Abstract
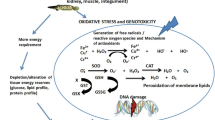
Studying the bioaccumulation behavior and toxicity of triazole fungicides is a crucial part of comprehensively evaluating the environmental fate and aquatic toxicity.The current research aimed to reveal the toxic effects of propiconazole and difenoconazole on fish through acute toxicity test, bioaccumulation test and oxidase system activity determination. Here, the propiconazole and difenoconazole concentrations were 11.3 mg/L and 31.2 mg/L for LC50-96 h, both having low toxicity. LC–MS/MS was used to determine the propiconazole and difenoconazole concentrations in five organs (muscle, gill, liver, intestine, and kidney) of Procypris meru. The findings indicate that the bioconcentration coefficients of propiconazole and difenoconazole in grass flower carp were 0.66–27.08 and 2.43–22.72, which belonged to medium enrichment pesticides. The bioconcentration coefficients decreased with the increase of exposure concentration. The two fungicides could induce oxidative stress in fish liver, and the activities of three antioxidant enzymes were inhibited in varying degrees (p < 0.05). The results showed that the content of T3 increased, and T4 decreased when exposed to one-tenth LC50 for 7 days. This study shows that triazole pesticides have bioaccumulation risks on aquatic organisms and clear environmental hormonal effects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castillo LE, Martínez E, Ruepert C, Savage C, Gilek M, Pinnock M, Solis E (2006) Water quality and macroinvertebrate community response following pesticide applications in a banana plantation, limon, costa rica. Sci Total Environ 367(1):418–432
Ding F, Song WH, Guo J, Gao ML, Wei XHU (2008) Oxidative stress and structure-activity relationship in the zebrafish (danio rerio) under exposure to paclobutrazol. J Environ Sci Health B 44(1):44–50
GB/T 31270.12-2014,Test guidelines on environmental safety assessment for chemical pesticides-Part 12: fish acute toxicity test
Hemalatha D, Muthukumar A, Rangasamy B, Nataraj B, Ramesh M (2016) Impact of sublethal concentration of a fungicide propiconazole on certain health biomarkers of Indian major carp Labeo rohita. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 8:321–327
Henriques MB, Rezende K, Castilho-Barros L, Barbieri E (2021) Sublethal effects of propiconazole on the metabolism of lambari Deuterodon iguape (Eigenmann 1907), a native species from Brazil. Fish Physiol Biochem 47:1–13
Jiang J, Chen L, Wu S, Lv L, Zhao X (2020) Effects of difenoconazole on hepatotoxicity, lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Pollut 265:114844
Kim JH, Kang JC (2015a) The arsenic accumulation and its effect on oxidative stress responses in juvenile rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, exposed to waterborne arsenic (As3+). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39(2):668–676
Kim JH, Kang JC (2015b) Oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and non-specific immune responses in juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major, exposed to different waterborne selenium concentrations. Chemosphere 135:46–52
Kim JH, Kang JC (2016) Oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and metallothionein (MT) gene expression in juvenile rock fish Sebastes schlegelii under the different levels of dietary chromium (Cr6+) exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:78–84
Kim JH, Oh CW, Kang JC (2017) Antioxidant responses, neurotoxicity, and metallothionein gene expression in juvenile Korean rock fish Sebastes schlegelii under dietary lead exposure. J Aquat Anim Health 29(2):112–119
Kim JH, Kang YJ, Kim KI, Kim SK, Kim JH (2019a) Toxic effects of nitrogenous compounds (ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate) on acute toxicity and antioxidant responses of juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 67:73–78
Kim JH, Kim SK, Hur YB (2019b) Hematological parameters and antioxidant responses in olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in biofloc depend on water temperature. J Therm Biol 82:206–212
Kim JH, Choi H, Sung G, Seo SA, Kim KI, Kang YJ, Kang JC (2019c) Toxic effects on hematological parameters and oxidative stress in juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus exposed to waterborne zinc. Aquacul Rep 15:100225
Kim JH, Sohn S, Kim SK, Hur YB (2020a) Effects on hematological parameters, antioxidant and immune responses, AChE, and stress indicators of olive flounders, Paralichthys olivaceus, raised in bio-floc and seawater challenged by Edwardsiella tarda. Fish Shellfish Immunol 97:194–203
Kim JH, Cho JH, Kim SR, Hur YB (2020b) Toxic effects of waterborne ammonia exposure on hematological parameters, oxidative stress and stress indicators of juvenile hybrid grouper, Epinephelus lanceolatus♂× Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 80:103453
