Abstract
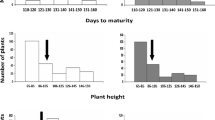
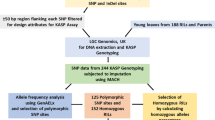
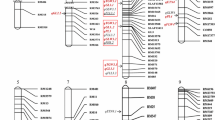
A BC2F2 population developed from an interspecific cross between Oryza sativa (cv IR64) and O. rufipogon (IRGC 105491) was used in an advanced backcross QTL analysis to identify and introduce agronomically useful genes from this wild relative into the cultivated gene pool. The objectives of this study were: (1) to identify putative yield and yield component QTLs that can be useful to improve the elite cultivar IR64; (2) to compare the QTLs within this study with previously reported QTLs in rice as the basis for identifying QTLs that are stable across different environments and genetic backgrounds; and (3) to compare the identified QTLs with previously reported QTLs from maize to examine the degree of QTL conservation across the grass family. Two hundred eighty-five families were evaluated in two field environments in Indonesia, with two replications each, for 12 agronomic traits. A total of 165 markers consisting of 131 SSRs and 34 RFLPs were used to construct the genetic linkage map. By employing interval mapping and composite interval mapping, 42 QTLs were identified. Despite its inferior performance, 33% of the QTL alleles originating from O. rufipogon had a beneficial effect for yield and yield components in the IR64 background. Twenty-two QTLs (53.4%) were located in similar regions as previously reported rice QTLs, suggesting the existence of stable QTLs across genetic backgrounds and environments. Twenty QTLs (47.6%) were exclusively detected in this study, uncovering potentially novel alleles from the wild, some of which might improve the performance of the tropical indica variety IR64. Additionally, several QTLs for plant height, grain weight, and flowering time detected in this study corresponded to homeologous regions in maize containing previously detected maize QTLs for these traits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin DF, Lee M (1996) Comparative mapping in F2:3 and F6:7 generations of quantitative trait loci for grain yield and yield components in maize. Theor Appl Genet 92:817–826
Austin DF, Lee M, Veldboom LR (2001) Genetic mapping in maize with hybrid progeny across testers and generations: plant height and flowering. Theor Appl Genet 102:163–176
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng Z-B (1997) QTL Cartographer: a reference manual and tutorial for QTL mapping. Raleigh, NC, Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University
Beavis WD, Smith OS, Grant D, Fincher R (1994) Identification of quantitative trait loci using a small sample of topcrossed and F4 progeny from maize. Crop Sci 34:882–896
Bernacchi D, Beck BT, Eshed Y, Lopez Y, Petiard V, Uhlig J, Zamir D, Tanksley SD (1998) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in tomato. I. Identification of QTLs for traits of agronomic importance from Lycopersicon hirsutum. Theor Appl Genet 97:381–397
Causse MA, Fulton TM, Cho YG, Ahn SN, Chunwongse J, Wu K, Xiao J, Yu Z, Ronald PC, Harrington SE, Second G, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD (1994) Saturated molecular map of the rice genome based on an interspecific backcross population. Genetics 138:1251–1274
Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, McCouch SR (1997) Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:553–567
Cho YG, Eun MY, McCouch SR, Cae YA (1994) The semi-dwarf gene, sd-1, of rice (Oryza sativa L.). II. Molecular mapping and marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 89:54–59
Davis GL, McMullen MD, Baysdorfer C, Musket T, Grant D, Staebell M, Xu G, Polacco M, Koster L, Melia HS, Houchins K, Chao S, Coe EH Jr. (1999) A maize map standard with sequenced core markers, grass genome reference points and 932 expressed sequence tagged sites (ESTs) in a 1736-locus map. Genetics 152:1137–1172
Doebley J, Bacigalupo A, Stec A (1994) Inheritance of kernel weight in two maize-teosinte hybrid populations: implications for crop evolution. J Heredity 85:191–195
Doi K, Yoshimura A, Iwata N (1998) RFLP mapping and QTL analysis of heading date and pollen sterility using backcross populations between Oryza sativa L. and Oryza glaberrima Steud. Breeding Sci 48:395–399
Fulton TM, Beck BT, Emmatty D, Eshed Y, Lopez J, Petiard V, Uhlig J, Zamir D, Tanksley SD (1997) QTL analysis of an advanced backcross of Lycopersicon peruvianum to the cultivated tomato and comparisons with QTLs found in other wild species. Theor Appl Genet 95:881–894
Fulton TM, Grandillo S, Beck BT, Fridman E, Frampton A, Lopez J, Petiard V, Uhlig J, Zamir D, Tanksley SD (2000) Advanced backcross QTL analysis of a Lycopersicon esculentum X Lycopersicon parviflorum cross. Theor Appl Genet 100:1025–1042
Harushima Y, Kurata N, Yano M, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T, Minobe Y, Nakagahra M (1996) Detection of segregation distortion in an indica-japonica rice cross using a high-resolution molecular map. Theor Appl Genet 92:145–150
