Abstract
Key message
KLW1 was localized to a 0.6 cM interval near the centromere of chromosome 4B and found to be dominant in conditioning longer kernels and higher kernel weight.
Abstract
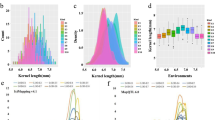
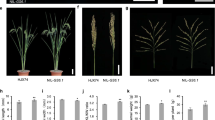
Kernel weight is a major wheat yield component and affected by kernel dimensions, filling process and kernel density. Because of this complexity, the mechanism underlying kernel weight is still far from clear. Qtgw.nau-4B or KLW1 was a major kernel weight QTL identified in the Nanda2419 × Wangshuibai population. We showed that introduction of the Nanda2419 allele into elite cultivar Wenmai6 resulted in longer kernels as well as higher kernel weight, without affecting other traits such as spike number per plant, plant height, spike length, spikelet number per spike, and kernel number per spike. KLW1 was dominant in conditioning higher kernel weight and functioned mainly through affecting kernel length. Using F2 plants derived from KLW1 NIL, a high-density genetic map covering the QTL was constructed. KLW1 was consequently confined to the 0.6 cM Xwgrc4219-Xwgrc4067 interval by evaluating the recombinant lines in three field trials. KLW1 is complementary to KT1, the QTL on chromosome 5A of Nanda2419 for thicker and heavier kernels, in producing larger kernels with higher commercial value, augmenting its usefulness in wheat breeding.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Available upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Brinton J, Simmonds J, Minter F, Leverington-Waite M, Snape J, Uauy C (2017) Increased pericarp cell length underlies a major quantitative trait locus for grain weight in hexaploid wheat. New Phytol 215:1026–1038. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14624
Brinton J, Uauy C (2019) A reductionist approach to dissecting grain weight and yield in wheat. J Integr Plant Biol 61:337–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12741
Buerstmayr M, Steiner B, Wagner C, Schwarz P, Brugger K, Barabaschi D, Volante A, Valè G, Cattivelli L, Buerstmayr H (2018) High-resolution mapping of the pericentromeric region on wheat chromosome arm 5AS harbouring the Fusarium head blight resistance QTL Qfhs.ifa-5A. Plant Biotechnol J 16:1046–1056. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12850
Cabral AL, Jordan MC, Larson G, Somers DJ, Humphreys DG, McCartney CA (2018) Relationship between QTL for grain shape, grain weight, test weight, milling yield, and plant height in the spring wheat cross RL4452/‘AC Domain.’ PLoS ONE 13:e0190681. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190681
Calderini DF, Castillo FM, Arenas-M A, Molero G, Reynolds MP, Craze M, Bowden S, Milner MJ, Wallington EJ, Dowle A, Gomez LD, McQueen-Mason SJ (2021) Overcoming the trade-off between grain weight and number in wheat by the ectopic expression of expansin in developing seeds leads to increased yield potential. New Phytol 230:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17048
Cao J, Shang Y, Xu D, Xu K, Cheng X, Pan X, Liu X, Liu M, Gao C, Yan S, Yao H, Gao W, Lu J, Zhang H, Chang C, Xia X, Xiao S, Ma C (2020) Identification and validation of new stable QTLs for grain weight and size by multiple mapping models in common wheat. Front Genet 11:584859. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.584859
Chastain TG, Ward KJ, Wysocki DJ (1995) Stand establishment response of soft white winter wheat to seedbed residue and seed size. Crop Sci 35:213–218. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1995.0011183X003500010040x
Chen D, Wu X, Wu K, Zhang J, Liu W, Yang X, Li X, Lu Y, Li L (2017) Novel and favorable genomic regions for spike related traits in a wheat germplasm Pubing 3504 with high grain number per spike under varying environments. J Integr Agric 16:2386–2401. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61711-8
Chen Z, Cheng X, Chai L, Wang Z, Bian R, Li J, Zhao A, Xin M, Guo W, Hu Z, Peng H, Yao Y, Sun Q, Ni Z (2020) Dissection of genetic factors underlying grain size and fine mapping of QTgw.cau-7D in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 133:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03447-5
