Abstract
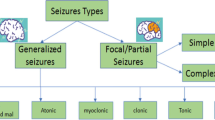
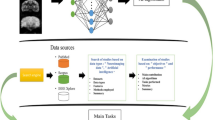
Epilepsy is a common non-communicable, group of neurological disorders affecting more than 50 million individuals worldwide. Researchers are working to automatically detect epileptic activities through Electroencephalography (EEG) signal analysis, and artificial intelligence techniques. Good quality, open-source, and free EEG data acts as a catalyst in the on-going research to early diagnose this disease. The present review focuses on reporting EEG datasets for automatic epilepsy diagnosis and seizure detection for the past three decades. Upon a thorough search analysis, 28 publicly available, and private EEG datasets have been compiled and compared for adult and paediatric human populations suffering from epilepsy. The discussion of the advantages and limitations of the present datasets has been done based on several parameters. Their associated, recent experimental pipelines have also been discussed. CHB-MIT and Bonn remain the benchmark datasets in this field. EEG meta-data has been released to tackle large EEG datasets like CHB-MIT and Siena Scalp. In conclusion, an increasing trend in the release of open-source EEG datasets has been observed with varied clinical setups and demographics. A standardized data development protocol is needed to develop generalized artificial intelligence techniques for the early detection of epileptic events.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Links to all the datasets have been provided in appropriate sections.
Code availability
Not applicable (NA).
References
Erik K. St. Louis. Eeg in the epilepsies. 1970. URL https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK390347/.
Thomas SV, Sarma PS, Alexander M, Pandit L, Shekhar L, Trivedi C, Vengamma B. Economic burden of epilepsy in India. Epilepsia. 2001;42(8):1052–60.
Abdulbaqi AS, Younis MT, Younus YT, Obaid AJ. A hybrid technique for eeg signals evaluation and classification as a step towards to neurological and cerebral disorders diagnosis. Int J Nonlinear Anal Appl. 2022;13(1): 773–781.
Andrzejak RG, Lehnertz K, Mormann F, Rieke C, David P, Elger CE. Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E. 2001;64(6): 061907
Choi G, Park C, Kim J, Cho K, Kim T-J, Bae HS, Min K, Jung K-Y, Chong J. A novel multi-scale 3d cnn with deep neural network for epileptic seizure detection. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE). 1–2. IEEE. 2019
Handa P, Goel N. Epileptic seizure detection using rhythmicity spectrogram and cross-patient test set. In: 2021 8th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN). 898–902. IEEE. 2021
Rout SK, Sahani M, Dora C, Biswal PK, Biswal B. An efficient epileptic seizure classification system using empirical wavelet transform and multi-fuse reduced deep convolutional neural network with digital implementation. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022;72: 103281
Madhurshalini M, Nair C, Goel N. Automatic identification of skin lesions using deep learning techniques. In: 2020 IEEE/ITU International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Good (AI4G). 2020; 230–235. IEEE
Anuragi A, Sisodia DS, Pachori RB. Epileptic-seizure classification using phase-space representation of fbse-ewt based eeg sub-band signals and ensemble learners. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022;71: 103138
Li RW, Limsoon W, Wilson WBG. Drug discovery today: how doppelgänger effects in biomedical data confound machine learning. 2021.
Bishnoi V, Goel N, Tayal A. Wrapper-based best feature selection approach for lung cancer detection. In: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Sustainable Computing. 2021;175–186. Springer
Kaur S, Goel N. A dilated convolutional approach for inflammatory lesion detection using multi-scale input feature fusion (workshop paper). In: 2020 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM). 2020; 386–393. IEEE
Erdem T, Emine Doğru B. Classification of epileptic seizures from electroencephalogram (eeg) data using bidirectional short-term memory (bi-lstm) network architecture. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022;73: 103462.
