Abstract
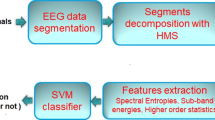
In this work, we investigate epilepsy seizure detection using machine learning. In the literature, a machine learning model is usually trained to help automate the epileptic detection process, eliminating the need for human intervention. Typically, the dataset is split into training and test sets in a way to maximize the detection accuracy. This requires the training set to include enough EEG samples for every possible patient in order to improve the accuracy numbers during the prediction. However, this might not be easy or practical in real life. A new patient might not have a previous record in the training set, and hence, the prediction for this particular patient might not meet the expected accuracy. The main contribution in this work is to study the impact of the training and test datasets selection from practical point of view on the accuracy and efficacy of the CNN prediction. In this work, a CNN model, namely AlexNet, is trained to detect epileptic states, namely preictal, interictal and ictal, in subjects using electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. The dataset includes the three epileptic zones of subjects taken from three medical centers, collected by the Fragility Multi-Center Retrospective Study. Furthermore, we propose a framework to utilize a feature extraction technique that exploits the available multiple channels of EEG signals to minimize information loss. As part of the main contribution, three different approaches are proposed to split the EEG sample dataset into the training and test sets. Thus, the prediction performance is evaluated based on the prior knowledge extracted from the particular samples picked for the training set. The results show that the proposed framework achieves an overall accuracy of 94.44% when the training contained samples from each patient. The accuracy is reduced to 92.98% when the training set contained a subset of the patient pool. A binary classification is also performed with up to 98% accuracy for both scenarios.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
U.R. Acharya, Y. Hagiwara, H. Adeli, Automated seizure prediction. Epilepsy Behav. 88, 251–261 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.09.030
U.R. Acharya, S.L. Oh, Y. Hagiwara, J.H. Tan, H. Adeli, Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 100, 270–278 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.09.017
U.R. Acharya, Y. Hagiwara, S.N. Deshpande, S. Suren, J.E.W. Koh, S.L. Oh, N. Arunkumar, E.J. Ciaccio, C.M. Lim, Characterization of focal EEG signals: a review. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 91, 290–299 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.08.044
T. Åkerstedt, M. Gillberg, Sleep duration and the power spectral density of the EEG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 64(2), 2520 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(86)90106-9
F. Al-Ali, T.D. Gamage, H.W.T.S. Nanayakkara, F. Mehdipour, S.K. Ray, Novel casestudy and benchmarking of AlexNet for edge AI: from CPU and GPU to FPGA. In: Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, vol. 2020-Augus (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CCECE47787.2020.9255739
E. Alickovic, J. Kevric, A. Subasi, Performance evaluation of empirical mode decomposition, discrete wavelet transform, and wavelet packed decomposition for automated epileptic seizure detection and prediction. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 39, 94–102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BSPC.2017.07.022
K.M. Almustafa, Classification of epileptic seizure dataset using different machine learning algorithms. Inf. Med. Unlocked 21, 100444 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100444
R.G. Andrzejak, K. Lehnertz, F. Mormann, C. Rieke, P. David, C.E. Elger, Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: Dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Topics 64(6), 8 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.64.061907
S. Appelhoff, M. Sanderson, T. Brooks, M. Vliet, R. Quentin, C. Holdgraf, M. Chaumon, E. Mikulan, K. Tavabi, R. Höchenberger, D. Welke, C. Brunner, A. Rockhill, E. Larson, A. Gramfort, M. Jas, MNE-BIDS: organizing electrophysiological data into the BIDS format and facilitating their analysis. J. Open Source Softw. 4(44), 1896 (2019). https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01896
E. Bou Assi, D.K. Nguyen, S. Rihana, M. Sawan, Towards accurate prediction of epileptic seizures: a review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 34, 144–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.02.001
CHB-MIT: CHB-MIT scalp EEG database. (2000). https://physionet.org/content/chbmit/1.0.0/
Freiburg: Freiburg seizure prediction project. Freiburg, Germany. https://epilepsy.uni-freiburg.de/freiburg-seizure-prediction-project/eeg-database
