Abstract
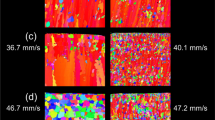
We study the deformation inducing heterogeneity in an aluminum alloy 6063-T6 in the form of a sheet processed at room temperature by equal channel angular sheet extrusion (ECASE) up to a maximum equivalent strain of 1.86 following route C. The through thickness strain distribution showed higher strains in the edge vicinities than in the sheet core. The texture was heterogeneous between the edges and the sheet core with a strong cube component in the initial deformation stages, and a rolling texture with the S component in the sheet edges. Different microstructural characteristics, like grain size, average misorientation, and fraction of high angle grain boundaries (HAGB), decreased by increasing the deformation. The geometrically necessary dislocation (GND) calculations corroborated the existence of a heterogeneous microstructure along the sheet thickness, giving rise to gradients of plastic deformation which allowed to obtain a good strength-ductility relationship. It was demonstrated that ECASE process was a good alternative to produce heterogeneous microstructures. The material heterogeneity was found not to be randomly distributed across the sheet thickness but rather showing higher dislocation concentration and bigger grain size reductions in the edge’s vicinities than in its middle zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valiev RZ, Alexandrov IV, Zhu YT, Lowe TC (2002) Paradox of strength and ductility in metals processed by severe plastic deformation. JMR 17:5–8
Muñoz JA, Higuera OF, Cabrera JM (2017) Microstructural and mechanical study in the plastic zone of ARMCO iron processed by ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A 697:24–36
Han J, Oh K, Lee J (2004) Effect of accumulative strain on texture evolution in 1050 Al alloys processed by continuous confined strip shearing. Mater Sci Eng A 387:240–243
Zisman A, Rybin V, Van Boxel S, Seefeldt M, Verlinden B (2006) Equal channel angular drawing of aluminium sheet. Mater Sci Eng A 427:123–129
Zeng Z, Li X, Xu D, Lu L, Gao H, Zhu T (2016) Gradient plasticity in gradient nano-grained metals. Extreme Mech Lett 8:213–219
Ma E, Zhu T (2017) Towards strength–ductility synergy through the design of heterogeneous nanostructures in metals. Mater Today 20:323–331
Kalsar R, Suwas S (2018) A novel way to enhance the strength of twinning induced plasticity (TWIP) steels. Scr Mater 154:207–211
Yin F, Cheng GJ, Xu R, Zhao K, Li Q, Jian J, Hu S, Sun S, An L, Han Q (2018) Ultrastrong nanocrystalline stainless steel and its hall-Petch relationship in the nanoscale. Scr Mater 155:26–31
Liu X, Yuan F, Zhu Y, Wu X (2018) Extraordinary Bauschinger effect in gradient structured copper. Scr Mater 150:57–60
Ashby MF (1970) The deformation of plastically non-homogeneous materials. Philos Mag 21:399–424
Sheppard T (1999) Processing of 6XXX alloys. In: Extrusion of aluminium alloys. Springer, Boston, pp 253–317
Xu C, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2011) Microstructural evolution in an aluminum solid solution alloy processed by ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A 528:6059–6065
Terhune SD, Swisher DL, Oh-ishi K, Horita Z, Langdon TG, McNelley TR (2002) An investigation of microstructure and grain-boundary evolution during ECA pressing of pure aluminum. Metall Mater Trans A 33:2173–2184
Kim WJ, Sa YK, Kim HK, Yoon US (2008) Plastic forming of the equal-channel angular pressing processed 6061 aluminum alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 487:360–368
Loucif A, Figueiredo RB, Baudin T, Brisset F, Langdon TG (2010) Microstructural evolution in an Al-6061 alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 527:4864–4869
Valiev RZ, Krasilnikov NA, Tsenev NK (1991) Plastic deformation of alloys with submicron-grained structure. Mater Sci Eng A 137:35–40
Claves SR, Elias DL, Misiolek WZ (2002) Analysis of the intermetallic phase transformation occurring during homogenization of 6XXX aluminum alloys. Mater Sci Forum 396:667–674
Zajac S, Hutchinson B, Johansson A, Gullman LO (1994) Microstructure control and extrudability of Al−mg−Si alloys microalloyed with manganese. Mater Sci Technol 10:323–333
Kuijpers NCW, Kool WH, Zwaag S (2002) DSC study on mg−Si phases in as-cast 6XXX. Mater Sci Forum 396:675–680
Suwas S, Ray RK (2014) Crystallographic texture of materials. Springer-Verlag, London
Bunge HJ (1981) Fabric analysis by orientation distribution functions. Tectonophysics 78:1–21
Schulz LG (1949) A direct method of determining preferred orientation of a flat reflection sample using a Geiger counter X-Ray spectrometer. J Appl Phys 20:1030–1033
Chateigner D, Germi P, Pernet M (1992) Texture analysis by the Schulz reflection method: Defocalization corrections for thin films. J Appl Crystallogr 25:766–769
Kallend JS, Kocks UF, Rollett AD, Wenk HR (1991) Operational texture analysis. Mater Sci Eng A 132:1–11
Bachmann F, Hielscher R, Schaeben H (2010) Texture analysis with MTEX - free and open source software toolbox. Solid State Phenom 160:63–68
Blaber J, Adair B, Antoniou A (2015) Ncorr: open-source 2D digital image correlation Matlab software. Exp Mech 55:1105–1122
