Abstract
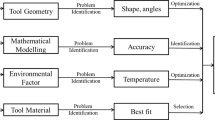
As an effective lightweight technique, reliability-based multi-objective optimization (RBMO) for welding process parameters of aluminum alloy sheets demonstrates the unprecedented potential and stability in the automobile manufacturing. In order to ensure load-bearing capacity and assembly feasibility of welded joints in the body structure, the process–property–performance (3P) relationship should be fully considered in optimizing double-pulse MIG (DP-MIG) welding process parameters. This study proposes an RBMO design of welding process parameters that employed a hybrid optimization strategy (HOS), which includes screening significant parameters, building process–property meta-models, and searching optimal solution under performance requirements. Combining entropy weight and technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution for Plackett–Burman design is used to screen significant parameters. Then, the response surface methodology based on central composite design is used to construct the regression models between significant factors and responses. Also, the reliability of each response is analysed through the Monte Carlo simulation and Design for Six Sigma design. The non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm and multi-objective decision criteria based on performance requirements are employed to find the optimal solution of RBMO. The effectiveness and applicability of the proposed HOS method are demonstrated by optimization of DP-MIG welding process parameters, which could yield improvements of load-bearing, geometry performance of welded joints and their robustness. The combination of 3P relationships and optimization design reveals the internal connection between design and manufacturing, and provides a guideline for DP-MIG welding parameters design. RBMO can be generally applied to types of jointing technology in automotive manufacturing and the proposed HOS method can be used in the optimization design of multiple influencing factors and multiple responses.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi K, Alam S, Khan MI (2014) An experimental study on the effect of MIG welding parameters on the weldability of galvenize steel. Int J Emerg Technol 5:146–152
Amir BA, Pougnet P, Hami A (2020) Embedded Mechatronics systems 2 (second edition) analysis of failures, modeling, simulation, and optimization. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 157–187
Arya DM, Chaturvedi V, Vimal J (2013) Parametric optimization of mig process parameters using Taguchi and grey Taguchi analysis. Int J Res Eng Appl Sci IJREAS 3:1–17
Cruz JG, Torres EM, Absi Alfaro SC (2015) A methodology for modeling and control of weld bead width in the GMAW process. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 37:1529–1541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-014-0299-8
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6:182–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017
Duan L, Li G, Cheng A, Sun G, Song K (2017) Multi-objective system reliability-based optimization method for design of a fully parametric concept car body. Eng Optim 49:1247–1263. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2016.1241780
DuPont JN, Marder AR (1995) Thermal efficiency of arc welding processes. Weld J (miami, Fla) 74:406–416
Feng L, Zhang L (2021) Reliability-based multi-objective optimization in tunneling alignment under uncertainty. Struct Multidisc Optim 63:3007–3025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-02846-x
Gu Q, Cui X, Shang H (2020) Optimization of a modular continuous flow bioreactor system for acid mine drainage treatment using Plackett–Burman design. Asia-Pacific J Chem Eng 15:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.2469
Hosder S, Watson LT, Grossman B, Mason WH, Kim H, Haftka RP, Cox SE (2002) Polynomial response surface approximations for the multidisciplinary design optimization of a high speed civil transport. Optim Eng 2:431–452
Ishak M, Noordin NF, Razali AS, Hakim L, Shah A (2015) The effect of filler ER4043 and ER5356 on weld metal structure of 6061 aluminium alloy by metal inert gas (MIG). Int J Eng Technol Sci 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.15282/ijets.3.2015.1.11.1028
Jogi BF, Awale AS, Nirantar SR, Bhusare HS (2018) Metal inert gas (MIG) welding process optimization using teaching-learning based optimization (TLBO) algorithm. Mater Today Proc 5:7086–7095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.373
Kanakavalli PB, Babu BN, Sai CPNV (2020) A hybrid methodology for optimizing MIG welding process parameters in joining of dissimilar metals. Mater Today Proc 23:507–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.05.396
Koçak M (2010) Structural integrity of welded structures: process–property–performance (3P) relationship. Proc Int Conf Adv Weld Sci Technol Constr Energy Transp AWST 2010, held Conj with 63rd Annu Assem IIW 2010 3–19
Koli Y, Yuvaraj N, Vipin AS (2019) Investigations on weld bead geometry and microstructure in CMT, MIG pulse synergic and MIG welding of AA6061-T6. Mater Res Express 6:1265e5. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab61b6
Kumar S, Singh R (2019) Optimization of process parameters of metal inert gas welding with preheating on AISI 1018 mild steel using grey based Taguchi method. Meas J Int Meas Confed 148:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.106924
Li P, Nie F, Dong H, Li S, Yang G, Zhang H (2018) Pulse MIG welding of 6061–T6/A356-T6 aluminum alloy dissimilar T-joint. J Mater Eng Perform 27:4760–4769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3528-y
Li S, Yuan S, Zhu J, Zhang W, Zhang H, Li J (2021) Multidisciplinary topology optimization incorporating process–structure–property–performance relationship of additive manufacturing. Struct Multidisc Optim 63:2141–2157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-02856-9
Liu L, Zhang S, Li X, Zhang B (2019) Six-sigma robust optimization on the nvh performance of the crfm based on isight. Lecture notes in electrical engineering. Springer, Singapore, pp 245–256
Malviya R, Pratihar DK (2011) Tuning of neural networks using particle swarm optimization to model MIG welding process. Swarm Evol Comput 1:223–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2011.07.001