K. Gadhoumi, J.-M. Lina, F. Mormann, J. Gotman, Seizure prediction for therapeutic devices: a review. J. Neurosci. Methods 260, 270–282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.06.010
Y. Gao, B. Gao, Q. Chen, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, Deep convolutional neural network-based epileptic electroencephalogram (EEG) signal classification. Front. Neurol. 11, 375 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00375
A.L. Goldberger, L.A.N. Amaral, L. Glass, J.M. Hausdorff, P.C. Ivanov, R.G. Mark, J.E. Mietus, G.B. Moody, C.-K. Peng, H.E. Stanley, PhysioBank, physioToolkit and physioNet. Circulation 101(23), 215 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.23.e215
C. Holdgraf, S. Appelhoff, S. Bickel, K. Bouchard, S. D’Ambrosio, O. David, O. Devinsky, B. Dichter, A. Flinker, B. L. Foster, K. J. Gorgolewski, I. Groen, D. Groppe, A. Gunduz, L. Hamilton, C. J. Honey, M. Jas, R. Knight, J.-P. Lachaux, J. C. Lau, C. Lee-Messer, B. N. Lundstrom, K. J. Miller, J.G. Ojemann, R. Oostenveld, N. Petridou, G. Piantoni, A. Pigorini, N. Pouratian, N. F. Ramsey, A. Stolk, N. C. Swann, F. Tadel, B. Voytek, B. A. Wandell, J. Winawer, K. Whitaker, L. Zehl, D. Hermes, BIDS-iEEG: an extension to the brain imaging data structure (BIDS) specification for human intracranial electrophysiology. Sci. Data 6(102), 26 (2019)
W. Hu, J. Cao, X. Lai, J. Liu, Mean amplitude spectrum based epileptic state classification for seizure prediction using convolutional neural networks. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01220-6
S. Ibrahim, S. Majzoub, Adaptive epileptic seizure prediction based on EEG synchronization. J. Biomim. Biomater. Biomed. Eng. 33, 52 (2017) https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JBBBE.33.52
E.M. Imah, A. Widodo, A comparative study of machine learning algorithms for epileptic seizure classification on EEG signals. In: 2017 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information Systems (ICACSIS), pp. 401–408 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACSIS.2017.8355065
P. Jahankhani, V. Kodogiannis, K. Revett, EEG Signal classification using wavelet feature extraction and neural networks. In: IEEE John Vincent Atanasoff 2006 International Symposium on Modern Computing (JVA’06), pp. 120–124 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/JVA.2006.17
H. Khan, L. Marcuse, M. Fields, K. Swann, B. Yener, Focal onset seizure prediction using convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 65(9), 2109–2118 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2017.2785401
M.A. Kramer, E.D. Kolaczyk, H.E. Kirsch, Emergent network topology at seizure onset in humans. Epilepsy Res. 79(2–3), 173–186 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2008.02.002
A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G.E. Hinton, ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
L. Kuhlmann, K. Lehnertz, M.P. Richardson, B. Schelter, H.P. Zaveri, Seizure prediction—ready for a new era. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 14(10), 618–630 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0055-2
Y. Kumar, M.L. Dewal, R.S. Anand, Epileptic seizures detection in EEG using DWT-based ApEn and artificial neural network. Signal Image Video Process. 8(7), 1323–1334 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-012-0362-9
A. Li, C. Huynh, Z. Fitzgerald, I. Cajigas, D. Brusko, J. Jagid, A.O. Claudio, A.M. Kanner, J. Hopp, S. Chen, J. Haagensen, E. Johnson, W. Anderson, N. Crone, S. Inati, K.A. Zaghloul, J. Bulacio, J. Gonzalez-Martinez, S.V. Sarma, Neural fragility as an EEG marker of the seizure onset zone. Nat. Neurosci. 24(10), 1465–1474 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00901-w
M. Moshinsky, Characterization of focal EEG signals: A review — Science direct (1959). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167739X18318818
S. Opałka, B. Stasiak, D. Szajerman, A. Wojciechowski, Multi-channel convolutional neural networks architecture feeding for effective EEG mental tasks classification. Sensors (Switzerland) 18(10), (2018) https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103451
C.R. Pernet, S. Appelhoff, K.J. Gorgolewski, G. Flandin, C. Phillips, A. Delorme, R. Oostenveld, EEG-BIDS, an extension to the brain imaging data structure for electroencephalography (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0104-8
F. Pisano, G. Sias, A. Fanni, B. Cannas, A. Dourado, B. Pisano, C.A. Teixeira, Convolutional neural network for seizure detection of nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy. Complexity 2020, 4825767 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4825767
