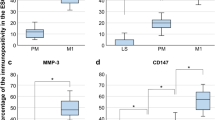
Abstract
NR4A1 (NUR77) is an orphan nuclear receptor that has been implicated in both cell survival and apoptosis. However, the role of NUR77 in trophoblast function during early placenta development has not been fully elucidated. In this study, we showed that NUR77 expression was significantly lower in the villi of the recurrent miscarriage (RM) group compared to that in the healthy controls (HCs) group. We used immunohistochemistry and found that NUR77 was highly expressed in human placental villi during early pregnancy, especially in syncytiotrophoblast (STB), and was expressed at a much lower level in STB from the RM group than in those from HC group. Western blotting data further confirmed that NUR77 was highly expressed in primary human term placental STB and the FSK-induced BeWo cell line. Moreover, antibody array screening and ELISA revealed that NUR77 promoted significant placental growth factor (PGF) expression during trophoblast fusion. Ectopic overexpression and knockdown experiments demonstrated that PGF was a novel downstream target of NUR77, and serum PGF expression correlated positively with trophoblast NUR77 mRNA levels in HCs and RM patients. Importantly, bioinformatics analysis identified two NUR77 binding sites in the PGF promoter region, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) coupled with Western blotting analysis further verified that NUR77 bound directly to the PGF promoter region and promoted PGF expression. Furthermore, in a BeWo/HTR-8 co-culture system, FSK-induced BeWo-secreted PGF promoted HTR-8 cell migration and invasion, and an anti-PGF antibody reversed this effect. Collectively, these results indicated that NUR77 may play a key role in regulating trophoblast invasion at early pregnancy.
Key messages
-
NUR77 expression was significantly decreased in the syncytiotrophoblast of the recurrent miscarriage group compared to that in the healthy control group.
-
NUR77 promoted PGF expression during trophoblast fusion.
-
ChIP and western blotting experiments verified that NUR77 bound directly to the PGF promoter region and activated PGF expression in trophoblast.
-
Trophoblast-derived PGF promoted HTR-8 cell migration and invasion in a cell co-culture system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Red-Horse K, Zhou Y, Genbacev O, Prakobphol A, Foulk R, McMaster M, Fisher SJ (2004) Trophoblast differentiation during embryo implantation and formation of the maternal–fetal interface. J Clin Invest 114:744–754
Staun-Ram E, Shalev E (2005) Human trophoblast function during the implantation process. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 3:56–61
Latos PA, Hemberger M (2016) From the stem of the placental tree: trophoblast stem cells and their progeny. Development 143:3650–3660
Castellucci M, Kosanke G, Verdenelli F, Huppertz B, Kaufmann P (2000) Villous sprouting: fundamental mechanisms of human placental development. Hum Reprod Update 6:485–494
Bischof P, Meisser A, Campana A (2001) Biochemistry and molecular biology of trophoblast invasion. Ann N Y Acad Sci 943:157–162
Genbacev O, Jensen KD, Powlin SS, Miller RK (1993) In vitro differentiation and ultrastructure of human extravillous trophoblast (EVT) cells. Placenta 14:463–475
Strickland S, Richards WG (1992) Invasion of the trophoblasts. Cell 71:355–357
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M, Herrlich P, Schütz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M, Chambon P, Evans RM (1995) The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell 83:835–839
Ranhotra HS (2015) The NR4A orphan nuclear receptors: mediators in metabolism and diseases. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 35:184–188
Giguere V (2008) Transcriptional control of energy homeostasis by the estrogen-related receptors. Endocr Rev 29:677–696
Hsu HC, Zhou T, Mountz JD (2004) NUR77 family of nuclear hormone receptors. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 3:413–423
Wilson TE, Fahrner TJ, Johnston M, Milbrandt J (1991) Identification of the DNA binding site for NGFI-B by genetic selection yeast. Science 252:1296–1300
Wilson TE, Fahrner TJ, Milbrandt J (1993) The orphan receptors NGFI-B and steroidogenic factor 1 establish monomer binding as a third paradigm of nuclear receptor-DNA interaction. Mol Cell Biol 13:5794–5804
Zhang X, Yan G, Diao Z, Sun H, Hu Y (2012) NUR77 inhibits the expression of TIMP2 and increases the migration and invasion of HTR-8/SVneo cells induced by CYR61. Placenta 33:561–567
