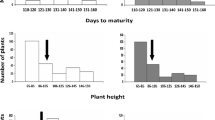
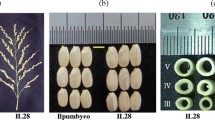
Abstract
Introgression has been achieved from wild species Oryza grandiglumis (2n=48, CCDD, Acc. No. 101154) into O. sativa subsp. japonica cv. Hwaseongbyeo as a recurrent parent. An advanced introgression (backcross) line, HG101, produced from a single plant from BC5F3 families resembled Hwaseongbyeo, but it showed differences from Hwaseongbyeo in several traits, including days to heading and culm length. To detect the introgressions, 450 microsatellite markers of known chromosomal position were used for the parental survey. Of the 450 markers, 51 (11.3%) detected O. grandiglumis segments in HG101. To characterize the effects of alien genes introgressed into HG101, an F2:3 population (150 families) from the cross Hwaseongbyeo/HG101 was developed and evaluated for 13 agronomic traits. Several lines outperformed Hwaseongbyeo in several traits, including days to heading. Genotypes were determined for 150 F2 plants using simple sequence repeat markers. Qualitative trait locus (QTL) analysis was carried out to determine the relationship between marker genotype and the traits evaluated. A total of 39 QTL and 1 gene conferring resistance to blast isolate were identified using single-point analysis. Phenotypic variation associated with each QTL ranged from 4.2 to 30.5%. For 18 (46.2%) of the QTL identified in this study, the O. grandiglumis-derived alleles contributed a desirable agronomic effect despite the overall undesirable characteristics of the wild phenotype. Favorable wild alleles were detected for days to heading, spikelets per panicle, and grain shape traits. Grain shape QTL for grain weight, thickness, and width identified in the F2:3 lines were further confirmed based on the F4 progeny test. The confirmed locus, tgw2 for grain weight is of particular interest because of its independence from undesirable height and maturity. Several QTL controlling amylose content and grain traits have not been detected in the previous QTL studies between Oryza cultivars, indicating potentially novel alleles from O. grandiglumis. The QTL detected in this study could be a rich source of natural genetic variation underlying the evolution and breeding of rice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn SN, Kim YK, Hong HC, Han SS, Kwon SJ, Choi HC, Moon HP, McCouch SR (2000) Molecular mapping of a new gene for resistance to rice blast. Euphytica 116:17–22
Ahn SN, Kwon SJ, Suh JP, Kang KH, Kim HJ, Song MT, Hwang HG, Moon HP (2001) Identification of introgressions in a backcross progeny derived from the cross between Oryza sativa and O grandiglumis. Korean J Breed 33:318–323
Ahn SN, Kwon SJ, Suh JP, Kang KH, Kim HJ, Hwang HG, Moon HP (2003) Introgression for agronomic from O grandiglumis into rice, O sativa. In: Mew TW, Brar DS, Peng S, Dawe D, Hardy B (eds) Rice science: innovations and impact for livelihood. IRRI, Los Banos, pp 265–274
Akimoto M, Morishima H (2003) Genetic population structures of Oryza glumaepatula and O. grandiglumis distributed in Amazon flood area. In: Khush GS, Brar DS, Hardy B (eds) Advances in rice genetics. IRRI, Los Banos, pp 126–127
Brar DS, Khush GS (1997) Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:35–47
Brondani C, Rangel PHN, Brondani RPV, Ferreira ME (2002) QTL mapping and introgression of yield-related traits from Oryza glumaepatula to cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1192–1203
Cai HW, Morishima H (2002) QTL clusters reflect character associations in wild and cultivated rice. Theor Appl Genet 104:1217–1228
Causse MA, Fulton TM, Cho YG, Ahn SN, Chunwongse J, Wu K, Xiao J, Yu Z, Ronald PC, Harrington SE, Second G, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD (1994) Saturated molecular map of the rice genome based on an interspecific backcross population. Genetics 138:1251–1274
Cho YG, Eun MY, McCouch SR, Chae YA (1994) The semidwarf gene, sd-1, of rice (Oryza sativa L). II. Molecular mapping and marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 89:54–59
Frary A, Nesbitt TC, Frary S, Grandillo S, van der Knapp E, Cong B, Lui J, Meller J, Elber R, Alpert KB, Tanksley SD (2000) fw2.2: a quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 289:85–88
Harushima Y, Kurata N, Yano M, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T, Minobe Y, Nakagara M (1996) Detection of segregation distortions in an indica–japonica rice cross using a high-resolution molecular map. Theor Appl Genet 92:145–190
Harushima Y, Nakagahra M, Yano M, Sasaki M, Sasaki T, Kurata N (2002) Diverse variation of reproductive barriers in three intraspecific rice crosses. Genetics 160:313–322
Heinrichs EA, Medrano FG, Rapusas HR (1985) Genetic evaluation for insect resistance in rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila
Hittalmani S, Huang N, Courtois B, Venuprasad R, Shashidhar HE, Zhuang JY, Zheng KL, Liu GF, Wang GC, Sidhu JS, Srivantaneeyakul S, Singh VP, Bagali PG, Prasanna HC, McLaren G, Khush GS (2003) Identification of QTL for growth- and grain yield-related traits in rice across nine locations of Asia. Theor Appl Genet 107:679–690
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (IRGSP) (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Ishii T, Brar DS, Multani DS, Khush GS (1994) Molecular tagging of genes for brown planthopper resistance and earliness introduced from Oryza australiensis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Genome 37:217–221
Ishimaru K (2003) Identification of a locus increasing rice yield and physiological analysis of its function. Plant Physiol 133:1083–1090
Jena KK, Kochert G (1991) Restriction fragment fragment polymorphism analysis of CCDD genome species of the genus Oryza L. Plant Mol Biol 5:109–118
Jena KK, Khush GS, Kochert G (1992) RFLP analysis of rice (Oryza sativa L) introgression lines. Theor Appl Genet 84:608–616
Jena KK, Pasalu IC, Rao YK, Varalaxmi Y, Krishnaiah K, Khush GS, Kochert G (2003) Molecular tagging of a gene for resistance to brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa L). Euphytica 129:81–88