Miller WS, Zhuang L, Bottema J, Wittebrood AJ, De Smet P, Haszler A, Vieregge (2000) Recent development in aluminium alloys for the automotive industry. Mater Sci Eng A 280:37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00653-X
Nejadali J (2021) Shape optimization of regenerative flow compressor with aero-foil type blades using response surface methodology coupled with CFD. Struct Multidisc Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-03020-z
Pepe N, Egerland S, Colegrove PA, Yapp D, Leonhartsberger A, Scotti A (2011) Measuring the process efficiency of controlled gas metal arc welding processes. Sci Technol Weld Join 16:412–417. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171810Y.0000000029
Pojananukij N, Wantala K, Neramittagapong S, Neramittagapong A (2014) Parameter screening for the important factors influencing the As(V) adsorption using a plackett-burman design. Adv Mater Res 931:178–182. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.931-932.178
Ravanfar R, Tamaddon AM, Niakousari M, Moein MR (2016) Preservation of anthocyanins in solid lipid nanoparticles: optimization of a microemulsion dilution method using the Placket–Burman and Box–Behnken designs. Food Chem 199:573–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.12.061
Sen M, Mukherjee M, Pal TK (2015) Evaluation of correlations between DP-GMAW process parameters and bead geometry. Weld J 94:265–279
Shimoyama K, Oyama A, Fujii K (2008) Development of multi-objective six-sigma approach for robust design optimization. J Aerosp Comput Inf Commun 5:215–233. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.30310
Singh RP, Garg RK, Shukla DK (2016) Mathematical modeling of effect of polarity on weld bead geometry in submerged arc welding. J Manuf Process 21:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2015.11.003
Smerd R, Winkler S, Salisbury C, Worswick M, Lloyd D, Finn M (2005) High strain rate tensile testing of automotive aluminum alloy sheet. Int J Impact Eng 32:541–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.04.013
Srivastava S, Garg RK (2017) Process parameter optimization of gas metal arc welding on IS:2062 mild steel using response surface methodology. J Manuf Process 25:296–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.12.016
Subramanian R, Natarajan B, Kaliyaperumal B, Chinnasamy R (2019) Effect of MIG welding process parameters on microstructure and tensile behavior of hastelloy C276 using response surface methodology. Mater Res Express 6:066540. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab093a
Sudhakar R, Sivasubramanian R, Yoganandh J (2018) Effect of automated MIG welding process parameters on ASTM A 106 Grade B pipe weldments used in high-temperature applications. Mater Manuf Process 33:749–758. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1401719
Szulc M, Malujda I, Talaśka K (2016) Method of determination of safety factor on example of selected structure. Procedia Eng 136:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.01.173
Wang L, Jin L, Huang W, Xu M, Xue J (2016) Effect of thermal frequency on AA6061 aluminum alloy double pulsed gas metal arc welding. Mater Manuf Process 31:2152–2157. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1103863
Wang D, Wang S, Xie C (2020) A multi-objective optimization approach for simultaneously lightweighting and maximizing functional performance of vehicle body structure. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part D J Automob Eng 234:2086–2102. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954407019868140
Warinsiriruk E, Greebmalai J, Sangsuriyun M (2019) Effect of double pulse MIG welding on porosity formation on aluminium 5083 fillet Joint. MATEC Web Conf 269:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201926901002
Xue J, Xu M, Huang W, Zhang Z, Wu W, Jin L (2019) Stability and heat input controllability of two different modulations for double-pulse MIG welding. Appl Sci 9:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010127
Yamamoto H, Harada S, Ueyama T, Ogawa S (1992) Development of low-frequency pulsed MIG welding for aluminium alloys. Weld Int 6:580–583. https://doi.org/10.1080/09507119209548246
Yamamoto H, Harada S, Ueyama T, Ogawa S, Matsuda F, Nakata K (1993) Beneficial effects of low-frequency pulsed MIG welding on grain refinement of weld metal and improvement of solidification crack susceptibility of aluminium alloys: study of low-frequency pulsed MIG welding. Weld Int 7:456–461. https://doi.org/10.1080/09507119309548425
Yang X (2014) Multi-objective optimization. In: Yang XS (ed) Nature-inspired optimization algorithms. Acadmic Press, London, pp 197–211
Yi J, Wang G, LiKang S, Li S, Liu Z, Gong Y (2019) Effect of post-weld heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of welded joints of 6061–T6 aluminum alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 29:2035–2046. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65110-1
Zhang W, He H, Xu C, Yu W, Li L (2019) Precipitates dissolution, phase transformation, and re-precipitation-induced hardness Variation in 6082–T6 alloy during MIG welding and subsequent baking. Jom 71:2711–2720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03375-1
Zhou J, Yu X, Ding C, Wang Z, Zhou Q, Pao H, Cai W (2011) Optimization of phenol degradation by Candida tropicalis Z-04 using Plackett–Burman design and response surface methodology. J Environ Sci 23:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60369-5
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Plan of China (Grant No. 2016YFB0101601-7) and Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University (Grant No.101832020CX134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research and publication of this article.
Replication of results
The results presented in this paper can be replicated using software Design-Expert, Isight, and Matlab. The data and codes will be available once requested.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Palaniappan Ramu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Chen, X. & Yang, L. Reliability-based multi-objective optimization incorporating process–property–performance relationship of double-pulse MIG welding using hybrid optimization strategy. Struct Multidisc Optim 65, 148 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-03103-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-021-03103-x