Abstract
Purpose
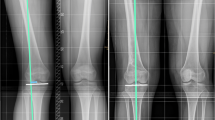
The purpose of the study was to investigate the influence of the mLDFA (mechanical lateral distal femur angle) as a parameter in varus realignment osteotomies for valgus deformities of the knee. We hypothesized that joint line obliquity with mLDFA > 90° after distal femur osteotomy (DFO) is associated with inferior clinical outcome.
Methods
In a retrospective study, a total of 52 patients with isolated femoral valgus deformities were included in the study. The mean postoperative follow-up was 70.5 (SD 33.3) months (standard deviation SD±33.3). In all patients, a distal femur osteotomy was performed. A clinical examination and survey of questionnaires was conducted with the HSS (Hospital for Special Surgery), LG (Lysholm-Gilquist), and KOOS (Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score) scores. Several radiological parameters were assessed on long-standing x-rays: mechanical tibio-femoral angle (mTFA), mLDFA, mechanical medial proximal tibia angle (mMPTA), joint-line convergence angle (JLCA). The t test was used for normally distributed data. The Mann-Whitney U test was performed in non-normally distributed data.
Results
The mLDFA was 84.9° (SD±2.3) preop and changed to 91.9° (SD±3, 22.9) postop. The mTFA (mechanical tibio-femoral angle) was 5.2° (SD±2.9°) preop and − 1.8° (SD±2.9) postop demonstrating a difference of 6.7°. For analysis, the data was divided into two groups based on postop mLDFA. Group 1: mLDFA ≤ 90°; Group 2: > 90°. Postoperatively, a mean mLDFA of 88.6° (SD±1.4°) was measured in group 1 and 93.9° (SD±2.1) in group 2. The change in mLDFA was 4.7° (SD±1.6) in group 1 and 8.4° (SD±2.8) in group 2. Preoperatively, the mTFA was 4.8° (SD±1.9) in group 1 and 5.5° (SD±3.3) in group 2. Postoperatively, the mTFA decreased in group 1 by 4.8° (SD±2.3) to − 0.1° (SD±2.1). In group 2, the mTFA decreased by 8.2° (SD±3.8) to − 2.8° (SD±2.9). Regarding the HSS, group 1 showed a 10.4 points better score than group 2 (p<0.01). Also, regarding the Lysholm, a significant difference of 16.9 points was found (p<0.01).
Conclusion
Correction of valgus knees using closed wedge DFO leads to good clinical results. A postoperative mLDFA of 85–90° results in superior clinical outcome compared to mLDFA > 90°. Joint-line obliquity should be avoided using double level osteotomy, if needed.
Level of evidence
III.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The paricipants of this study gave written consent for their data to be shared publicly.
References
Ahmad SS, Kerber V, Konrads C, Ateschrang A, Hirschmann MT, Stöckle U et al (2021) The ischiofemoral space of the hip is influenced by the frontal knee alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 29:2446–2452
Ahrend M-D, Baumgartner H, Ihle C, Histing T, Schröter S, Finger F (2022) Influence of axial limb rotation on radiographic lower limb alignment: a systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 142:3349–3366
Babis GC, An KN, Chao EY, Rand JA, Sim FH (2002) Double level osteotomy of the knee: a method to retain joint-line obliquity. Clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A:1380–1388
Brinkman J-M, Freiling D, Lobenhoffer P, Staubli AE, van Heerwaarden RJ (2014) Suprakondyläre Femurosteotomien in Kniegelenknähe. Orthopade 43:988–999
Cameron HU, Botsford DJ, Park YS (1997) Prognostic factors in the outcome of supracondylar femoral osteotomy for lateral compartment osteoarthritis of the knee. Canadian journal of surgery. J Canad Chirurgie 40:114–118
Chien RS, Yang CP, Chaung CR, Ho CS, Chan YS (2022) Functional and radiographic results of arthroscopy-assisted lateral open-wedge distal femur osteotomy for lateral compartment osteoarthritis with valgus knee. J Clin Med 12:176
Ciolli G, Proietti L, Mercurio M, Corona K, Maccauro G, Schiavone Panni A et al (2022) Return to sport following distal femur osteotomy: a systematic review. Orthop Rev (Pavia) 14:33774
Doll LC (2014) Die Wertigkeit der Ganzbeinstandaufnahme zur präoperativen Planung von Korrekturosteotomien. Open Access Repositorium der Universität Ulm und Technischen Hochschule Ulm. Dissertation. https://doi.org/10.18725/OPARU-3107
Duchow J, Kohn D (2003) Die Behandlung der beginnendenGonarthrose im mittleren Lebensalter. Orthopade 32:920–930
Eberbach H, Mehl J, Feucht MJ, Bode G, Sudkamp NP, Niemeyer P (2017) Geometry of the valgus knee: contradicting the dogma of a femoral-based deformity. Am J Sports Med 45:909–914
Finkelstein JA, Gross AE, Davis A (1996) Varus osteotomy of the distal part of the femur. A survivorship analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78:1348–1352