Jiang Y, Hu Y, Zhao J, Zhen X, Yan G, Sun H (2011) The orphan nuclear receptor NUR77 regulates decidual prolactin expression in human endometrial stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:628–633
Maglione D, Guerriero V, Viglietto G, Delli-Bovi P, Persico MG (1991) Isolation of a human placenta cDNA coding for a protein related to the vascular permeability factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:9267–9271
Khaliq A, Li XF, Shams M, Sisi P, Acevedo CA, Whittle MJ, Weich H, Ahmed A (1996) Localisation of placenta growth factor (PGF) in human term placenta. Growth Factors 13:243–250
Shore VH, Wang TH, Wang CL, Torry RJ, Caudle MR, Torry DS (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor, placenta growth factor and their receptors in isolated human trophoblast. Placenta 18:657–665
Hanna J, Goldman-Wohl D, Hamani Y, Avraham I, Greenfield C, Natanson-Yaron S, Prus D, Cohen-Danie L, Arnon TI, Manaster I, Gazit R, YutkinVet L (2006) Decidual NK cells regulate key developmental processes at the human fetal-maternal interface. Nat Med 12:1065–1074
Fischer C, Mazzone M, Jonckx B, Carmeliet P (2008) FLT1 and its ligands VEGFB and PlGF: drug targets for anti-angiogenic therapy? Nat Rev Cancer 8:942–956
Ahmed A, Dunk C, Ahmad S, Khaliq A (2000) Regulation of placental vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and placenta growth factor (PIGF) and soluble Flt-1 by oxygen--a review. Placenta 21:S16–S24
Maynard SE, Min JY, Merchan J, Lim KH, Li J, Mondal S, Libermann TA, Morgan JP, Sellke FW, Stillman IE, Epstein FH, Sukhatme VP, Karumanchi SA (2003) Excess placental soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt1) may contribute to endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and proteinuria in preeclampsia. J Clin Invest 111:649–658
Regnault TR, Orbus RJ, de Vrijer B, Davidsen ML, Galan HL, Wilkening RB, Anthony RV (2002) Placental expression of VEGF, PlGF and their receptors in a model of placental insufficiency-intrauterine growth restriction (PI-IUGR). Placenta 23:132–144
Schiettecatte J, Russcher H, Anckaert E, Mees M, Leeser B, Tirelli AS, Fiedler GM, Luthe H, Denk B, Smitz J (2010) Multicenter evaluation of the first automated Elecsys sFlt-1 and PlGF assays in normal pregnancies and preeclampsia. Clin Biochem 43:768–770
Chen J, Ye L, Zhang L, Jiang WG (2008) Placenta growth factor, PLGF, influences the motility of lung cancer cells, the role of rho associated kinase, Rock1. J Cell Biochem 105:313–320
Li B, Wang C, Zhang Y, Zhao XY, Huang B, Wu PF, Li Q, Li H, Liu YS, Cao LY, Dai WM, Fang WG, Shang DS, Cao L, Zhao WD, Chen YH (2013) Elevated PLGF contributes to small-cell lung cancer brain metastasis. Oncogene 32:2952–2962
Zhang Y, Zhao A, Wang X, Shi G, Jin H, Lin Q (2008) Expressions of natural cytotoxicity receptors and NKG2D on decidual natural killer cells in patients having spontaneous abortions. Fertil Steril 90:1931–1937
Kliman HJ, Nestler JE, Sermasi E, Sanger JM, Strauss JF (1986) Purification, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of cytotrophoblasts from human term placentae. Endocrinology. 118:1567–1582
Tian FJ, Cheng YX, Li XC, Wang F, Qin CM, Ma XL, Yang J, Lin Y (2016) The YY1/MMP2 axis promotes trophoblast invasion at the maternal-fetal interface. J Pathol 239:36–47
Graham CH, Hawley TS, Hawley RG, MacDougall JR, Kerbel RS, Khoo N, Lala PK (1993) Establishment and characterization of first trimester human trophoblast cells with extended lifespan. Exp Cell Res 206:204–211
Tian FJ, He XY, Wang J, Li X, Ma XL, Wu F, Zhang J, Liu XR, Qin XL, Zhang Y, Zeng WH, Lin Y (2018) Elevated tristetraprolin impairs trophoblast invasion in women with recurrent miscarriage by destabilization of HOTAIR. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 12:600–609
Wice B, Menton D, Geuze H, Schwartz AL (1990) Modulators of cyclic AMP metabolism induce syncytiotrophoblast formation in vitro. Exp Cell Res 186:306–316
Ordentlich P, Yan Y, Zhou S, Heyman RA (2003) Identification of the antineoplastic agent 6-mercaptopurine as an activator of the orphan nuclear hormone receptor NURr1. J Biol Chem 278:24791–24799
Zeng HY, Qin LL, Zhao DZ, Tan XL, Manseau EJ, Hoang MV, Senger DR, Brown LF, Nagy JA, Dvorak HF (2006) Orphan nuclear receptor TR3/NUR77 regulates VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis through its transcriptional activity. J Exp Med 203:719–729