Juliano BO (1971) A simplified assay for milled-rice amylose. Cereal Sci Today 16:334–360
Kim YK, Kim YJ, Choi HC, Han SS (1995) Inheritance of leaf blast reactions to four races of blast fungus in segregating populations of eight rice crosses (In Korean). RDA J Agric Sci 37:283–298
Kwon SJ, Ahn SN, Hong HC, Cho YC, Suh JP, Kim YK, Kang KH, Han SS, Choi HC, Moon HP, Hwang HG (2002) Identification of DNA markers linked to resistance genes to rice blast (Pyricularia grisea Sacc). Korean J Breed 34:105–110
Li JM, Thomson M, McCouch SR (2004) Fine mapping of a grain-weight quantitative trait locus in the pericentromeric region of rice chromosome 3. Genetics 168:2187-2195
Liu G, Lu G, Zeng L, Wang G-L (2002) Two broad-spectrum blast resistance genes, Pi9(t) and Pi2(t), are physically linked on rice chromosome 6. Mol Genet Genomics 267:472–480
McCouch SR, Doerge RW (1995) QTL mapping in rice. Trends Genet 11:482–487
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L). DNA Res 9:199–207
Mei HW, Luo LJ, Ying CS, Wang YP, Yu XQ, Guo LB, Paterson AH, Li ZK (2003) Gene actions of QTLs affecting several agronomic traits resolved in a recombinant inbred rice population and two testcross populations. Theor Appl Genet 107:89–101
Moncada P, Martínez CP, Borrero J, Chatel M, Gauch Jr H, Guimarães E, Tohme J, McCouch SR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa ( Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment. Theor Appl Genet 102:41–52
Nelson JC (1997) QGENE: software for marker-based genome analysis and breeding. Mol Breed 3:239–245
Nguyen BD, Brar DS, Bui BC, Nguyen TV, Pham LN, Nguyen HT (2003) Identification and mapping of the QTL for aluminum tolerance introgressed from the new source, Oryza rufipogon Griff. into indica rice (O. sativa L). Theor Appl Genet 106:583–593
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch SR (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L). Mol Gen Genet 252:597–607
Paterson AH, DeVerna JW, Lanini B, Tanksley SD (1990) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci using selected overlapping recombinant chromosomes in an interspecies cross of tomato. Genetics 124:735-742
Ryu JD, Yeh WH, Han SS, Lee YH, Lee EJ (1987) Regional and annual fluctuation of races of Pyricularia oryzae during 1977–1985 in Korea. Korean J Plant Pathol 3:174–179
Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush GS, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2002) Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature 416:701–702
Septiningsih EM, Prasetiyono J, Lubis ET, Tai TH, Tjubaryat T, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003a) Molecular marker detection of rice (Oryza sativa L) plant architecture under temperate and tropical climates. Theor Appl Genet 107:1350–1356
Septiningsih EM, Trijatmiko KR, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003b) Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1419–1432
Tanksley SD (1993) Mapping polygenes. Annu Rev Genet 27:205–233
Temnykh S, Cartinhour S, Park W, Ayres N, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho YG, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Temnykh S, De Clerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovitch L, Cartinhour S, McCouch SR (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Thomson MJ, Tai TH, McClung AM, Lai XH, Hinga ME, Lobos KB, Xu Y, Martinez CP, McCouch SR (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor Appl Genet 107:479–493
Vaughan DA, Morishima H, Kadowaki K (2003) Diversity in the Oryza genus. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:139–146
Wang ZY, Second G, Tanksley SD (1992) Polymorphism and phylogenetic relationships among species in the genus Oryza as determined by analysis of nuclear RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 83:565–581
Williams VR, Wu WT, Tsai HY, Bates HG (1958) Varietal differences in amylase content of rice starch. J Agric Food Chem 8:47–48
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan L, Tanksley SD (1996) Identification of QTLs affecting traits of agronomic importance in a recombinant inbred population derived from a subspecific cross. Theor Appl Genet 92:230–244
Xiao J, Li J, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan L, Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from a wild rice relative, Oryza rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Xiong LZ, Liu KD, Dai XK, Xu CG, Zhang Q (1999) Identification of genetic factors controlling domestication-related traits of rice using an F2 population of a cross between Oryza sativa and O rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 98:243–251
Xu Y, Zhu L, Xiao J, Huang N, McCouch SR (1997) Chromosomal regions associated with segregation distortion of molecular markers in F2, backcross, doubled haploid, and recombinant inbred populations in rice (Oryza sativa L). Mol Gen Genet 253:535–545
Yano M, Sasaki T (1997) Genetic and molecular dissection of quantitative traits in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:145–153
Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Baba T, Yamamoto K, Umehara Y, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T (2000) Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS. Plant Cell 12:2473–2484
Yu GJ, Kwak TS, Kang KH, Moon HP (1997) Efficiency of backcrossing and ovule culture in an interspecific cross between O sativa L and O grandiglumis. Prod Korean J Breed 29:448–452
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Bio Green 21 project of the Rural Development Administration and from the Crop Functional Genomics Center of the 21st Century Frontier Research Program (Project code no. CG3112) funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Q. Zhang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, DB., Kang, KH., Kim, HJ. et al. Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza grandiglumis and the O. sativa japonica cultivar Hwaseongbyeo. Theor Appl Genet 112, 1052–1062 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0207-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0207-4