Harushima Y, Yano M, Shomura A, Sato M, Shimano T, Kuboki Y, Yamamoto T, Lin SY, Antonio BA, Parco A, Kajiya H, Huang N, Yamamoto K, Nagamura Y, Kurata N, Khush GS, Sasaki T (1998) A high-density rice genetic linkage map with 2275 markers using a single F2 population. Genetics 148:479–494
Huang N, Courtois B, Khush GS, Lin H, Wang G, Wu P, Zheng K (1996) Association of quantitative trait loci for plant height with major dwarfing genes in rice. Heredity 77:130–137
Huang N, Parco A, Mew T, Magapantay G, McCouch S, Guiderdoni E, Xu J, Subudhi P, Angelos ER, Khush GS (1997) RFLP mapping of isozymes, RAPD and QTLs for grain shape, brown planthopper resistance in a doubled haploid rice population. Mol Breeding 3:105–113
Jiang C, Edmeades GO, Armstead I, Lafitte HR, Hayward MD, Hoisington D (1999) Genetic analysis of adaptation differences between highland and lowland tropical maize using molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 99:1106–1119
Khairallah MM, Bohn M, Jiang C, Deutsch JA, Jewell DC, Mihm JA, Melchinger AE, Gonzalez DLD, Hoisington DA (1998) Molecular mapping of QTLs for southwestern corn borer resistance, plant height, and flowering in tropical maize. Plant Breeding 117:309–318
Kinoshita T (1995) Report of committee on gene symbolization, nomenclature, and linkage groups. Rice Genet Newsl 12:9–93
Koester RP, Sisco PH, Stuber CW (1993) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling days to flowering and plant height in two near isogenic lines of maize. Crop Sci 33:1209–1216
Kohn JR, Leyva N, Dossey R, Sobral B, Morishima H (1997) Quantitative trait locus analysis of trait variation among annual and perennial ecotypes of Oryza rufipogon. Int Rice Res Notes 22:4–5
Lander R, Green P, Abrahamson L, Barlow A, Daley M, Lincoln, S, Newburg L (1987) Mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Li JX, Yu SB, Xu CG, Tan YF, Gao YJ, Li XH, Zhang Q (2000) Analyzing quantitative trait loci for yield using a vegetatively-replicated F2 population from a cross between the parents of an elite rice hybrid. Theor Appl Genet 101:248–254
Li Z, Pinson SRM, Stansel JW, Park WD (1995) Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for heading date and plant height in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 91:374–381
Lin HX, Qian HR, Zhuang JY, Lu J, Min SK, Xiong ZM (1996) RFLP mapping of QTLs for yield and other related characters in rice. Int Rice Res Notes 21:17–19
Lin HX, Yamamoto T, Sasaki T, Yano M (2000) Characterization and detection of epistatic interactions of 3 QTLs, Hd1, Hd2, and Hd3, controlling heading date in rice using nearly isogenic lines. Theor Appl Genet 101:1021–1028
Lin YR, Schertz KF, Paterson AH (1995) Comparative analysis of QTLs affecting plant height and maturity across the Poaceae, in reference to an interspecific sorghum population. Genetics 141:391–411
Lu C, Shen L, Tan Z, Xu Y, He P, Chen Y, Zhu L (1997) Comparative mapping of QTLs for agronomic traits of rice across environments by using a doubled-haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 94:145–150
Lubberstedt T, Melchinger AE, Fahr S, Klein D, Dally A, Westhoff P (1998) QTL mapping in testcrosses of flint lines of maize. III. Comparison across population for forage traits. Crop Sci 38:1278–1289
Maheswaran M, Huang N, Sreerangasamy SR, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with days to flowering and photoperiod sensitivity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breeding 6:145–155
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman RW, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829
McCouch SR, Thomson MJ, Septiningsih EM, Moncada P, Li J, Xiao J, Martinez C, Tohme J, Moelpojawiro S, Yuan LP, McClung A, Tai T, Guimaraes E, Moon HP, Ahn SN (2001) Wild QTLs for rice improvement. In: Rockwood W (ed) Proceedings of the Chandler symposium: rice research and production in the 21st century, 15–17 June 2000. IRRI, Philippines, pp 151–169
Moncada P, Martinez CP, Borrero J, Chatel M, Gauch H, Guimaraes E, Tohme J, McCouch SR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa x Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment. Theor Appl Genet 102:41–52
Nelson JC (1997) QGENE: software for marker-based genomic analysis and breeding. Mol Breeding 3:239–245
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch SR (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 252:597–607
Paterson AH, Lin YR, Li Z, Schertz KF, Doebley JF, Pinson SRM, Liu SC, Stansel JW, Irvine JE (1995) Convergent domestication of cereal crops by independent mutations at corresponding genetic loci. Science 269:1714–1718
Ribaut JM, Hoisington DA, Deutsch JA, Jiang C, Gonzalez-de-Leon D (1996) Identification of quantitative trait loci under drought conditions in tropical maize. I. Flowering parameters and the anthesis-silking interval. Theor Appl Genet 92:905–914
Schon CC, Melchinger AE, Boppenmaier J, Brunklaus-Jung E, Herrmann RG, Seitzer JF (1994) RFLP mapping in maize: quantitative trait loci affecting testcross performance of elite European flint lines. Crop Sci 34:378–389
Septiningsih EM, Trijatmiko KR, MoeljopawiroS, McCouchSR (2003b) Identification of quantitative trait loci for grain quality in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet (in press)