Cheng R, Kong Z, Zhang L, Xie Q, Jia H, Yu D, Huang Y, Ma Z (2017) Mapping QTLs controlling kernel dimensions in a wheat inter-varietal RIL mapping population. Theor Appl Genet 130:1405–1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2896-2
Cui F, Ding A, Li J, Zhao C, Li X, Feng D, Wang X, Wang L, Gao J, Wang H (2011) Wheat kernel dimensions: how do they contribute to kernel weight at an individual QTL level? J Genet 90:409–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-011-0103-9
Deng Q, Kong Z, Wu X, Ma S, Yuan Y, Jia H, Ma Z (2019) Cloning of a COBL gene determining brittleness in diploid wheat using a MapRseq approach. Plant Sci 285:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.05.011
Dewey DR, Lu KH (1959) A correlation and path-coefficient analysis of components of crested wheatgrass seed production. Agron J 51:515–518. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1959.00021962005100090002x
Dholakia BB, Ammiraju JSS, Singh H, Lagu MD, Röder MS, Rao VS, Dhaliwal HS, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS, Weber WE (2003) Molecular marker analysis of kernel size and shape in bread wheat. Plant Breed 122:392–395. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0523.2003.00896.x
Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0218-1
Gegas VC, Nazari A, Griffiths S, Simmonds J, Fish L, Orford S, Sayers L, Doonan JH, Snape JW (2010) A genetic framework for grain size and shape variation in wheat. Plant Cell 22:1046–1056. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.074153
Gnirke A, Melnikov A, Maguire J, Rogov P, LeProust EM, Brockman W, Fennell T, Giannoukos G, Fisher S, Russ C, Gabriel S, Jaffe DB, Lander ES, Nusbaum C (2009) Solution hybrid selection with ultra-long oligonucleotides for massively parallel targeted sequencing. Nat Biotechnol 27:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1523
Guan P, Lu L, Jia L, Kabir MR, Zhang J, Lan T, Zhao Y, Xin M, Hu Z, Yao Y, Ni Z, Sun Q, Peng H (2018) Global QTL analysis identifies genomic regions on chromosomes 4A and 4B harboring stable loci for yield-related traits across different environments in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front Plant Sci 9:529. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00529
Guan P, Shen X, Mu Q, Wang Y, Wang X, Chen Y, Zhao Y, Chen X, Zhao A, Mao W, Guo Y, Xin M, Hu Z, Yao Y, Ni Z, Sun Q, Peng H (2020) Dissection and validation of a QTL cluster linked to Rht-B1 locus controlling grain weight in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using near-isogenic lines. Theor Appl Genet 133:2639–2653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03622-z
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kumar N (2006) Genetic and molecular basis of grain size and grain number and its relevance to grain productivity in higher plants. Genome 49:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1139/g06-063
Huang Y, Kong Z, Wu X, Cheng R, Yu D, Ma Z (2015) Characterization of three wheat grain weight QTLs that differentially affect kernel dimensions. Theor Appl Genet 128:2437–2445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2598-6
IWGSC (2018) Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar7191
Jia H, Wan H, Yang S, Zhang Z, Kong Z, Xue S, Zhang L, Ma Z (2013) Genetic dissection of yield-related traits in a recombinant inbred line population created using a key breeding parent in China’s wheat breeding. Theor Appl Genet 126:2123–2139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2123-8
Jobson EM, Martin JM, Schneider TM, Giroux MJ (2018) The impact of the Rht-B1b, Rht-D1b, and Rht-8 wheat semi-dwarfing genes on flour milling, baking, and micronutrients. Cereal Chem 95:770–778. https://doi.org/10.1002/cche.10091
Kong Z, Cheng R, Yan H, Yuan H, Zhang Y, Li G, Jia H, Xue S, Zhai W, Yuan Y, Ma Z (2022) Fine mapping KT1 on wheat chromosome 5A that conditions kernel dimensions and grain weight. Theor Appl Genet 135:1101–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-04020-9
Kumari S, Jaiswal V, Mishra VK, Paliwal R, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2018) QTL mapping for some grain traits in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 24:909–920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-018-0552-1