Akrami H, Mahmoodi F, Havasi S, Sharifi A (2016) PlGF knockdown inhibited tumor survival and migration in gastric cancer cell via PI3K/Akt and p38MAPK pathways. Cell Biochem Funct 34:173–180
Matys V, Fricke E, Geffers R, Gössling E, Haubrock M, Hehl R, Hornischer K, Karas D, Kel AE, Kel-Margoulis OV, Kloos DU, Land S, Lewicki-Potapov B, Michael H, Münch R, Reuter I, Rotert S, Saxel H, Scheer M, Thiele S, Wingender E (2003) TRANSFAC: transcriptional regulation, from patterns to profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 31:374–378
Martin LJ, Tremblay JJ (2005) The human 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/ Delta5-Delta4 isomerase type 2 promoter is a novel target for the immediate early orphan nuclear receptor NUR77 in steroidogenic cells. Endocrinology. 146:861–869
Prakobphol A, Genbacev O, Gormley M, Kapidzic M, Fisher SJ (2006) A role for the L-selectin adhesion system in mediating cytotrophoblast emigration from the placenta. Dev Biol 298:107–117
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Luttun A, Vincenti V, Compernolle V, De Mol M, Wu Y, Bono F, Devy L, Beck H, Scholz D, Acker T, DiPalma T, Dewerchin M, Noel A, Stalmans I, Barra A, Blacher S, VandenDriessche T, Ponten A, Eriksson U, Plate KH, Foidart JM, Schaper W, Charnock-Jones DS, Hicklin DJ, Herbert JM, Collen D, Persico MG (2001) Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat Med 7:575–583
Reuvekamp A, Velsing-Aarts FV, Poulina IE, Capello JJ, Duits AJ (1999) Selective deficit of angiogenic growth factors characterises pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 106:1019–1022
Muttukrishna S, Swer M, Suri S, Jamil A, Calleja-Agius J, Gangooly S, Ludlow H, Jurkovic D, Jauniaux E (2011) Soluble Flt-1 and PlGF: new markers of early pregnancy loss? PLoS One 6:e18041
Chang M, Mukherjea D, Gobble RM, Groesch KA, Torry RJ, Torry DS (2008) Glial cell missing 1 regulates placental growth factor (PGF) gene transcription in human trophoblast. Biol Reprod 78:841–851
Depoix C, Tee MK, Taylor RN (2011) Molecular regulation of human placental growth factor (PlGF) gene expression in placental villi and trophoblast cells is mediated via the protein kinase a pathway. Reprod Sci 18:219–228
Martin LJ, Boucher N, Brousseau C, Tremblay JJ (2008) The orphan nuclear receptor NUR77 regulates hormone-induced StAR transcription in Leydig cells through a cooperation with CaMKI. Mol Endocrinol 22:2021–2037
Li W, Amri H, Huang H, Wu C, Papadopoulos V (2004) Gene and protein profiling of the response of MA-10 Leydig tumor cells to human chorionic gonadotropin. J Androl 25:900–913
Katagiri Y, Takeda K, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Ozato K, Guroff G (2000) Modulation of retinoid signalling through NGF-induced nuclear export of NGFI-B. Nat Cell Biol 2:435–440
Li H, Kolluri SK, Gu J, Dawson MI, Cao X, Hobbs PD, Lin BZ, Chen GQ, Lu JS, Lin F, Xie ZH, Fontana JA, Reed JC, Zhang XK (2000) Cytochrome c release and apoptosis induced by mitochondrial targeting of nuclear orphan receptor TR3. Science 289:1159–1164
Rai R, Regan L (2006) Recurrent miscarriage. Lancet 368:601–611
Stirrat GM (1990) Recurrent miscarriage. Lancet 336:673–675
Tian FJ, Qin CM, Li XC, Wu F, Liu XR, Xu WM, Lin Y (2015) Decreased stathmin-1 expression inhibits trophoblast proliferation and invasion and is associated with recurrent miscarriage. Am J Pathol 185:2709–2721
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81401218 to F.-J.T.) and by the Family Planning Project of the Shanghai Health and Family Planning Commission (20164037 to X.-C.L.), the key projects of the Shanghai Municipal Health and Family Planning Commission (201640012 to F.-J.T.), and the Shanghai Jiao Tong University Medicine-Engineering Fund (YG2017 MS38 to F.-J.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.-C.L., X.-J.Y., and F. -J.T. performed the experiments; W. H, F. J, and J.L. contributed to the statistical analyses; P.-Y.W. provided material support; Y.-M. W. contributed valuable advice to the development of the manuscript; X.-C.L., X.-J.Y., and F.-J.T. wrote the manuscript; and F.-J.T. designed the study and directed the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 160 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, XC., Yin, XJ., Hong, W. et al. The orphan nuclear receptor NUR77 promotes trophoblast invasion at early pregnancy through paracrine placental growth factor. J Mol Med 97, 1359–1373 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01819-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01819-4