Kim JH, Kim SK, Hur YB (2020) Toxic effects of waterborne nitrite exposure on antioxidant responses, acetylcholinesterase inhibition, and immune responses in olive flounders, Paralichthys olivaceus, reared in bio-floc and seawater. Fish Shellfish Immunol 97:581–586
Kim JH, Jeong EH, Jeon YH, Kim SK, Hur YB (2021a) Salinity-mediated changes in hematological parameters, stress, antioxidant responses, and acetylcholinesterase of juvenile olive flounders (Paralichthys olivaceus). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 83:103597
Kim JH, Kim SR, Kim SK, Kang HW (2021b) Effects of pH changes on blood physiology, antioxidant responses and Ig M of juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys Olivaceus. Aquac Rep 21:100790
Kongcharoen N, Kaewsalong N, Dethoup T (2020) Efficacy of fungicides in controlling rice blast and dirty panicle diseases in Thailand. Sci Rep 10:16233
Kumar P, Ahlawat S, Chauhan R, Kumar A, Singh R (2018) Bio-efficacy and post harvest residual toxicity of new fungicides against sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani) of rice (Oryza sativa). Indian J Agri Sci 88(10):1587–1592
Lee JW, Choi H, Hwang UK, Kang JC, Kang YJ, Kim KI, Kim JH (2019) Toxic effects of lead exposure on bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and immune responses in fish: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 68:101–108
Li ZH, Zlabek V, Velíšek J, Grabic R, Randák T (2011) Antioxidant responses and plasma biochemical characteristics in the freshwater rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, after acute exposure to the fungicide propiconazole. Czech J Anim Sci 56:61–69
Liang Yu, Chen M, Liu Y, Gui W, Zhu G (2013) Thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae following exposure to hexaconazole and tebuconazole. Aquatic Toxicol 24:138–139
Lin X, Yu R, Hu G (2009) Recent Progress in environmental hormones research: mechanism and interference effects on aquatic animals. Enuivon Sci Technol 32(9):98–104
Liu S, Clnang J, Zhao Y, Zhu G (2011) Changes of thyroid hormone levels and related gene expression in zebrafish on early life stage exposure to triadimefon. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 32:472–477
Chengzhu M, Zhenrong G (2003) Environmental hormone chemical pesticide pollution and its monitoring (review). J Shanghai Agric 4:98–103
Merrill MA, Vandenberg LN, Smith MT, Goodson W, Browne P, Patisaul HB, Guyton KZ, Kortenkamp A, Cogliano VJ, Woodruff TJ (2020) Consensus on the key characteristics of endocrine-disrupting chemicals as a basis for hazard identification. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16:45–57
Min EY, Kim JH, Lee JS, Kang JC (2021) Nickel bioaccumulation and the antioxidant response in Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai, Ino 1953 exposed to waterborne nickel during thermal stress. Aquac Rep 20:100726
Mu X, Chai T, Wang K, Zhang J, Zhu L, Li X, Wang X (2015) Occurrence and origin of sensitivity toward difenoconazole in zebrafish (Danio reio) during different life stages. Aquat Toxicol 160:57–68
OECD (1992) Guideline 203. Fish, acute toxicity test
Pandya P, Parikh P, Ambegaonkar A (2020) Evaluating the toxic potential of agrochemicals on the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). J Appl Ichthyol 36:203–211
Tabassum H, Khan J, Salman M, Raisuddin S, Parvez S (2016) Propiconazole induced toxicological alterations in brain of freshwater fish Channa punctata Bloch. Ecol Indic 62:242–248
Taxvig C, Vinggaard AM, Hass U, Axelstad M, Nellemann C (2008) Endocrine-disrupting properties in vivo of widely used azole fungicides. Int J Androl 31:170–177
Teng M, Zhu W, Wang D, Jin Y, Qi S, Min S, Wang C (2018) Acute exposure of zebrafish embryo (Danio rerio) to flutolanil reveals its developmental mechanism of toxicity via disrupting the thyroid system and metabolism. Environ Pollut 242:1157–1165
Tian W, Wang L, Lei H, Sun Y, Xiao Z (2018) Antibody production and application for immunoassay development of environmental hormones: a review. Chem Biol Technol Agric 5:1
Valadas J, Mocelin R, Sachett A, Marcon M, Piato A (2019) Propiconazole induces abnormal behavior and oxidative stress in zebrafish. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:27808–27815
Van De Steene JC, Lambert WC (2008) Validation of a solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of nine basic pharmaceuticals in wastewater and surface water samples. J Chromatogr A 24:153–160
Zhao F, Cao F, Li H, Teng M, Qiu L (2020) The effects of a short-term exposure to propiconazole in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:3821–38220
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Guangxi science and technology major projects (AA17204043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Wang, Z., Zhang, C. et al. Environmental Hormone Effects and Bioaccumulation of Propiconazole and Difenoconazole in Procypris merus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 823–830 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03609-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03609-0