Le TDQ, Alvarado C, Girousse C, Legland D, Chateigner-Boutin A-L (2019) Use of X-ray micro computed tomography imaging to analyze the morphology of wheat grain through its development. Plant Methods 15:84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-019-0468-y
Li T, Deng G, Su Y, Yang Z, Tang Y, Wang J, Zhang J, Qiu X, Pu X, Yang W, Li J, Liu Z, Zhang H, Liang J, Yu M, Wei Y, Long H (2022) Genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci for grain size and weight by high-resolution genetic mapping in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 135:257–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03964-2
Liu RH, Meng JL (2003) MapDraw: a microsoft excel macro for drawing genetic linkage maps based on given genetic linkage data. Yi Chuan 25:317–321
Muehlbauer GJ, Feuillet C (eds) (2009). Springer, US, New York, NY, pp 317–335
Nave M, Avni R, Ben-Zvi B, Hale I, Distelfeld A (2016) QTLs for uniform grain dimensions and germination selected during wheat domestication are co-located on chromosome 4B. Theor Appl Genet 129:1303–1315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2704-4
Nothnagel EA (1997) Proteoglycans and related components in plant cells. Int Rev Cytol 174:195–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7696(08)62118-X
Pingault L, Choulet F, Alberti A, Glover N, Wincker P, Feuillet C, Paux E (2015) Deep transcriptome sequencing provides new insights into the structural and functional organization of the wheat genome. Genome Biol 16:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0601-9
Quintero A, Molero G, Reynolds MP, Calderini DF (2018) Trade-off between grain weight and grain number in wheat depends on GxE interaction: a case study of an elite CIMMYT panel (CIMCOG). Eur J Agron 92:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2017.09.007
Ramírez-González RH, Borrill P, Lang D, Harrington SA, Brinton J, Venturini L, Davey M, Jacobs J, van Ex F, Pasha A, Khedikar Y, Robinson SJ, Cory AT, Florio T, Concia L, Juery C, Schoonbeek H, Steuernagel B, Xiang D, Ridout CJ, Chalhoub B, Mayer KFX, Benhamed M, Latrasse D, Bendahmane A, International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium, Wulff BBH, Appels R, Tiwari V, Datla R, Choulet F, Pozniak CJ, Provart NJ, Sharpe AG, Paux E, Spannagl M, Bräutigam A, Uauy C, Korol A, Sharpe AG, Juhász A, Rohde A, Bellec A, Distelfeld A, Akpinar BA, Keller B, Darrier B, Gill B, Chalhoub B, Steuernagel B, Feuillet C, Chaudhary C, Uauy C, Pozniak C, Ormanbekova D, Xiang D, Latrasse D, Swarbreck D, Barabaschi D, Raats D, Sergeeva E, Salina E, Paux E, Cattonaro F, Choulet F, Kobayashi F, Keeble-Gagnere G, Kaur G, Muehlbauer G, Kettleborough G, Yu G, Šimková H, Gundlach H, Berges H, Rimbert H, Budak H, Handa H, Small I, Bartoš J, Rogers J, Doležel J, Keilwagen J, Poland J, Melonek J, Jacobs J, Wright J, Jones JDG, Gutierrez-Gonzalez J, Eversole K, Nilsen K, Mayer KFX, Kanyuka K, Singh K, Gao L, Concia L, Venturini L, Cattivelli L, Spannagl M, Mascher M, Hayden M, Abrouk M, Alaux M, Luo M, Valárik M, Benhamed M, Singh NK, Sharma N, Guilhot N, Ravin N, Stein N, Olsen O-A, Gupta OP, Khurana P, Chhuneja P, Bayer PE, Borrill P, Leroy P, Rigault P, Sourdille P, Hernandez P, Flores R, Ramirez-Gonzalez RH, King R, Knox R, Appels R, Zhou R, Walkowiak S, Galvez S, Biyiklioglu S, Nasuda S, Sandve S, Chalabi S, Weining S, Sehgal S, Jindal S, Belova T, Letellier T, Wicker T, Tanaka T, Fahima T, Barbe V, Tiwari V, Kumar V, Tan Y (2018) The transcriptional landscape of polyploid wheat. Science 361:eaar6089. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar6089
Ramya P, Chaubal A, Kulkarni K, Gupta L, Kadoo N, Dhaliwal HS, Chhuneja P, Lagu M, Gupta V (2010) QTL mapping of 1000-kernel weight, kernel length, and kernel width in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Appl Genet 51:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03208872
Rius SP, Casati P, Iglesias AA, Gomez-Casati DF (2008) Characterization of Arabidopsis lines deficient in GAPC-1, a cytosolic NAD-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Plant Physiol 148:1655–1667. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.128769