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066
Tanksley SD, Nelson JC (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis: a method for the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTLs from unadapted germplasm into elite-breeing lines. Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203
Tanksley SD, Grandillo S, Fulton TM, Zamir D, Eshed Y, Petiard V, Lopez J, Beck-Bunn T (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in a cross between an elite processing line of tomato and its wild relative L. pimpinellifolium. Theor Appl Genet 92:213–224
Temnykh S, Park W, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho YG, Ishii T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Temnykh S, DeClerk G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computations and experimental analysis of microsatellites of rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Thomson MJ, Tai TH, McClung AM, Hinga ME, Lobos KB, Xu Y, Martinez C, McCouch SR (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components, and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor Appl Genet 107:479-493
Veldboom LR, Lee M (1994) Molecular-marker-facilitated studies of morphological traits in maize. II. Determination of QTLs for grain yield and yield components. Theor Appl Genet 89:451–458
Wilson WA, Harrington SE, Woodman WL, Lee M, Sorrells ME, McCouch SR (1999) Inferences on the genome structure of progenitor maize through comparative analysis of rice, maize, and the domesticated panicoids. Genetics 153:453–473
Wu P, Zhang G, Huang N (1996) Identification of QTLs controlling quantitative characters in rice using RFLP markers. Euphytica 89:349–354
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan L, Tanksley SD (1995) Dominance is the major genetic basis of heterosis in rice as revealed by QTL analysis using molecular markers. Genetics 140:745–754
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan L, Tanksley SD (1996) Identification of QTLs affecting traits of agronomic importance in a recombinant inbred population derived from a subspecific cross. Theor Appl Genet 92:230–244
Xiao J, Li J, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan L, Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from a wild rice relative, Oryza rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Xiong LZ, Liu KD, Dai XK, Xu CG, Zhang Q (1999) Identification of genetic factors controlling domestication-related traits of rice using an F2 population of a cross between Oryza sativa and O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 98:243–251
Xu Y, Zhu L, Xiao J, Huang N, McCouch SR (1997) Chromosomal regions associated with segregation distortion of molecular markers in F2, backcross, doubled haploid, and recombinant inbred populations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 253:535–545
Yamamoto T, Kuboki Y, Lin S Y, Sasaki T, Yano M (1998) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci Hd-1, Hd-2 and Hd-3, controlling heading date of rice, as single Mendelian factors. Theor Appl Genet 97:37–44
Yamamoto T, Lin H, Sasaki T, Yano M (2000) Identification of heading date quantitative trait locus Hd6 and characterization of its epistatic interactions with Hd2 in rice using advanced backcross progeny. Genetics154:885–891
Yan J, Zhu J, He C, Benmoussa M, Wu P (1998) Molecular dissection of developmental behavior of plant height in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 150:1257–1265
Yan J, Zhu J, He C, Benmoussa M, Wu P (1999) Molecular marker-assisted dissection of genotype X environment interaction for plant type traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Crop Sci 39:538–544
Yano M, Harushima Y, Nagamura Y, Kurata N, Minobe Y, Sasaki T (1997) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling heading date in rice using a high-density linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 95:1025–1032
Yu SB, Li JX, Xu CG, Tan YF, Gao YJ, Li XH, Zhang Q, Maroof MAS (1997) Importance of epistasis as the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite rice hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9226–9231
Zhuang JY, Lin HX, Lu J, Qian HR, Hittalmani S, Huang N, Zheng KL (1997) Analysis of QTL x times environment interaction for yield components and plant height in rice. Theor Appl Genet 95:799–808
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank F. Onishi and N. VanNeck for technical assistance in the greenhouse, M. J. Thomson, K. Chen, and M. Yunus for critical reading of the manuscript, and L. Swales for formatting. A Ph.D. fellowship for E. Septiningsih and much of the field evaluation in Indonesia were funded by the Rockefeller Foundation, and a postdoctoral fellowship for E.S. was funded through NSF Plant Genome Award DBI-0110004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D.J. Mackill
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Septiningsih, E.M., Prasetiyono, J., Lubis, E. et al. Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon . Theor Appl Genet 107, 1419–1432 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1373-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1373-2