Abstract
Key message
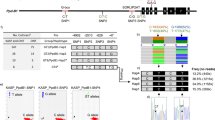
Here, a novel pleiotropic QTL qSS14 simultaneously regulating four seed size traits and two consistently detected QTLs qSW17 and qSLW02 were identified across multiple years.
Abstract
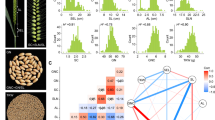
Seed-related traits were the key agronomic traits that have been artificially selected during the domestication of wild soybean. Identifying the genetic loci and genes that regulate seed size could clarify the genetic variations in seed-related traits and provide novel insights into high-yield soybean breeding. In this study, we used a high-density genetic map constructed by F10 RIL populations from a cross between Glycine max and Glycine soja to detect additive QTLs for seven seed-related traits over the last three years. As a result, we identified one novel pleiotropic QTL, qSS14, that simultaneously controlled four seed size traits (100-seed weight, seed length, seed width, and seed thickness) and two consistently detected QTLs, qSW17, and qSLW02, in multiple years of phenotypic data. Furthermore, we predicted two, two and three candidate genes within these three critical loci based on the parental resequencing data and gene function annotations. And the relative expression of four candidate genes GLYMA_14G155100, GLYMA_17G061000, GLYMA_02G273100, and GLYMA_02G273300 showed significant differences among parents and the extreme materials through qRT-PCR analysis. These findings could facilitate the determination of beneficial genes in wild soybean and contribute to our understanding of the soybean domestication process.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available in the NCBI SRA database below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA848661.
References
Arends D, Prins P, Jansen RC, Broman KW (2010) R/qtl: high-throughput multiple QTL mapping. Bioinformatics 26(23):2990–2992. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq565
Barrero JM, Rodriguez PL, Quesada V et al (2006) Both abscisic acid (ABA)-dependent and ABA-independent pathways govern the induction of NCED3, AAO3 and ABA1 in response to salt stress. Plant Cell Environ 29(10):2000–2008. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01576.x
Carter TE Jr, Nelson RL, Sneller CH, Cui ZL (2004) Genetic diversity in soybean. In: Shibles RM, Harper JE, Wilson RF, Shoemaker RC (eds) Soybeans: improvement, production, and uses, 3rd edn. American Society of Agronomy-Crop Science Society of America-Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 303–416
Cheng X, Wang S, Wang L, Wang S, Zong X, Wang P (2006) Descriptors and data standard for adzuki Bean [Vigna angularis (Willd) Ohwi & Ohashi]. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138(3):963–971. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/138.3.963
Clark CB, Wang WD, Wang Y, Fear GJ, Wen ZX, Wang DC, Ren B, Ma JX (2022) Identification and molecular mapping of a major quantitative trait locus underlying branch angle in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 135(3):777–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03995-9
Csanádi GY, Vollmann J, Stift G, Lelley T (2001) Seed quality QTLs identified in a molecular map of early maturing soybean. Theor Appl Genet 103(6):912–919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220100621
Dong Y, Yang X, Liu J, Wang BH, Liu BL, Wang YZ (2014) Pod shattering resistance associated with domestication is mediated by a NAC gene in soybean. Nat Commun 5:3352. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4352
Du J, Wang SD, He CM, Zhou B, Ruan YL, Shou HX (2017) Identification of regulatory networks and hub genes controlling soybean seed set and size using RNA sequencing analysis. J Exp Bot 68(8):1955–1972. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw460
Du HP, Qin R, Li HY, Du Q, Li X et al (2022) Genome-wide association studies reveal novel loci for herbivore resistance in wild soybean (Glycine soja). Int J Mol Sci 23(14):8016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23148016
Duan ZB, Zhang M, Zhang ZF, Liang S, Fan L et al (2022) Natural allelic variation of GmST05 controlling seed size and quality in soybean. Plant Biotechnol J 20(9):1807–1818. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13865