Forkel P, Achtnich A, Metzlaff S, Zantop T, Petersen W (2015) Midterm results following medial closed wedge distal femoral osteotomy stabilized with a locking internal fixation device. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23:2061–2067
Franco V, Cipolla M, Gerullo G, Gianni E, Puddu G (2004) Open wedge osteotomy of the distal femur in the valgus knee. Orthopade 33:185–192
Freiling D, Lobenhoffer P, Staubli A (2008) Die varisierende schließende Femurosteotomie zur Behandlung der Valgusarthrose am Kniegelenk. Arthroskopie 21:6–14
Freiling D, Lobenhoffer P, Staubli A, Heerwaarden RV (2008) Die varisierende schließende Femurosteotomie zur Behandlung der Valgusarthrose am Kniegelenk. Arthroskopie 21:6–14
Freiling D, van Heerwaarden R, Staubli A, Lobenhoffer P (2010) The medial closed-wedge osteotomy of the distal femur for the treatment of unicompartmental lateral osteoarthritis of the knee. Oper Orthop Traumatol 22:317–334
Fuchs J, Rabenberg M, Scheidt-Nave C (2013) Prävalenz ausgewählter muskuloskelettaler Erkrankungen. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 56:678–686
Halder A, Kutzner I, Graichen F, Heinlein B, Beier A, Bergmann G (2012) Influence of limb alignment on mediolateral loading in total knee replacement: in vivo measurements in five patients. JBJS 94:1023–1029
Healy WL, Anglen JO, Wasilewski SA, Krackow KA (1988) Distal femoral varus osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 70:102–109
Hofmann S, Lobenhoffer P, Staubli A, Van Heerwaarden R (2009) Osteotomien am Kniegelenk bei Monokompartmentarthrose. Orthopade 38:755–770
Konrads C, Ahmad SS, Histing T, Ibrahim M (2022) Iatrogenic ischiofemoral impingement due to high tibial osteotomy with overvalgization: a case report. J Med Case Rep 16:1–4
Lobenhoffer P, Kley K, Freiling D, van Heerwaarden R (2017) Medial closed wedge osteotomy of the distal femur in biplanar technique and a specific plate fixator. Oper Orthop Traumatol 29:306–319
Lysholm J, Gillquist J (1982) Evaluation of knee ligament surgery results with special emphasis on use of a scoring scale. Am J Sports Med 10:150–154
Meisterhans M, Flury A, Zindel C, Zimmermann SM, Vlachopoulos L, Snedeker JG et al (2023) Finite element analysis of medial closing and lateral opening wedge osteotomies of the distal femur in relation to hinge fractures. J Exp Orthop 10:33
Mereb T, Favreau H, Ollivier M, Jmal H, Bonnomet F, Bahlouli N et al (2023) Experimental study of risk of medial hinge fracture during distal femoral varus osteotomy. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 109:103527
Michael JWP, Schlüter-Brust KU, Eysel P (2010) The epidemiology, etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Deutsches Arzteblatt Int 107:152–162
Nakamura R, Amemiya M, Shimakawa T, Takahashi M, Kuroda K, Katsuki Y, Okano A (2023) Femoral-varus tibial-valgus osteotomy (FVTVO) for neutrally-algined knee osteoarthritis with severe joint line obliquity enables return to sports activities: a case series study. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol 31:11–17
Nakayama H, Iseki T, Kanto R, Kambara S, Kanto M, Yoshiya S et al (2020) Physiologic knee joint alignment and orientation can be restored by the minimally invasive double level osteotomy for osteoarthritic knees with severe varus deformity. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28:742–750
Nakayama H, Schroter S, Yamamoto C, Iseki T, Kanto R, Kurosaka K et al (2018) Large correction in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with resultant joint-line obliquity induces excessive shear stress on the articular cartilage. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26:1873–1878
Oda T, Maeyama A, Yoshimura I, Ishimatsu T, Miyazaki K, Tachibana K et al (2022) Soft tissue stabilization of the hinge position in medial closed wedge distal femoral osteotomy: an anatomical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 23:1105
Orth P, Kohn D, Madry H (2016) Degenerative Kniegelenkerkrankungen – Gonarthrose. Lege artis 6:81–98
Petersen W, Forkel P (2013) Medial closing wedge osteotomy for correction of genu valgum and torsional malalignment. Oper Orthop Traumatol 25:593–607
Pioger C, Mabrouk A, siboni R, Jacquet C, Seil R, Ollivier M (2023) Double-level knee osteotomy accurately corrects lower limb deformity and provides satisfactory functional outcomes in bifocal (femur and tibia) valgus malaligned knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-023-07325-y
