Abstract
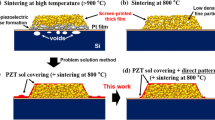
The fabrication and structuring of multilayer-thick film piezoelectric (PZT-lead zirconate titanate) structures, using composite sol-gel techniques and wet etching is described. The composite sol-gel technique involves producing a PZT powder/sol composite slurry which when spun down, yields films a few micrometres thick. Repeated layering and infiltration has been used to produce PZT films between 10 and 40 μm thick. Due to the low firing temperature (<720°C), it has also been possible to produce PZT films with embedded thin (ca. 100 nm thick) metal electrodes. The PZT thick films have also been structured using a wet etching technique. Examples of features and cavities with lateral dimensions in the order of tens of micrometres are presented. The ability to fabricate and structure thick functional films with embedded metal electrode structures offers the possibility to create novel micro-device structures suitable for use in micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scharzer S, Roosen A (1999) Tape casting of piezoceramic/polymer composites. J Euro Ceram Soc 19:1007–1010
Liliehorn T, Johanson S (2004) Fabrication of multilayer 2D ultrasonic transducer microarrays by green machining. J Micromaching Microengineering 14:702–709
Simon Seveyrat L, Gonnard P (2003) Processing and characterization of piezoelectric thick films screen-printed on silicon and glass-ceramic substrates. Integr Ferroelectr 50:1–18
Cannell D, Trigg P (1990) Advanced ceramic processing and technology, Chap 4. Processing of electronic ceramics, pp 95
Ledermann N, Muralt P, Baborowski J, Gentil S, Mukati K, Cantoni M, Seifert A, Setter N (2003){1 0 0}-Textured, piezoelectric Pb(Zrx, Ti1-x)O3 thin films for MEMS: integration, deposition and properties. Sens Actuators A 105:162–170
Meyerhofer D (1978) Characteristics of resist films produce by spinning. J Appl Phys 49(7):3993–3997
Livage J, Sanchez C (1992) Sol-gel chemistry. J Non-Cryst Solids 8:145
Whatmore RW, Zhang Q, Huang Z, Dorey RA (2003) Ferroelectric thin and thick films for microsystems. Mater Sci Semicond Process 5:65–76
Dorey RA, Stringfellow SB, Whatmore RW (2002) Effect of sintering aid and repeat sol infiltration on the dielectric and piezoelectric properties of a composite thick film. J Euro Ceram Soc 22:2921–2926
Duval FFFC, Dorey RA, Zhang Q, Whatmore RW (2003) Lead germanium oxide sinter-assisted PZT composite thick films. J Euro Ceram Soc 23:1935–1941
Zheng K, Lu J, Chu J (2003) Study on wet-etching of PZT thin film. Microprocesses and nanotechnology conference international 2003. Dig Pap 29–31:248–249
Zhang Q, Corkovic S, Shaw CP, Huang Z, Whatmore RW (2005) Effect of porosity on the ferroelectric properties of sol-gel prepared lead titanate thin films. Thin Solid Films 488:258–264
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dauchy, F., Dorey, R.A. Patterned crack-free PZT thick films for micro-electromechanical system applications. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 33, 86–94 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-0968-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-0968-1