Eckert C, Offenborn JN, Heinz T, Armarego Marriott T, Schültke S et al (2014) The vacuolar calcium sensors CBL 2 and CBL 3 affect seed size and embryonic development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 78(1):146–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12456
Elattar MA, Karikari B, Li S, Song SY, Cao YC, Aslam M, Hina A, Abou-Elwafa SF, Zhao TJ (2021) Identification and validation of major QTLs, epistatic interactions, and candidate genes for soybean seed shape and weight using two related RIL populations. Front Genet 12:666440. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.666440
Goettel W, Zhang HY, Li Y, Qiao ZZ, Jiang H et al (2022) POWR1 is a domestication gene pleiotropically regulating seed quality and yield in soybean. Nat Commun 13(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30314-7
Grienenberger E, Besseau S, Geoffroy P et al (2009) A BAHD acyltransferase is expressed in the tapetum of Arabidopsis anthers and is involved in the synthesis of hydroxycinnamoyl spermidines. Plant J 58(2):246–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03773.x
Gu YZ, Li W, Jiang HW, Wang Y, Gao HH, Liu M, Chen QS, Lai YC, He CY (2017) Differential expression of a WRKY gene between wild and cultivated soybeans correlates to seed size. J Exp Bot 68(11):2717–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx147
Han YP, Li DM, Zhu D, Li HY, Li XP, Teng WL, Li WB (2012) QTL analysis of soybean seed weight across multi-genetic backgrounds and environments. Theor Appl Genet 125(4):671–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1859-x
Han YP, Zhao X, Liu DY, Li YH, Lightfoot DA et al (2015) Domestication footprints anchor genomic regions of agronomic importance in soybeans. New Phytol 2(209):871–884. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13626
Hoeck JA, Fehr WR, Shoemaker RC, Welke GA, Johnson SL, Cianzio SR (2003) Molecular marker analysis of seed size in soybean. Crop Sci 43(1):68–74. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2003.6800
Hu Z, Zhang H, Kan G et al (2013) Determination of the genetic architecture of seed size and shape via linkage and association analysis in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Genetica 141:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-013-9723-8
Huang XH, Huang SW, Han B, Li JY (2022) The integrated genomics of crop domestication and breeding. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.036
Hyten DL, Pantalone VR, Sams CE, Saxton AM, Landau-Ellis D, Stefaniak TR, Schmidt ME (2004) Seed quality QTL in a prominent soybean population. Theor Appl Genet 109(3):552–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1661-5
Hyten DL, Song QJ, Zhu YL, Choi I, Nelson RL, Costa JM, Specht JE, Shoemaker RC, Cregan PB (2006) Impacts of genetic bottlenecks on soybean genome diversity. Proc Nat Acad Sci 103(45):16666–16671. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.060437910
Jun TH, Freewalt K, Michel AP, Mian R (2014) Identification of novel QTL for leaf traits in soybean. Plant Breed 133(1):61–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12107
Karikari B, Chen SX, Xiao YT, Chang FG, Zhou YL, Kong JJ, Bhat JA, Zhao TJ (2019) Utilization of interspecific high-density genetic map of RIL population for the QTL detection and candidate gene mining for 100-seed weight in soybean. Front Plant Sci 10:1001. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01001
Kato S, Sayama T, Fujii K, Yumoto S, Kono Y et al (2014) A major and stable QTL associated with seed weight in soybean across multiple environments and genetic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet 127(6):1365–1374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2304-0
Kaushik N, Kumar K, Kumar S, Kaushik N, Roy S (2007) Genetic variability and divergence studies in seed traits and oil content of Jatropha (Jatropha curcas L.) accessions. Biomass Bioenergy 31(7):497–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2007.01.021
Kim H, Kim Y, Kim S, Son B, Choi Y, Kang J, Park Y, Cho Y, Choi I (2010) Analysis of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for seed size and fatty acid composition using recombinant inbred lines in soybean. J Life Sci 20(8):1186–1192. https://doi.org/10.5352/JLS.2010.20.8.1186
Kim M, Lozano R, Kim JH, Bae DN, Kim S et al (2021) The patterns of deleterious mutations during the domestication of soybean. Nat Commun 12(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20337-3