Sánchez-Martín J, Steuernagel B, Ghosh S, Herren G, Hurni S, Adamski N, Vrána J, Kubaláková M, Krattinger SG, Wicker T, Doležel J, Keller B, Wulff BBH (2016) Rapid gene isolation in barley and wheat by mutant chromosome sequencing. Genome Biol 17:221. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1082-1
Sen M, Shah B, Rakshit S, Singh V, Padmanabhan B, Ponnusamy M, Pari K, Vishwakarma R, Nandi D, Sadhale PP (2011) UDP-glucose 4, 6-dehydratase activity plays an important role in maintaining cell wall integrity and virulence of Candida albicans. PLoS Pathog 7(11):e1002384. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002384
Song J, Xu D, Dong Y, Li F, Bian Y, Li L, Luo X, Fei S, Li L, Zhao C, Zhang Y, Xia X, Ni Z, He Z, Cao S (2022) Fine mapping and characterization of a major QTL for grain weight on wheat chromosome arm 5DL. Theor Appl Genet 135:3237–3246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04182-0
Singh K, Saini DK, Saripalli G, Batra R, Gautam T, Singh R, Pal S, Kumar M, Jan I, Singh S, Kumar A, Sharma H, Chaudhary J, Kumar K, Kumar S, Singh VK, Singh VP, Kumar D, Sharma S, Kumar S, Kumar R, Sharma S, Gaurav SS, Sharma PK, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2022) WheatQTLdb V2.0: a supplement to the database for wheat QTL. Mol Breed 42:56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01329-1
Su Z, Jin S, Lu Y, Zhang G, Chao S, Bai G (2016) Single nucleotide polymorphism tightly linked to a major QTL on chromosome 7A for both kernel length and kernel weight in wheat. Mol Breed 36:15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0436-4
Su Q, Zhang X, Zhang W, Zhang N, Song L, Liu L, Xue X, Liu G, Liu J, Meng D, Zhi L, Ji J, Zhao X, Yang C, Tong Y, Liu Z, Li J (2018) QTL detection for kernel size and weight in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using a high-density SNP and SSR-based linkage map. Front Plant Sci 9:1484. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01484
Tanabata T, Shibaya T, Hori K, Ebana K, Yano M (2012) SmartGrain : high-throughput phenotyping software for measuring seed shape through image analysis. Plant Physiol 160:1871–1880. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.205120
Turner EH, Lee C, Ng SB, Nickerson DA, Shendure J (2009) Massively parallel exon capture and library-free resequencing across 16 genomes. Nat Methods 6:315–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.248
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap® 4, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Wageningen, Kyazma BV
Wang J, Liu W, Wang H, Li L, Wu J, Yang X, Li X, Gao A (2011) QTL mapping of yield-related traits in the wheat germplasm 3228. Euphytica 177:277–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-010-0267-z
Wang S, Wong D, Forrest K, Allen A, Chao S, Huang BE, Maccaferri M, Salvi S, Milner SG, Cattivelli L, Mastrangelo AM, Whan A, Stephen S, Barker G, Wieseke R, Plieske J, International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium, Lillemo M, Mather D, Appels R, Dolferus R, Brown‐Guedira G, Korol A, Akhunova AR, Feuillet C, Salse J, Morgante M, Pozniak C, Luo M, Dvorak J, Morell M, Dubcovsky J, Ganal M, Tuberosa R, Lawley C, Mikoulitch I, Cavanagh C, Edwards KJ, Hayden M, Akhunov E (2014) Characterization of polyploid wheat genomic diversity using a high‐density 90,000 single nucleotide polymorphism array. Plant Biotechnol J 12:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12183
Watanabe S, Xia Z, Hideshima R, Tsubokura Y, Sato S, Yamanaka N, Takahashi R, Anai T, Tabata S, Kitamura K, Harada K (2011) A map-based cloning strategy employing a residual heterozygous line reveals that the GIGANTEA gene is involved in soybean maturity and flowering. Genetics 188:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.110.125062
Xie Q, Sparkes DL (2021) Dissecting the trade-off of grain number and size in wheat. Planta 254:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03658-5
Xin F, Zhu T, Wei S, Han Y, Zhao Y, Zhang D, Ma L, Ding Q (2020) QTL mapping of kernel traits and validation of a major QTL for kernel length-width ratio using SNP and bulked segregant analysis in wheat. Sci Rep 10:25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56979-7
