Abstract
Purpose
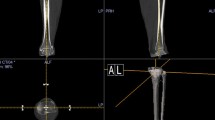
The aim of this study is to evaluate the accuracy of a patient-specific instrumentation (PSI) as assessed by the intraoperative use of knee navigation software during the surgical procedure.
Methods
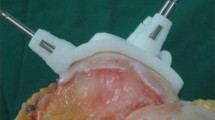
Fifteen patients with primary gonarthrosis were selected for unilateral total knee arthroplasty. The first three patients were excluded from this study, as they were considered to be a warm up to set-up the procedure. All patients were operated on with a cemented posterior-stabilised prosthesis cruciate ligament-sacrificing by the same surgeon using the patient matched cutting jigs. The size of the implant, level of resection, and alignment in the coronal and sagittal planes were evaluated. An unsatisfactory result was considered an error ≥2° in both planes for each component as a possible error of 4° could result in aggravation.
Results
On the coronal plane the mean deviation of the tibial guide from the ideal alignment was 1.2 ± 1.5 (range 0–5°) and in the sagittal plane was 3.8 ± 2.4 (range 0–7.5°). On the coronal plane the mean deviation of the femoral guide from the ideal alignment was 1.2 ± 0.6 and in the sagittal was 3.7 ± 2.
Conclusion
On the basis of this preliminary experience the PSI system based only on data acquisition with A-P radiograms and RMN cannot be defined as accurate. In cases of the use of the custom made cutting jigs it is recommended to perform an accurate control of the alignment before making the cuts, for any step of the procedure.
Level of evidence
II.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MA (1983) Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Correlated biomechanical and clinical observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res 173:178–183
Barrett WP, Mason JB, Moskal JT, Dalury DF, Oliashirazi A, Fisher DA (2011) Comparison of radiographic alignment of imageless computer-assisted surgery vs conventional instrumentation in primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 26(8):1273–1284
Bellemans J, Robijns F, Duerinckx J, Banks S, Vandenneucker H (2005) The influence of tibial slope on maximal flexion after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13(3):193–196
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Catani F, Biasca N, Ensini A, Leardini A, Bianchi L, Digennaro V, Giannini S (2008) Alignment deviation between bone resection and final implant positioning in computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am 90(4):765–771
Catani F, Digennaro V, Ensini A, Leardini A, Giannini S (2012) Navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty in knees with osteoarthritis due to extra-articular deformity. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(3):546–551
Cheng T, Pan XY, Mao X, Zhang GY, Zhang XL (2011) Little clinical advantage of computer-assisted navigation over conventional instrumentation in primary total knee arthroplasty at early follow-up. Knee PMID: 22130355
Cheng T, Zhao S, Peng X, Zhang X (2011) Does computer-assisted surgery improve postoperative leg alignment and implant positioning following total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. PMID: 21732057
Hafez MA, Chelule KL, Seedhom BB, Sherman KP (2006) Computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty using patient-specific templating. Clin Orthop Relat Res 444:184–192
Hernández-Vaquero D, Suarez-Vazquez A, Iglesias-Fernandez S (2011) Can computer assistance improve the clinical and functional scores in total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:3436–3442
Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Tsumura N, Kubo S, Kitagawa A, Chin T, Iguchi T, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2011) Mid-term outcomes of computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(7):1107–1112
Klatt BA, Goyal N, Austin MS, Hozack WJ (2008) Custom-fit total knee arthroplasty (OtisKnee) results in mal-alignment. J Arthroplast 23(1):26–29
Magnussen RA, Weppe F, Demey G, Servien E, Lustig S (2011) Residual varus alignment does not compromise results of TKAs in patients with preoperative varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:3443–3450
Moreland JR (1998) Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:49–64
Noble JW Jr, Moore CA, Liu N (2012) The value of patient-matched instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 27:153–155
Novak EJ, Silverstein MD, Bozic KJ (2007) The cost-effectiveness of computer-assisted navigation in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am 89:2389–2397
Pang HN, Yeo SJ, Chong HC, Chin PL, Ong J, Lo NN (2011) Computer-assisted gap balancing technique improves outcome in total knee arthroplasty, compared with conventional measured resection technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:1496–1503
Spencer BA, Mont MA, McGrath MS, Boyd B, Mitrick MF (2009) Initial experience with custom-fit total knee replacement: intra-operative events and long-leg coronal alignment. Int Orthop 33:1571–1575
Stulberg BN, Zadzilka JD (2006) Computer-assisted surgery: a wine before its time: in opposition. J Arthroplast 21:29–32
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose any possible conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conteduca, F., Iorio, R., Mazza, D. et al. Evaluation of the accuracy of a patient-specific instrumentation by navigation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21, 2194–2199 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2098-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2098-z