Kulkarni KP, Asekova S, Lee D, Bilyeu K, Song JT, Lee J (2017) Mapping QTLs for 100-seed weight in an interspecific soybean cross of Williams 82 (Glycine max) and PI 366121 (Glycine soja). Crop Pasture Sci 68(2):148–155. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP16246
Kuroda Y, Kaga A, Tomooka N, Yano H, Takada Y, Kato S, Vaughan D (2013) QTL affecting fitness of hybrids between wild and cultivated soybeans in experimental fields. Ecol Evol 3(7):2150–2168. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.606
Li N, Xu R, Li YH (2019) Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70:435–463. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-095851
Li J, Zhang YH, Ma RR, Huang WX, Hou JJ et al (2022) Identification of ST1 reveals a selection involving hitchhiking of seed morphology and oil content during soybean domestication. Plant Biotechnol J 20(6):1110–1121. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13791
Liu WX, Kim MY, Van K, Lee Y, Li HL, Liu XH, Lee S (2011) QTL identification of yield-related traits and their association with flowering and maturity in soybean. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 14(1):65–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-010-0115-7
Liu JF, Chen J, Zheng XM, Wu FQ, Lin QB et al (2017) GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. Nat Plants 3(5):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2017.43
Liu DQ, Yan YL, Fujita Y, Xu DH (2018) Identification and validation of QTLs for 100-seed weight using chromosome segment substitution lines in soybean. Breed Sci 68(4):442–448. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.17127
Liu JY, Zhang YW, Han X, Zuo JF, Zhang ZB, Shang HH, Song QJ, Zhang YM (2020) An evolutionary population structure model reveals pleiotropic effects of GmPDAT for traits related to seed size and oil content in soybean. J Exp Bot 71(22):6988–7002. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa426
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu SJ, Zhao XH, Hu YL, Liu SL, Nan HY et al (2017) Natural variation at the soybean J locus improves adaptation to the tropics and enhances yield. Nat Genet 49(5):773–779. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3819
Lu SJ, Fang C, Abe J, Kong FJ, Liu BH (2022) Current overview on the genetic basis of key genes involved in soybean domestication. aBIOTECH 3:126–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42994-022-00074-5
Mao ZZ, Gong Y, Shi GX, Li YL, Yu Y, Huang F (2020) Cloning of the soybean E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme GmUBC1 and its expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Hereditas 42(8):788–798. https://doi.org/10.16288/j.yczz.20-141
Maughan PJ, Maroof MA, Buss GR (1996) Molecular-marker analysis of seed-weight: genomic locations, gene action, and evidence for orthologous evolution among three legume species. Theor Appl Genet 93(4):574–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417950
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E et al (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20(9):1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.107524.110
Mian M, Bailey MA, Tamulonis JP, Shipe ER, Carter TE, Parrott WA, Ashley DA, Hussey RS, Boerma HR (1996) Molecular markers associated with seed weight in two soybean populations. Theor Appl Genet 93(7):1011–1016. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230118
Murphy D, Rawsthorne S, Hills M (1993) Storage lipid formation in seeds. Seed Sci Res 3(2):79–95. https://doi.org/10.1017/S096025850000163X
Niu Y, Xu Y, Liu XF et al (2013) Association mapping for seed size and shape traits in soybean cultivars. Mol Breed 31:785–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9833-5
Omokhafe KO, Alika JE (2004) Clonal variation and correlation of seed characters in Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg Ind Crop Prod 19(2):175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2003.09.004
Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Mansur LM, Cregan PB, Adler FR, Lark KG (1999) Genetics of soybean agronomic traits: I. Comparison of three related recombinant inbred populations. Crop Sci 39(6):1642–1651. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1999.3961642x