Xu D, Wen W, Fu L, Li F, Li J, Xie L, Xia X, Ni Z, He Z, Cao S (2019) Genetic dissection of a major QTL for kernel weight spanning the Rht-B1 locus in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 132:3191–3200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03418-w
Xue S, Xu F, Li G, Zhou Y, Lin M, Gao Z, Su X, Xu X, Jiang G, Zhang S, Jia H, Kong Z, Zhang L, Ma Z (2013) Fine mapping TaFLW1, a major QTL controlling flag leaf width in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 126:1941–1949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2108-7
Xue S, Li G, Jia H, Xu F, Lin F, Tang M, Wang Y, An X, Xu H, Zhang L, Kong Z, Ma Z (2010) Fine mapping Fhb4, a major QTL conditioning resistance to Fusarium infection in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 121:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1298-5
Yang F, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Liu Q, Islam S, Yang W, Ma W (2022) Wheat glutamine synthetase TaGSr-4B is a candidate gene for a QTL of thousand grain weight on chromosome 4B. Theor Appl Genet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04118-8
Yang L, Zhao D, Meng Z, Xu K, Yan J, Xia X, Cao S, Tian Y, He Z, Zhang Y (2020) QTL mapping for grain yield-related traits in bread wheat via SNP-based selective genotyping. Theor Appl Genet 133:857–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03511-0
Zamir D (2001) Improving plant breeding with exotic genetic libraries. Nat Rev Genet 2:983–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/35103590
Zhao D, Yang L, Liu D, Zeng J, Cao S, Xia X, Yan J, Song X, He Z, Zhang Y (2021) Fine mapping and validation of a major QTL for grain weight on chromosome 5B in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 134:3731–3741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03925-9
Zhang Y, Held MA, Showalter AM (2020) Elucidating the roles of three β-glucuronosyltransferases (GLCATs) acting on arabinogalactan-proteins using a CRISPR-Cas9 multiplexing approach in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 20,221. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02420-5
Zhu T, Wang L, Rimbert H, Rodriguez JC, Deal KR, De Oliveira R, Choulet F, Keeble-Gagnère G, Tibbits J, Rogers J, Eversole K, Appels R, Gu YQ, Mascher M, Dvorak J, Luo M-C (2021) Optical maps refine the bread wheat Triticum aestivum cv. Chinese Spring genome assembly. Plant J 107:303–314. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15289
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872867, 31430064), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFF1002902), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu (BK20221509), Seed Industry Revitalization Project of Jiangsu Province (JBGS2021013, and Jiangsu collaborative innovation initiative for modern crop production. We thank all the laboratory staff and graduate students for support of all experiments.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872867, 31430064), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFF1002902), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu (BK20221509), Seed Industry Revitalization Project of Jiangsu Province (JBGS2021013, and Jiangsu collaborative innovation initiative for modern crop production partially supported this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY, LZ, RC, WH conduced genotyping and phenotyping. YY performed data analysis and prepared the draft; ZY, XQ, GL and YZ contributed to field trials; ZK, QX and HJ contributed to phenotyping, data collection and project supervision, YW helped project implementation, and ZM conceived the project and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Susanne Dreisigacker.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Kong, Z., Xie, Q. et al. Fine mapping of KLW1 that conditions kernel weight mainly through regulating kernel length in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 136, 110 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04353-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04353-7