Goel N Kaur S, Gunjan D, Mahapatra SJ. Dilated cnn for abnormality detection in wireless capsule endoscopy images. Soft Comput. 2022; 1–17
Gao B, Zhou J, Yang Y, Chi J, Yuan Q. Generative adversarial network and convolutional neural network-based eeg imbalanced classification model for seizure detection. Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2022;42(1):1–15.
Howbert JJ, Patterson EE, Stead SM, Brinkmann B, Vasoli V, Crepeau D, Vite CH, Sturges B, Ruedebusch V, Mavoori J, et al. Forecasting seizures in dogs with naturally occurring epilepsy. PloS One. 2014;9 (1): e81920
Cserpan D, et al. Dataset of eeg recordings of pediatric patients with epilepsy based on the 10-20 system. 2021.
Selvaraj TG, Ramasamy B, Jeyaraj SJ, Suviseshamuthu ES. Eeg database of seizure disorders for experts and application developers. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2014;45(4): 304–309
Andrzejak RG, Schindler K, Rummel C. Nonrandomness, nonlinear dependence, and nonstationarity of electroencephalographic recordings from epilepsy patients. Phys. Rev. E. 2012; 86(4): 046206
Obeid I, Picone J. The temple university hospital eeg data corpus. Front Neurosci. 2016;10:196.
Swami P, Panigrahi B, Nara S, Bhatia M, Gandhi T. ERG epilepsy datasets. 2016.
Detti P, Vatti G, Manrique GZ, de Lara. Eeg synchronization analysis for seizure prediction: a study on data of noninvasive recordings. Processes. 2020;8(7):846.
Detti P. Siena scalp eeg database (version 1.0.0). 2020. https://doi.org/10.13026/5d4a-j060.
Panwar S, Joshi SD, Gupta A, Agarwal P. Automated epilepsy diagnosis using eeg with test set evaluation. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabilit Eng. 2019;27(6): 1106–1116
Panwar S. Single electrode EEG data of healthy and epileptic patients. 2020. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3684992.
Nasreddine W. Epileptic eeg dataset. 2021. https://doi.org/10.17632/5pc2j46cbc.1.
Hunter MRLL, Smith Robert LL, Hyslop W, Rosso OA, Gerlach R, Rostas JAP, Williams DB, Henskens F. The australian eeg database. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2005;36(2): 76–81.
A comprehensive list of asc data resources. https://autismresearchlab.group.shef.ac.uk/ASD_resources.html.
Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov Plamen C, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB. Chung-Kang Peng, and H Eugene Stanley. Physiobank, physiotoolkit, and physionet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. circulation. 2000;101(23): e215–e220.
Stevenson N, Tapani K, Lauronen L, Vanhatalo S. A dataset of neonatal EEG recordings with seizures annotations. 2018. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2547147.
Deepa B, Ramesh K. Preprocessed chb-mit scalp eeg database. 2021. https://doi.org/10.21227/awcw-mn88.
Handa P, Goel N. Peri-ictal and non-seizure eeg event detection using generated metadata. Expert Syst. e12929. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12929.
Gupta M, Sachdeva RA, Gupta E, Handa P, Goel N. Meta-eeg of siena scalp eeg database v1.0.0. 2022a. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6061290.
Esha G, Muskan G, Rishita AS, Palak H, Nidhi G. Meta-eeg of chb-mit scalp eeg database v1.0.0.0. 2022b. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6062372.
Kuhlmann L, Karoly P, Freestone DR, Brinkmann BH, Temko A, Barachant A, Li F, Titericz Jr G, Lang BW, Lavery D, et al. Epilepsyecosystem. org: crowd-sourcing reproducible seizure prediction with long-term human intracranial eeg. Brain. 2018;141(9): 2619–2630.
Nejedly P, Kremen V, Sladky V, Cimbalnik J, Klimes P, Plesinger Filip, Mivalt Filip, Travnicek Vojtech, Viscor Ivo, Pail Martin, et al. Multicenter intracranial eeg dataset for classification of graphoelements and artifactual signals. Sci data. 2020;7(1):1–7.