Ab Ghani AF, Ali MB, DharMalingam S, Mahmud J (2016) Digital image correlation (DIC) technique in measuring strain using Opensource platform Ncorr. J Adv Res Appl Mech 26:10–21
Hollomon JH (1945) Tensile deformation. Aime Trans 12:1–22
Khelfa T, Rekik MA, Khitouni M, Cabrera-Marrero JM (2017) Structure and microstructure evolution of Al–mg–Si alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:1731–1740
Panigrahi SK, Jayaganthan R, Pancholi V, Gupta M (2010) A DSC study on the precipitation kinetics of cryorolled Al 6063 alloy. Mater Chem Phys 122:188–193
Yassar RS, Field DP, Weiland H (2005) The effect of cold deformation on the kinetics of the β″ precipitates in an Al-mg-Si alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 36:2059–2065
Gavgali M, Totik Y, Sadeler R (2003) The effects of artificial aging on wear properties of AA 6063 alloy. Mater Lett 57:3713–3721
Fandiño EM, Bolmaro RE, Risso P, Tartalini V, Morales PF, Ávalos M (2018) Texture, microstructure, and surface mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloys processed by ECASD. Adv Eng Mater 20(4):1700228
Khelfa T, Rekik MA, Muñoz-Bolaños JA, Cabrera-Marrero JM, Khitouni M (2017) Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms in an Al-mg-Si alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing (ECAP). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95:1165–1177
Qian T, Marx M, Schüler K, Hockauf M, Vehoff H (2010) Plastic deformation mechanism of ultra-fine-grained AA6063 processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Acta Mater 58:2112–2123
Samaee M, Najafi S, Eivani AR, Jafarian HR, Zhou J (2016) Simultaneous improvements of the strength and ductility of fine-grained AA6063 alloy with increasing number of ECAP passes. Mater Sci Eng A 669:350–357
Zendehdel H, Hassani A (2012) Influence of twist extrusion process on microstructure and mechanical properties of 6063 aluminum alloy. Mater Des 37:13–18
Valiev RZ, Estrin Y, Horita Z, Langdon TG, Zehetbauer MJ, Zhu YT (2016) Fundamentals of superior properties in bulk nanoSPD materials. Mater Res Lett 4:1–21
Humphreys F, Hatherly M (1996) Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena. Pergamon, Oxford
De La Chapelle S, Duval P (2002) Recrystallization in a hot deformed Al-mg-Si alloy: The effect of fine precipitates. Texture Microstruct 35:55–70
Engler O, Randle V (2010) Introduction to Texture Analysis –Macrotexture, Microtexture, and Orientation Mapping, 2nd edn. United States of America, Taylor & Francis Group
Naseri M, Reihanian M, Borhani E (2016) A new strategy to simultaneous increase in the strength and ductility of AA2024Nalloy via accumulative roll bonding (ARB). Mater Sci Eng A 656:12–20
Li S, Beyerlein IJ, Bourke MAM (2005) Texture formation during equal channel angular extrusion of fcc and bcc materials: comparison with simple shear. Mater Sci Eng A 394:66–77
Canova GR, Kocks UF, Jonas JJ (1984) Theory of torsion texture development. Acta Metall 32:211–226
Beyerlein IJ, Tóth LS (2009) Texture evolution in equal-channel angular extrusion. Prog Mater Sci 54:427–510
Tóth LS (2003) Texture evolution in severe plastic deformation by Equal Channel angular extrusion. Adv Eng Mater 5:308–316
Bolmaro RE, Kocks UF (1992) A comparison of the texture development in pure and simple shear and during path changes. Scr Metall Mater 27:1717–1722
Pasebani S, Toroghinejad MR, Hosseini M, Szpunar J (2010) Textural evolution of nano-grained 70/30 brass produced by accumulative roll-bonding. Mater Sci Eng A527 527:2050–2056
Jamaati R, Toroghinejad MR (2014) Effect of alloy composition, stacking fault energy, second phase particles, initial thickness, and measurement position on deformation texture development of nanostructured FCC materials fabricated via accumulative roll bonding process. Mater Sci Eng A 598:77–97
Bobor K, Krallics G (2010) Characterization of severe plastic deformation techniques with respect to non-monotonity. Rev Adv Mater Sci 25:32–41
Jin H, Lloyd DJ (2010) The different effects of asymmetric rolling and surface friction on formation of shear texture in aluminium alloy AA5754. Mater Sci Technol 26(6):754–760
Kim HK, Kim HW, Cho JH, Lee JC (2013) High-formability Al alloy sheet produced by asymmetric rolling of strip-cast sheet. Mater Sci Eng A 574:31–36
Tomita Y, Okabayashi K (1985) Tensile stress-strain analysis of cold worked metals and steels and dual-phase steels. Metall Trans A 16:865–872
Pantleon W (2008) Resolving the geometrically necessary dislocation content by conventional electron backscattering diffraction. Scr Mater 58:994–997
Nye JF (1953) Some geometrical relations in dislocated crystals. Acta Metall 1:153–162
Funding
JAMB received the Latin-American Postdoctoral scholarship (Grant number CONICET D 4263) received from the Argentine Ministry of Science, Technology and Productive Innovation and the National Council of Scientific and Technical Research (CONICET).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muñoz, J.A., Higuera, O.F., Tartalini, V. et al. Equal channel angular sheet extrusion (ECASE) as a precursor of heterogeneity in an AA6063-T6 alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102, 3459–3471 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03425-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03425-7