Abstract
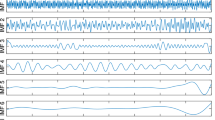
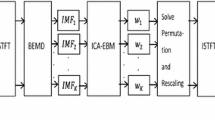
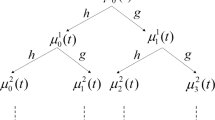
In this paper, the problem of single-channel blind source separation (SCBSS) is addressed using a novel approach that combines the adaptive mode separation-based wavelet transform (AMSWT) and the density-based clustering with sparse reconstruction. The proposed method is performed in the time–frequency domain and in a reverberant environment. First, using the Fourier transform, the amplitude spectrum of the observed mixture signal is obtained. Then, using variational scaling and wavelet functions, the AMSWT is used to adaptively extract spectral intrinsic components (SICs). To obtain a better time–frequency resolution, the AMSWT is applied to each mode. Thus, the SCBSS problem is transformed into a non-underdetermined. Then, for each frequency bin, the density-based clustering, reformulated to the eigenvector clustering problem, is performed to estimate the mixing matrix. Finally, sparse reconstruction is used to reconstruct the sources. The proposed method is evaluated using objective measures of separation quality. A computational complexity evaluation based on time consumption is also performed. Simulation results show that the proposed method is very effective for solving the SCBSS problem and provides better separation performances than the reference methods. However, the proposed method is computationally expensive.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
NOIZEUS database. http://ecs.utdallas.edu/loizou/speech/noizeus/
S. Al-Baddai, and al., Combining EMD with ICA to Analyze Combined EEG-fMRI Data. in Proceeding of the MIUA. UK. pp 223–228. (2014).
T. Barker, T. Virtanen, Blind separation of audio mixtures through nonnegative tensor factorization of modulation spectrograms. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 24(12), 2377–2389 (2016)
I. Bekkerman, J. Tabrikian, Target detection and localization using mimo radars and sonars. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(10), 3873–3883 (2006)
M. Bouchard, F. Albu, The Gauss-Seidel fast affine projection algorithm for multichannel active noise control and sound reproduction systems. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process 19, 107–123 (2005)
X. Chen, A. Liu, Removing muscle artifacts from EEG data: multichannel or single-channel techniques? IEEE Sens J 16(7), 1986–1997 (2016)
A. Cichocki, S. Amari, Adaptive Blind Signal and Image Processing (Wiley, New York, 2003)
I. Darazirar, M. Djendi, A two-sensor Gauss-Seidel fast affine projection algorithm for speech enhancement and acoustic noise reduction. Appl. Acoustics 96, 39–52 (2015)
I. Daubechies, Ten Lectures on Wavelets (SIAM, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992)
K. Dragomiretskiy, D. Zosso, Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(3), 531–544 (2014)
B.A. Draper et al., Recognizing faces with PCA and ICA. Comput Vis Image Underst 91, 115–137 (2003)
Z. Duan, Y. Zhang, C. Zhang, Z. Shi, Unsupervised single-channel music source separation by average harmonic structure modeling. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 16, 766–778 (2008)
A. Eronen, Musical instrument recognition using ICA-based transform of features and discriminatively trained HMMs. In proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Signal processing and Its Applications, Paris (2003).