Das K, Daschakladar D, Roy PP, Chatterjee A, Saha SP. Epileptic seizure prediction by the detection of seizure waveform from the pre-ictal phase of eeg signal. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2020;57: 101720.
Shivarudhrappa R, Natarajan S, Yasin T, Shyam VR, Alangar SH, Pieter LK. Performance evaluation of dwt based sigmoid entropy in time and frequency domains for automated detection of epileptic seizures using svm classifier. Comput Biol Med. 2019;110:127–143.
Duanpo W, Wang Z, Jiang L, Dong F, Xunyi W, Wang S, Ding Y. Automatic epileptic seizures joint detection algorithm based on improved multi-domain feature of ceeg and spike feature of aeeg. IEEE Access. 2019;7:41551–64.
Avcu MT, Zhang Z, Chan DWS. Seizure detection using least eeg channels by deep convolutional neural network. In: ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP). 2019; 1120–1124. IEEE.
Muhammad B, Muhammad R, Sajid S, Muhammad MK, Mohammed SA, Mohammed A. Automatic seizure detection using multi-resolution dynamic mode decomposition. IEEE Access. 2019;7: 61180–61194.
Yedurkar DP, Metkar SP. Multiresolution approach for artifacts removal and localization of seizure onset zone in epileptic eeg signal. Biomed Signal Processing and Control. 2020;57:101794
Yan PZ, Wang F, Kwok N, Allen BB, Keros S, Grinspan Z. Automated spectrographic seizure detection using convolutional neural networks. Seizure. 2019;71:124–131.
Cao J, Zhu J, Wenbin H, Kummert A. Epileptic signal classification with deep eeg features by stacked cnns. IEEE Trans Cogn Dev Syst. 2019;12(4):709–22.
Matthias I, Hinnerk F-D, César AT, Adrien W, Björn S, Jens T, Andreas S-B. Epilepsiae—a european epilepsy database. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. 2012;106(3): 127–138.
Schelter B, Winterhalder M, Maiwald T, Brandt A, Schad A, Timmer Jens, Schulze-Bonhage Andreas. Do false predictions of seizures depend on the state of vigilance? A report from two seizure-prediction methods and proposed remedies. Epilepsia. 2006;47(12):2058–70.
Piotr Z, Marcin R, Jaroslaw Ż, Stefan H, Guido N, Piotr JD. Open database of epileptic eeg with mri and postoperational assessment of foci-a real world verification for the eeg inverse solutions. Neuroinformatics. 2010;8(4): 285–299.
Esha G, Muskan G, Rishita AS, Palak H, Nidhi G. Automatic seizure detection using rhythmicity spectrograms and inception-v3 architecture. 2023; 131–136. https://doi.org/10.1109/SPIN57001.2023.10117093.
Syed FH, Saeed MQ. Epileptic seizure classification using level-crossing eeg sampling and ensemble of sub-problems classifier. Expert Syst Appl. 2022;191:116356.
Hassan KM, Islam MR, Nguyen TT, Molla MKI. Epileptic seizure detection in eeg using mutual information-based best individual feature selection. Expert Syst Appl. 2022;116414.
Ilakiyaselvan N, Nayeemulla Khan A, Shahina A. Reconstructed phase space portraits for detecting brain diseases using deep learning. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022;71: 103278.
Khansa R, Junaid Q, Terence JO, Levin K, Adeel R. A generative model to synthesize eeg data for epileptic seizure prediction. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehab Eng. 2021;29:2322–2332.
Steele AG, Parekh S, Azgomi HF, Ahmadi MB, Craik A, Pati S, Francis JT, Contreras-Vidal JL, Faghih RT. A mixed filtering approach for real-time seizure state tracking using multi-channel electroencephalography data. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabilit Eng. 2021;29:2037–2045.
Romney A, Manian V. Optimizing seizure prediction from reduced scalp eeg channels based on spectral features and maml. IEEE Access. 2021;9:164348–57.
Deba PD, Maheshkumar HK, Kamlesh J. Surface eeg based epileptic seizure detection using wavelet based features and dynamic mode decomposition power along with knn classifier. Multimed Tools Appl. 2021;1–21.
