Abstract
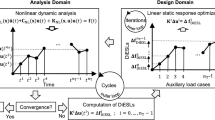
The standard equivalent static loads (ESLs) method for stiffness topology optimization under crash condition may lead to exaggerated equivalent loads, which is not appropriate to be incorporated into the linear static topology optimization and whereby hinder the optimization process. To overcome this disadvantage, an improved ESLs algorithm based on energy-scaling ratio is proposed to guarantee the numerical stability, especially for the first several cycles with relatively larger differences of strain energy between the original crash simulation and equivalent static analysis. At each cycle, the equivalent external static forces are calculated by multiplying the stiffness matrix and the displacement vector at the time with maximal strain energy during the crash simulation. A further adaptive energy-scaling operation for those forces are performed by a weighting factor of square root of the energy ratio to the standard equivalent static loads for the crash problem based on the judging criterion. The newly equivalent loads are incorporated into the static topology optimization, and topology results are filtered into a black-white design for the crash simulation to avoid the numerical issues due to existing of low-density elements. The process is repeated until the convergence criteria is satisfied. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated by investing two crash design problems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreassen E, Clausen A, Schevenels M et al (2011) Efficient topology optimization in MATLAB using 88 lines of code. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-010-0594-7
Bai YC, Jiang C, Han X, Hu DA (2013) Evidence-theory-based structural static and dynamic response analysis under epistemic uncertainties. Finite Elem Anal Des 68:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2013.01.007
Bendsøe MP (1995) The homogenization approach to topology design. In: Optimization of Structural Topology, Shape, and Material. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 5–77
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2003) Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods and Applications. Springer
Bruns TE, Tortorelli DA (2003) An element removal and reintroduction strategy for the topology optimization of structures and compliant mechanisms. Int J Numer Methods Eng 57:1413–1430
Chen S, Chen W, Lee S (2010) Level set based robust shape and topology optimization under random field uncertainties. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41:507–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-009-0449-2
Da DC, Chen JH, Cui XY, Li GY (2017) Design of materials using hybrid cellular automata. Struct Multidiscip Optim 56:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1652-1
Duddeck F, Bujny M, Zeng D (2017) Topology optimization methods based on nonlinear and dynamic crash simulations. In: 11th European LS-DYNA Conference 2017. Salzburg, Austria
Guest JK, Prévost JH, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61:238–254
Guo X, Zhang W, Zhang L (2013) Robust structural topology optimization considering boundary uncertainties. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 253:356–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2012.09.005
Huang X, Xie YM (2007) A new look at ESO and BESO optimization methods. Struct Multidiscip Optim 35:89–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-007-0140-4
Jang HH, Lee HA, Lee JY, Park GJ (2012) Dynamic Response Topology Optimization in the Time Domain Using Equivalent Static Loads. AIAA J 50:226–234. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J051256
Kang B, Choi W, Park G (2001) Structural optimization under equivalent static loads transformed from dynamic loads based on displacement. Comput Struct 79:145–154
Kang Z, Wang Y (2013) Integrated topology optimization with embedded movable holes based on combined description by material density and level sets. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 255:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2012.11.006
Kaushik A, Ramani A (2014) Topology optimization for nonlinear dynamic problems: Considerations for automotive crashworthiness. Eng Optim 46:487–502. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2013.776553
Langelaar M (2017) An additive manufacturing filter for topology optimization of print-ready designs. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55:871–883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1522-2
Lazarov BS, Wang F (2017) Maximum length scale in density based topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 318:826–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2017.02.018
Lee HA, Kim YI, Park GJ et al (2007) Structural Optimization of a Joined Wing Using Equivalent Static Loads. J Aircr 44(4):1302–1309
Lee H-A, Park G-J (2015a) A software development framework for structural optimization considering non linear static responses. Struct Multidiscip Optim 52:197–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1228-x
Lee H-A, Park G-J (2015b) Nonlinear dynamic response topology optimization using the equivalent static loads method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 283:956–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2014.10.015
Ortmann C, Schumacher A (2013) Graph and heuristic based topology optimization of crash loaded structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47:839–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0872-7
Park GJ (2011) Technical Overview of the Equivalent Static Loads Method for Non-linear Static Response Structural Optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43:319–337
Sigmund O (1997) On the Design of Compliant Mechanisms Using Topology Optimization. Mech Struct Mach 25:493–524. https://doi.org/10.1080/08905459708945415
Sigmund O (2001) A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct Multidiscip Optim 21:120–127
Suresh K (2010) A 199-line Matlab code for Pareto-optimal tracing in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 42:665–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-010-0534-6
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes - a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24:359–373
Wang F, Lazarov BS, Sigmund O (2010) On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43:767–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-010-0602-y
Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:227–246
Wu J, Clausen A, Sigmund O (2017) Minimum compliance topology optimization of shell-infill composites for additive manufacturing. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2017.08.018
Xia Q, Shi T (2016) Optimization of structures with thin-layer functional device on its surface through a level set based multiple-type boundary method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 311:56–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2016.08.001
Xie YM, Steven GP (1993) A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Comput Struct 49:885–896
Yan X, Huang X, Zha Y, Xie YM (2014) Concurrent topology optimization of structures and their composite microstructures. Comput Struct 133:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2013.12.001
Yoon GH, Kim YY (2005) Element connectivity parameterization for topology optimization of geometrically nonlinear structures. Int J Solids Struct 42:1983–2009
Zheng J, Luo Z, Jiang C, Ni B, Wu J (2017) Non-probabilistic reliability-based topology optimization with multidimensional parallelepiped convex model. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57:2205–2221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1851-9
Zhou M, Lazarov BS, Wang F, Sigmund O (2015) Minimum length scale in topology optimization by geometric constraints. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 293:266–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2015.05.003
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Beijing Institute of Technology Research Fund Program for Young Scholars, the Science and Technology Planning Project of Beijing City (NO. Z161100001416007) and the National Key R&D Program of China (NO. 2017YFB0103801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Responsible Editor: Erdem Acar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Y.C., Zhou, H., Lei, F. et al. An improved numerically-stable equivalent static loads (ESLs) algorithm based on energy-scaling ratio for stiffness topology optimization under crash loads. Struct Multidisc Optim 59, 117–130 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-2054-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-2054-8