Abstract
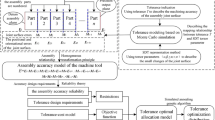
Due to the effect of gravity on machine tools, the small deformations inevitably exist. The existing tolerance allocation methods are based on the rigid body assumption, which ignore the small deformations. It will make optimization results inaccurate and increase manufacturing cost. Therefore, a new optimal tolerance allocation method, which integrates the small deformations, is presented in this paper. The establishment of a geometric error model based on tolerance is involved at first. Based on this model and multi-body system theory, the mapping relationship between tolerance and volumetric error of the five-axis machine tool (FAMT) is formulated. Secondly, the small deformations of the FAMT are obtained based on finite element analysis. Then, the optimal tolerance allocation model is established by integrating the small deformations into the constraint conditions. Thirdly, simulation analysis is carried out with this model by using a genetic algorithm. Then, the optimal tolerance allocation scheme is obtained, and the total manufacturing cost after optimization is reduced by approximately 11.5%. Finally, the volumetric errors of the FAMT are calculated based on the two tolerance allocation schemes. The results show that the volumetric errors are within the permitted ranges. Therefore, the proposed method in consideration of the small deformation is feasible and effective.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu CJ, Fan JW, Wang QH, Pan R, Tang YH, Li ZS (2018) Prediction and compensation of geometric error for translational axes in multi-axis machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95:3413–3435
Pezeshki M, Arezoo B (2016) Kinematic errors identification of three-axis machine tools based on machined work pieces, vol 43, pp 493–504
Wu C, Fan J, Wang Q, Chen D (2018) Machining accuracy improvement of non-orthogonal five-axis machine tools by a new iterative compensation methodology based on the relative motion constraint equation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 124(1):80–98
Cheng Q, Qi B, Liu Z, Zhang C, Xue D (2019) An accuracy degradation analysis of ball screw mechanism considering time-varying motion and loading working conditions. Mech Mach Theory 134:1–23
Qiao Y, Chen Y, Yang J, Chen B (2017) Five-axis geometric errors calibration model based on the common perpendicular line (CPL) transformation using the product of exponentials (POE) formula. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 118-119:49–60
Cheng Q, Zhao H, Zhang G, Gu P, Cai L (2014) An analytical approach for crucial geometric errors identification of multi-axis machine tool based on global sensitivity analysis [J]. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 75:107–121
Sivakumar K, Balamurugan C, Ramabalan S (2011) Simultaneous optimal selection of design and manufacturing tolerances with alternative manufacturing process selection. Comput Aided Des 43:207–218
Cai L, Zhang Z, Cheng Q, Liu Z, Gu P, Qi Y (2016) An approach to optimize the machining accuracy retainability of multi-axis NC machine tool based on robust design. Precis Eng 43:370–386
Fan J, Tao H, Wu C, Pan R, Tang Y, Li Z (2018) Kinematic errors prediction for multi-axis machine tools’ guideways based on tolerance. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 98(5-8):1131–1144
Wu F, Dantan J, Etienne A, Siadat A, Martin P (2009) Improved algorithm for tolerance allocation based on Monte Carlo simulation and discrete optimization. Comput Ind Eng 56:1402–1413
Sivakumar K, Balamurugan C, Ramabalan S (2011) Concurrent multi-objective tolerance allocation of mechanical assemblies considering alternative manufacturing process selection. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53:711–732
Geetha K, Ravindran D, Siva Kumar M, Islam M (2013) Multi-objective optimization for optimum tolerance synthesis with process and machine selection using a genetic algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67:2439–2457
Zhao Y, Liu D, Wen Z (2016) Optimal tolerance design of product based on service quality loss. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82:1715–1724
Ghali M, Tlija M, Aifaoui N, Pairel E (2017) Optimal tolerance design of product based on service quality loss. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91:2435–2446
Guo J, Liu Z, Li B, Hong J (2015) Optimal tolerance allocation for precision machine tools in consideration of measurement and adjustment processes in assembly. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80:1625–1640
Zhang Y, Ji S, Zhao J, Xiang L (2016) Tolerance analysis and allocation of special machine tool for manufacturing globoidal cams. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87:1597–1607
Zhang Z, Liu Z, Cheng Q, Qi Y, Cai L (2017) An approach of comprehensive error modeling and accuracy allocation for the improvement of reliability and optimization of cost of a multi-axis NC machine tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 89:561–579
Guo S, Jiang G, Mei X (2017) Investigation of sensitivity analysis and compensation parameter optimization of geometric error for five-axis machine tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93:3229–3243
Zhang Z, Cai L, Cheng Q, Liu Z, Gu P (2019) A geometric error budget method to improve machining accuracy reliability of multi-axis machine tools. J Intell Manuf 30:495–519
Zhu S, Ding G, Qin S, Lei J, Zhuang L, Yan K (2012) Integrated geometric error modeling, identification and compensation of CNC machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 52:24–29
Chase K, Greenwood WK (1990) Least cost tolerance allocation for mechanical assemblies with automated process selection. Manuf Rev 3:49–59
Taguchi G, Elsayed E, Hsiang T (1989) Quality engineering in production system [M]. McGraw- Hill, New York
Cheng Q, Zhang Z, Zhang G, Gu P, Cai L (2015) Geometric accuracy allocation for multi-axis CNC machine tools based on sensitivity analysis and reliability theory. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci 229:1134–1149
Wang G, Yang Y, Wang W, Si-Chao L (2016) Variable coefficients reciprocal squared model based on multi-constraints of aircraft assembly tolerance allocation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82:227–234
Haq A, Sivakumar K, Saravanan R, Muthiah V (2005) Tolerance design optimization of machine elements using genetic algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25:385–391
Balamurugan C, Saravanan A, Babu P, Jagan S, Narasimman S (2017) Concurrent optimal allocation of geometric and process tolerances based on the present worth of quality loss using evolutionary optimisation techniques. Res Eng Des 28:185–202
Prabhaharan G, Asokan P, Rajendran S (2005) Sensitivity-based conceptual design and tolerance allocation using the continuous ants colony algorithm (CACO). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25:516–526
Zahara E, Kao Y (2009) A hybridized approach to optimal tolerance synthesis of clutch assembly. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40:1118–1124
Forouraghi B (2009) Optimal tolerance allocation using a multi objective particle swarm optimizer. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44:710–724
Yılmaz S, Kücüksille E (2015) A new modification approach on bat algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 28:259–275
Beitz W, Küttner K (1990) Dubbel Handbook of mechanical engineering [M]. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp k1–k107
Chen H (2016) Handbook of practical machining technology [M]. China Machine Press, Beijing, China
Jiang P (2019) Research on modeling and compensation of the position independent geometric errors in five-axis denture machining center [D]. Hefei University of Technology, Hefei
Funding
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51775010 and 51705011) and Science and Technology Major Projects of High-end CNC Machine Tools and Basic Manufacturing Equipment of China (No. 2016ZX04003001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, J., Tao, H., Pan, R. et al. Optimal tolerance allocation for five-axis machine tools in consideration of deformation caused by gravity. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 111, 13–24 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06096-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06096-x