Piovan G, Farinelli L, Screpis D, Iacono V, Povegliano L, Bonomo M et al (2022) Distal femoral osteotomy versus lateral unicompartmental arthroplasty for isolated lateral tibiofemoral osteoarthritis with intra-articular and extra-articular deformity: a propensity score-matched analysis. Knee Surg Relat Res 34:34
Puddu G, Cipolla M, Cerullo G, Franco V, Giannì E (2010) Which osteotomy for a valgus knee? Int Orthop 34:239–247
Ranawat CS, Shine JJ (1973) Duo-condylar total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-197307000-00023185-195
Roos EM, Roos HP, Lohmander LS, Ekdahl C, Beynnon BD (1998) Knee injury and osteoarthritis outcome score (KOOS)—development of a self-administered outcome measure. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 28:88–96
Roos EM, Toksvig-Larsen S (2003) Knee injury and osteoarthritis outcome score (KOOS)—validation and comparison to the WOMAC in total knee replacement. Health Qual Life Outcomes 1:17
Roos H, Lauren M, Adalberth T, Roos EM, Jonsson K, Lohmander LS (1998) Knee osteoarthritis after meniscectomy: prevalence of radiographic changes after twenty-one years, compared with matched controls. Arthritis Rheum 41:687–693
Saragaglia D, Chedal-Bornu B (2014) Computer-assisted osteotomy for valgus knees: medium-term results of 29 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 100:527–530
Schroter S, Ihle C, Mueller J, Lobenhoffer P, Stockle U, van Heerwaarden R (2013) Digital planning of high tibial osteotomy. Interrater reliability by using two different software. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:189–196
Schröter S, Nakayama H, Ihle C, Ahrend M-D, Kuwashima U (2020) Minimal-invasive biplanare Closed-wedge-DFO (Distale Femurosteotomie). Knie J 2:212–219
Schroter S, Nakayama H, Yoshiya S, Stockle U, Ateschrang A, Gruhn J (2019) Development of the double level osteotomy in severe varus osteoarthritis showed good outcome by preventing oblique joint line. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 139:519–527
Schuster P, Rathgeb F, Mayer P, Michalski S, Hielscher L, Buchholz J et al (2023) Double level osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis and bifocal varus malalignment has excellent short-term results whhile maintaining physiologic radiographic joint parameters. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-022-07247-1
Söder S, Aigner T (2011) Arthrose. Pathologe 32:183–192
Taylor S, Getgood A (2022) Genu valgum correction and biplanar osteotomies. Clin Sports Med 41:47–63
van Heerwaarden R, Najfeld M, Brinkman M, Seil R, Madry H, Pape D (2012) Wedge volume and osteotomy surface depend on surgical technique for distal femoral osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2127-y
Wang J-W, Hsu C-C (2005) Distal femoral varus osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the knee. JBJS 87:127–133
Wu Y, Jin X, Zhao X, Wang Y, Bai H, Lu B et al (2022) Computer-aided design of distal femoral osteotomy for the valgus knee and effect of correction angle on joint loading by finite element analysis. Orthop Surg 14:2904–2913
Wylie JD, Jones DL, Hartley MK, Kapron AL, Krych AJ, Aoki SK et al (2016) Distal femoral osteotomy for the valgus knee: medial closing wedge versus lateral opening wedge: a systematic review. Arthroscopy 32:2141–2147
Funding
The study was performed without any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS: had the idea of the study. He performed the surgery of the majority of the patients. He developed together with DS: the study protocol. Moreover, he was involved in the data analysis and correction of the manuscript. CK: was involved in writing the manuscript and data analysis. He corrected and revised the manuscript. MM: made corrections of the manuscript and was involved in data analysis as well as literature review. MM: wrote part of the manuscript and made review of the literature. CF: was involved in data analysis and manuscript draft. DS: made the data analysis and statistics. I was involved in the manuscript draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The ethical committee of the University of Tübingen, Germany, approved the study (636/2016BO2).
Informed consent
All patients confirmed their participation by a signed informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Schröter, S., Konrads, C., Maiotti, M. et al. In closed wedge distal femur osteotomies for correction of valgus malalignment overcorrection of mLDFA should be avoided. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 31, 3992–3999 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-023-07449-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-023-07449-1