C. Févotte, N. Bertin, J.-L. Durrieu, Nonnegative matrix factorization with the itakura-saito divergence: with application to music analysis. Neural Comput. 21(3), 793–830 (2009)
C. Févotte, R. Gribonval, E. Vincent, BSS EVAL toolbox user guide, IRISA (2005). http://www.irisa.fr/metiss/bss_eval
J. Gilles, Empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Sign. Process. 61(16), 3999–4010 (2013)
E.A.P. Habets, Room impulse response generator. Tech. Rep. 2(24), 1 (2006)
M.A. Haile, B. Dykas, Blind source separation for vibrationbased diagnostics of rotorcraft bearings. J. Vib. Control 22(18), 3807–3820 (2016)
M.R. Hestenes, Multiplier and gradient methods. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 4(5), 303–320 (1969)
N.E. Huang, et al., The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and nonstationary time series analysis. in Proceedings of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences 454(1971) pp 903–995 (1998)
X. Huang, L. Yang, R. Song, W. Lu, Effective pattern recognition and find-density-peaks clustering based blind identification for underdetermined speech mixing systems. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(17), 22115–22129 (2018)
M. Kemiha, A. Kacha, Complex blind source separation. Circ. Syst. Sign. Pr 36(11), 4670–4687 (2017)
A. Kumar, C.V. Rama Rao, A. Dutta, Performance analysis of blind source separation using canonical correlation. Circuits. Syst. Sign. Process. 37(2), 658–673 (2018)
F. Li et al., Seismic time–frequency analysis via adaptive mode separation-based wavelet transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 17(4), 696–700 (2020)
L. Li, C.K. Chui, Q. Jiang, Direct signal separation via extraction of local frequencies with adaptive time-varying parameters. IEEE Trans. Sign. Process. 70, 2321–2333 (2022)
Y. Litvin, I. Cohen, Single-channel source separation of audio signals using bark scale wavelet packet decomposition. J. Sign. Process. Syst. 65, 339–350 (2010)
W. Liu, S.Y. CaoChen, Applications of variational mode decomposition in seismic time-frequency analysis. Geophysics 81(5), V365–V378 (2016)
X. Liu, A. Srivastava, K. Gallivan optimal linear representations of images for object recognition. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (Madison, WI, USA pp 18–20, 2003)
C.F. Van Loan, Matrix computations (Johns Hopkins Studies in the Mathematical Sciences) (The Johns Hopkins Univ. Press, MD, USA, 1996)
S. Makino, T.W. Lee, H. Sawada, Blind speech separation (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, 2007)
B. Mijovic et al., Source separation from single-channel recordings by combining empirical-mode decomposition and independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57, 2188–2196 (2010)
A. Nagathil, C. Weihs, K. Neumann, R. Martin, Spectral complexity reduction of music signals based on frequency-domain reduced-rank approximations: an evaluation with cochlear implant listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Amer. 142(3), 1219–1228 (2017)
D. Nuzillard, A. Bijaoui, Blind source separation and analysis of multispectral astronomical images. Astron Astrophys Suppl Ser. 147(1), 129–138 (2000)
R.B. Randall, A history of cepstrum analysis and its application to mechanical problems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 97, 3–19 (2017)
A.K. Takahata et al., Unsupervised processing of geophysical signals: a review of some key aspects of blind deconvolution and blind source separation. IEEE Sign. Process. Mag. 29(4), 27–35 (2012)
N. Tengtrairat, W.L. Woo, S.S. Dlay, B. Gao, Online noisy single-channel source separation using adaptive spectrum amplitude estimator and masking. IEEE Trans. Sign. Process. 64(7), 1881–1895 (2016)
TIMIT database. https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/Ldc93s1.
J. Traa, P. Smaragdis, Multichannel source separation and tracking with RANSAC and directional statistics. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 22(12), 2233–2243 (2014)
B. Wang, M.D, Plumbley, investigating single-channel audio source separation methods based on non-negative matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the ICA Research Network InternationalWorkshop (Liverpool, UK, pp. 17–20 2006)
S. Wilson, J. Yoon, Bayesian ICA-based source separation of Cosmic Microwave Background by a discrete functional approximation. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1011.4018.
J. Yang, Y. Guo, Z. Yang, Under-Determined Convolutive Blind Source Separation Combining Density-Based Clustering and Sparse Reconstruction in Time-Frequency Domain. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.–i:Regular Papers 66(8), 3015–3027 (2019)
J.J. Yang, H.-L. Liu, Blind identification of the underdetermined mixing matrix based on K-weighted hyperline clustering. Neurocomputing 149, 483–489 (2015)
J. Yang, D.B. Williams, MIMO transmission subspace tracking with low rate feedback. In proceedings of the ICASSP, Philadelphia (2005)
X. Zeng et al., Fetal ECG extraction by combining single-channel SVD and cyclostationarity-based blind source separation. Int. J. Sig. Process. 6(4), 367–376 (2013)
Y. Zhang, S. Qi, L. Zhou, Single-channel blind source separation for wind turbine aeroacoustics signals based on variational mode decomposition. IEEE Access 6, 73952–73964 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kemiha, M., Kacha, A. Single-Channel Blind Source Separation using Adaptive Mode Separation-Based Wavelet Transform and Density-Based Clustering with Sparse Reconstruction. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 5338–5357 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02350-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02350-1