Palomeque L, Li-Jun L, Li WB, Hedges B, Cober ER, Rajcan I (2009) QTL in mega-environments: II. Agronomic trait QTL co-localized with seed yield QTL detected in a population derived from a cross of high-yielding adapted × high-yielding exotic soybean lines. Theor Appl Genet 119(3):429–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1048-8
Reinprecht Y, Poysa VW, Yu KF, Rajcan I, Ablett GR, Pauls KP (2006) Seed and agronomic QTL in low linolenic acid, lipoxygenase-free soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) germplasm. Genome 49(12):1510–1527. https://doi.org/10.1139/g06-112
Salas P, Oyarzo-Llaipen JC, Wang D, Chase K, Mansur L (2006) Genetic mapping of seed shape in three populations of recombinant inbred lines of soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Theor Appl Genet 113(8):1459–1466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0392-1
Sebolt AM, Shoemaker RC, Diers BW (2000) Analysis of a quantitative trait locus allele from wild soybean that increases seed protein concentration in soybean. Crop Sci 40(5):1438–1444. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2000.4051438x
Sedivy EJ, Wu F, Hanzawa Y (2017) Soybean domestication: the origin, genetic architecture and mo-lecular bases. New Phytol 214(2):539–553. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14418
Specht JE, Chase K, Macrander M, Graef GL, Chung J, Markwell JP, Germann M, Orf JH, Lark KG (2001) Soybean response to water: a QTL analysis of drought tolerance. Crop Sci 41(2):493–509. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2001.412493x
Stombaugh SK, Orf JH, Jung HG, Chase K, Lark KG, Somers DA (2004) Quantitative trait loci associated with cell wall polysaccharides in soybean seed. Crop Sci 44(6):2101–2106. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2004.2101
Sun YN, Pan JB, Shi XL, Du XY, Wu Q et al (2012) Multi-environment mapping and meta-analysis of 100-seed weight in soybean. Mol Biol Rep 39(10):9435–9443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1808-4
Swarm SA, Sun LJ, Wang XT, Wang W, Brown PJ, Ma JX, Nelson RL (2019) Genetic dissection of domestication-related traits in soybean through genotyping-by-sequencing of two interspecific mapping populations. Theor Appl Genet 132(4):1195–1209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3272-6
Swift ML (1997) GraphPad prism, data analysis, and scientific graphing. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 37(2):411–412. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci960402j
Teng W, Han Y, Du Y, Sun D, Zhang Z, Qiu L, Sun G, Li W (2009) QTL analyses of seed weight during the development of soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Heredity 102(4):372–380. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2008.108
Tian P, Liu JF, Mou CL, Shi CL, Zhang H et al (2019) GW5-Like, a homolog of GW5, negatively regulates grain width, weight and salt resistance in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 61(11):1171–1185. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12745
Tomooka N, Vaughan D, Maxted N, Moss H (2002) The Asian Vigna: genus Vigna subgenus Ceratotropis genetic resources. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Wang K, Li MY, Hakonarson H (2010) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38(16):e164. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq603
Wang WB, He QY, Yang HY, Xiang SH, Xing GN, Zhao TJ, Gai JY (2014) Identification of QTL/segments related to seed-quality traits in G. Soja using chromosome segment substitution lines. Plant Genet Resour 12(S1):S65–S69. https://doi.org/10.1017/S147926211400029X
Wang J, Chen PY, Wang DC, Shannon G, Shi AN, Zeng AL, Orazaly M (2015) Identification of quantitative trait loci for oil content in soybean seed. Crop Sci 55(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2014.04.0280
Wang W, Liu M, Wang Y, Li X, Cheng S, Shu L et al (2016) Characterizing two inter-specific bin maps for the exploration of the QTLs/Genes that confer three soybean evolutionary traits. Front Plant Sci 7:1248. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01248
Wang M, Li WZ, Fang C, Xu F, Liu YC et al (2018) Parallel selection on a dormancy gene during domestication of crops from multiple families. Nat Genet 50(10):1435–1441. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0229-2