Rajinikanth V, Kadry S, Taniar D, Kamalanand K, Elaziz MA, Palani TK. Detecting epilepsy in eeg signals using synchro-extracting-transform (set) supported classification technique. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput. 2022; 1–19.
Shahab A, Mohammed D, Sarmad KDA, Jonathan HG, Hanan A-H, Atheer YO, Haydar AM. Determinant of covariance matrix model coupled with adaboost classification algorithm for eeg seizure detection. Diagnostics. 2022;12(1):74.
Rishita AS, Esha G, Muskan G, Palak H, Nidhi G. Dataset of rhythmicity spectrogram based images of seizure and non-seizure EEG signals. 2022.
Xin Q, Hu S, Liu S, Zhao L, Wang S. Wtrpnet: an explainable graph feature convolutional neural network for epileptic eeg classification. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl (TOMM). 2021;17(3s): 1–18.
Wessam A-S, Yan L, Peng W, Firas Sabar M, Atheer YO, Hadi Ratham AG. Extracting epileptic features in eegs using a dual-tree complex wavelet transform coupled with a classification algorithm. Brain Res. 2022;147777.
Muhammad TS, Hesam A, Ateeq UR, Zuhaib N, Bilal M, Mahdieh G, Jingwei T, Nastaran H, Mohammed KAK. Exploiting feature selection and neural network techniques for identification of focal and nonfocal eeg signals in tqwt domain. J Healthc Eng. 2021.
Delal Şeker and Mehmet Siraç ÖZERDEM. A classification approach for focal/non-focal eeg detection using cepstral analysis. Dicle Üniversitesi Mühendislik Fakültesi Mühendislik Dergisi. 2021;12(4):603–13.
Handa P, Goel N. Epileptic seizure detection using rhythmicity spectrogram and cross-patient test set. pages 898–902. 2021b. https://doi.org/10.1109/SPIN52536.2021.9566078.
Ji Z, Qin S, Peng C. Study on separation for the frequency bands of eeg signal and frequency band relative intensity analysis based upon emd. In Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Signal Processing, Robotics and Automation, pages 151–155. Citeseer. 2008.
Jobst BC, Bartolomei F, Diehl B, Frauscher B, Kahane P, Minotti L, Sharan A, Tardy N, Worrell G, Gotman J. Intracranial eeg in the 21st century. Epilepsy Curr. 2020;20(4):180–188.
Thomas S, Ung-il C, Shinichi T, Mitsuteru N, Akiko Kishi S. A validation study of a consumer wearable sleep tracker compared to a portable eeg system in naturalistic conditions. J Psychosom Res. 2019;126:109822.
Birjandtalab J, Pouyan MB, Cogan D, Nourani M, Harvey J. Automated seizure detection using limited-channel eeg and non-linear dimension reduction. Comput Biol Med. 2017;82:49–58.
Sonya BD, Ekemini AUR, La Tese B, YooRi K, Erik L, Danielle S, Melissa S. Opportunities for epilepsy: Outcomes of the milken institute state of the science retreat. Epilepsy Behav. 2017;68: 174–176
Wusthoff CJ, Shellhaas RA, Clancy RR. Limitations of single-channel eeg on the forehead for neonatal seizure detection. J Perinatol. 2009;29(3):237–42.
Duun-Henriksen J, Baud M, Richardson MP, Cook M, Kouvas G, Heasman JM, Friedman D, Peltola J, Zibrandtsen IC, Kjaer TW. A new era in electroencephalographic monitoring? Subscalp devices for ultra–long-term recordings. Epilepsia. 2020;61(9): 1805–1817.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no personal, academic, or financial conflicts of interest associated with this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Handa, P., Mathur, M. & Goel, N. EEG Datasets in Machine Learning Applications of Epilepsy Diagnosis and Seizure Detection. SN COMPUT. SCI. 4, 437 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-01958-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-01958-z