Abstract
Introduction:
The anterior delto-pectoral approach is the standard approach for the fixation of proximal humeral fractures with the PHILOS®-Plate system. However, this approach can impair the vascular supply and can increase avascular necrosis. The objective of this study was to evaluate the results and complexity of surgery of proximal humeral fractures with a minimal invasive (MIPO) approach.
Methods:
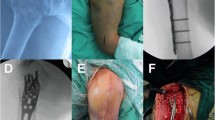
All PHILOS®-plate osteosynthesis operated between Januray 2003 and June 2006 were evaluated prospectively. A minimal invasive antero-lateral deltasplit-approach was performed in all two to four fragment instable fractures meeting the indication for osteosynthesis according to Neer. An open approach (ORIF) was chosen in all other fractures mainly dislocated fractures and particularly in fractures with major subcapital displacement.
Results:
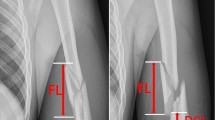
A cohort of 68 patients suffered a proximal humerus fracture and qualified for a minimal invasive approach with a PHILOS®-plate osteosynthesis. Of these 68 patients, 41 were locally resident. Eight patients refused a follow-up, two patients were in constant care, and two patients died; 29 patients (71%) (20 females, 9 males) could be documented entirely with a median age of 64 years. The median operation time amounted to 75 min with a fluoroscopic time of 160 s. The median Constant score was 78 after 12 months. All fractures healed in adequate time. One patient showed a lesion of the ventral part of the axillary nerve. No patient suffered an avascular necrosis.
Discussion:
The minimal invasive PHILOS® plate osteosynthesis through an antero-lateral delta-split approach proved to be an elegant procedure for selected fractures of the proximal humerus with a low morbidity and good functional outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kettler M, Biberthaler P, Braunstein V, et al. Treatment of proximal humeral fractures with the PHILOS angular stable plate: presentation of 225 cases of dislocated fractures. Unfallchirurg 2006;109:1032–40.
Giannoudis PV, Schneider E. Principles of fixation of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2006;88:1272–8.
Neer CS II. Displaced proximal humeral fractures: I. Classification and evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1970;52:1077–89.
Neer CS II. Displaced proximal humeral fractures: II. Treatment of three-part and four-part displacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1970;52:1090–103.
Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1987;214:160–4.
Helmy N, Hintermann B. New trends in the treatment of proximal humerus fractures (review). Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006;442:100–8.
Brooks CH, Revell WJ, Heatley FW. Vascularity of the humeral head after proximal humeral fractures: an anatomical cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993;75:132–6.
Gerber C, Schneeberger AG, Vinh TS. The arterial vascularization of the humeral head: an anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1990;72:1486–94.
Smith J, Berry G, Laflamme Y, et al. Percutaneous insertion of a proximal humeral locking plate: an anatomic study. Injury 2007;38:206–11Epub 2006 Oct 25.
Gardner MJ, Voos JE, Wanich T, et al. Vascular implications of minimally invasive plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2006;20:602–7.
Bjorkenheim JM, Pajarinen J, Savolainen V. Internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with a locking compression plate: a retrospective evaluation of 72 patients followed for a minimum of 1 year. Acta Orthop Scand 2004;75:741–5.
Plecko M, Kraus A. Internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the locking proximal humerus plate. Oper Orthop Traumatol 2005;17:25–50.
Bono CM, Grossman MG, Hochwald N, et al. Radial and axillary nerves: anatomic considerations for humeral fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2000;379:259–64.
Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Dines JS, et al. The extended anterolateral acromial approach allows minimally invasive access to the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005;434:123–9.
Gardner MJ, Lawrence BD, Griffith MH. A minimally invasive approach for plate fixation of the proximal humerus. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 2004;62:18–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acklin, Y.P., Jenni, R., Walliser, M. et al. Minimal Invasive PHILOS®-Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Humeral Fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 35, 35–39 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-008-7154-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-008-7154-5