Wang XJ, Liang HY, Guo DL et al (2019) Integrated analysis of transcriptomic and proteomic data from tree peony (P. ostii) seeds reveals key developmental stages and candidate genes related to oil biosynthesis and fatty acid metabolism. Hortic Res 6:111. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-019-0194-7
Wang SD, Liu SL, Wang J, Yokosho K, Zhou B et al (2020) Simultaneous changes in seed size, oil content and protein content driven by selection of SWEET homologues during soybean domestication. Natl Sci Rev 7(11):1776–1786. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa110
Wang FF, Sun X, Liu BH, Kong FJ, Pan XW, Zhang HY (2022a) A polygalacturonase gene PG031 regulates seed coat permeability with a pleiotropic effect on seed weight in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 135(5):1603–1618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04057-4
Wang Q, Li X, Chen HW, Wang F et al (2022b) Mapping combined with principal component analysis identifies excellent lines with increased rice quality. Sci Rep 12:5969. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09976-2
Yang K, Moon J, Jeong N, Chun H, Kang S, Back K, Jeong S (2011) Novel major quantitative trait loci regulating the content of isoflavone in soybean seeds. Genes Genomics 33(6):685–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-011-0043-z
Yu LL, Liu YM, Zeng S, Yan JH, Wang E, Luo L (2019) Expression of a novel PSK-encoding gene from soybean improves seed growth and yield in transgenic plants. Planta 249(4):1239–1250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03101-w
Yuan B, Yuan C, Wang Y, Liu X, Qi G, Dong L, Zhao H, Li Y, Dong Y (2022) Identification of genetic loci conferring seed coat color based on a high-density map in soybean. Front Plant Sci 13:968618. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.968618
Zhang WK, Wang YJ, Luo GZ, Zhang JS, He CY, Wu XL, Gai JY, Chen SY (2004) QTL mapping of ten agronomic traits on the soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) genetic map and their association with EST markers. Theor Appl Genet 108(6):1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1527-2
Zhang W, Xu WJ, Zhang HM, Liu X, Cui XY et al (2021) Comparative selective signature analysis and high-resolution GWAS reveal a new candidate gene controlling seed weight in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 134(5):1329–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03774-6
Zheng H, Rowland O, Kunst L (2005) Disruptions of the Arabidopsis enoyl-CoA reductase gene reveal an essential role for very-long-chain fatty acid synthesis in cell expansion during plant morphogenesis. Plant Cell 17(5):1467–1481. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.030155
Zhu WW, Yang C, Yong B, Wang Y, Li BB et al (2022) An enhancing effect attributed to a nonsynonymous mutation in SOYBEAN SEED SIZE 1, a SPINDLY-like gene, is exploited in soybean domestication and improvement. New Phytol 236:1375–1392. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.18461
Zhuang Y, Li X, Hu J, Xu R, Zhang D (2022) Expanding the gene pool for soybean improvement with its wild relatives. Abiotech 22:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42994-022-00072-7
Zuo JF, Ikram M, Liu JY, Han CY, Niu Y, Dunwell JM, Zhang YM (2022) Domestication and improvement genes reveal the differences of seed size-and oil-related traits in soybean domestication and improvement. Comput Struct Biotechnol 20:2951–2964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.014
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFD1200103-1) and the Jilin Academy of Agricultural Sciences Balance Fund Project (Y81980401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BQY performed the experiments and drafted the manuscript. YSD and BQY conceived and designed the experiments and methods. YMW provided the material. GXQ, YNW, LCD performed the field management. CPY, XDL, HKZ, YQL reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Dechun Wang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, B., Qi, G., Yuan, C. et al. Major genetic locus with pleiotropism determined seed-related traits in cultivated and wild soybeans. Theor Appl Genet 136, 125 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04358-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04358-2