T. Radüntz, J. Scouten, O. Hochmuth, B. Meffert, Automated EEG artifact elimination by applying machine learning algorithms to ICA-based features. J. Neural Eng. 14, 46004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aa69d1
M. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, U. Rajendra Acharya, A new approach to characterize epileptic seizures using analytic time-frequency flexible wavelet transform and fractal dimension. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 94, 172–179 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2017.03.023
M. Sharma, R.B. Pachori, U. Rajendra Acharya, A new approach to characterize epileptic seizures using analytic time-frequency flexible wavelet transform and fractal dimension. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 94, 172–179 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PATREC.2017.03.023
A. Shoeibi, M. Khodatars, N. Ghassemi, M. Jafari, P. Moridian, R. Alizadehsani, M. Panahiazar, F. Khozeimeh, A. Zare, H. Hosseini-Nejad, A. Khosravi, A.F. Atiya, D. Aminshahidi, S. Hussain, M. Rouhani, S. Nahavandi, U.R. Acharya, Epileptic seizures detection using deep learning techniques: a review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2021, Vol. 18, Page 5780 18(11), 5780 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH18115780, arXiv:2007.01276
M.K. Siddiqui, R. Morales-Menendez, X. Huang, N. Hussain, A review of epileptic seizure detection using machine learning classifiers. Brain Inf. 7(1), 1–18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40708-020-00105-1
Y. Song, J. Crowcroft, J. Zhang, Automatic epileptic seizure detection in EEGs based on optimized sample entropy and extreme learning machine. J. Neurosci. Methods 210(2), 132–146 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2012.07.003
A. Subasi, J. Kevric, M. Abdullah Canbaz, Epileptic seizure detection using hybrid machine learning methods. Neural Comput. Appl. 31(1), 317–325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3003-y
D.K. Thara, B.G. PremaSudha, F. Xiong, Auto-detection of epileptic seizure events using deep neural network with different feature scaling techniques. Pattern Recog. Lett. 128, 544–550 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.10.029
P. Thodoroff, J. Pineau, A. Lim, Learning robust features using deep learning for automatic seizure detection. (2016) CoRR abs/1608.0
N.D. Truong, A.D. Nguyen, L. Kuhlmann, M.R. Bonyadi, J. Yang, S. Ippolito, O. Kavehei, Convolutional neural networks for seizure prediction using intracranial and scalp electroencephalogram. Neural Netw. 105, 104–111 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.04.018
S. Yang, B. Deng, J. Wang, H. Li, M. Lu, Y. Che, X. Wei, K.A. Loparo, Scalable digital neuromorphic architecture for large-scale biophysically meaningful neural network with multi-compartment neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(1), 148–162 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2899936
S. Yang, J. Tan, B. Chen, Robust spike-based continual meta-learning improved by restricted minimum error entropy criterion. Entropy 24(4), 24040455 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/e24040455
S. Yang, B. Linares-Barranco, B. Chen, Heterogeneous ensemble-based spike-driven few-shot online learning. Front. Neurosci. 16, 850932 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.850932
S. Yang, T. Gao, J. Wang, B. Deng, M.R. Azghadi, T. Lei, B. Linares-Barranco, SAM: a unified self-adaptive multicompartmental spiking neuron model for learning With working memory. Front. Neurosci. 16, 850945 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.850945
S. Yang, J. Wang, B. Deng, M.R. Azghadi, B. Linares-Barranco, Neuromorphic context-dependent learning framework with fault-tolerant spike routing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33(12), 7126–7140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3084250
S. Yang, J. Wang, X. Hao, H. Li, X. Wei, B. Deng, K.A. Loparo, BiCoSS: toward large-scale cognition brain with multigranular neuromorphic architecture. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33(7), 2801–2815 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3045492
M. Zhou, C. Tian, R. Cao, B. Wang, Y. Niu, T. Hu, H. Guo, J. Xiang, Epileptic seizure detection based on EEG signals and CNN. Front. Neuroinform. 12, 95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2018.00095
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Can be downloaded from https://openneuro.org/datasets/ds003029/versions/1.0.3.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Majzoub, S., Fahmy, A., Sibai, F. et al. Epilepsy Detection with Multi-channel EEG Signals Utilizing AlexNet. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 6780–6797 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02423-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02423-1