirian A, Shariati M, Morshedi E, Barati M (2016) Comparison of carbon dioxide laser with surgical blade for removal of Epulis Fissuratum. A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Lasers Med Sci 7(3):201
Sabah M, Aldabagh AN, Mahmood AS (2020) Histological assessment for healing of intraoral surgical wounds produced by diode laser 940 nm versus surgical scalpel blade (an in vivo study). Al-Rafidain Dent J 20(2):233–243. https://doi.org/10.33899/rden.2020.127185.1037
Ismail A, Abushouk AI, Elmaraezy A, Menshawy A, Menshawy E, Ismail M, Samir E, Khaled A, Zakarya H, El-Tonoby A, Ghanem E (2017) Cutting electrocautery versus scalpel for surgical incisions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Surg Res 220:147–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2017.06.093
Scott JE, Swanson EA, Cooley J, Wills RW, Pearce EC (2017) Healing of canine skin incisions made with monopolar electrosurgery versus scalpel blade. Vet Surg 46(4):520–529. https://doi.org/10.1111/vsu.12650
Gray BBP, Huang LC, Hill J, Salvador-Silva M, Gwon A (2016) Penetrating and intrastromal corneal arcuate incisions in rabbit and human cadaver eyes: manual diamond blade and femtosecond laser-created incisions. Eye Contact Lens 42(4):7. https://doi.org/10.1097/ICL.0000000000000204
Izmaĭlov GA, Orenburov PI, Repin VA, Gorbunov SM, Izmaĭlov SG, Otsenka zazhivleniia kozhnykh ran, zatochkoĭ nslslsr (1989) Evaluation of the healing of skin wounds inflicted by steel scalpels with various degrees of sharpness. Khirurgiia (Mosk) 6:75–78
Creton C, Ciccotti M (2016) Fracture and adhesion of soft materials: a review. Rep Prog Phys 79(4):046601. https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/79/4/046601
Agrawal Y, Sharma S, Chopra S, Purohit DK (2017) Retrieval of a retained broken scalpel blade from lumbar intervertebral disc space - a case report. https://doi.org/10.1515/romneu-2017-0020
Caballero AD, Dunoyer AT, Ligardo RH, Vergara ÁC, Mesa NF (2017) Deformation of scalpel blades after incision of gingival tissue in pig mandibles. An ex vivo study. Rev Odon Mex 21(3):7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rodmex.2017.09.013
Roscioli G, Taheri-Mousavi SM, Tasan CC (2020) How hair deforms steel. Science 369(6504):689–694. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba9490
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51735003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhihua Liu contributed significantly to perform the analyses and write the manuscript; Zhihua Liu, Chengyong Wang, and Zhihua Chen helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions; Chengyong Wang, Zhihua Chen and Jianbo Sui helped to revise the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Wang, C., Chen, Z. et al. The advance of surgical blades in cutting soft biological tissue: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 113, 1817–1832 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06615-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06615-4