Abstract
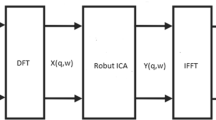
Blind source separation (BSS) techniques aim at recovering the original source signals from observed mixtures without a priori information. The bivariate empirical mode decomposition (BEMD) algorithm combined with complex independent component analysis by entropy bound minimization (ICA-EBM) technique is proposed as an alternative to separate convolutive mixtures of speech signals. The empirical mode decomposition (EMD) is a local self-adaptive decomposition method that allows analyzing data from non-stationary and/or nonlinear processes. Its principle is based on the sequential extraction of different amplitude and frequency modulation single-component contributions called intrinsic mode functions (IMFs). The BEMD is an extension of the EMD to complex-valued signals. First, the convolutive mixtures in the frequency domain are decomposed into a set of IMFs using the BEMD algorithm, and then, the complex ICA-EBM method is applied to extract the independent sources. The performance of the proposed approach is tested on real speech sounds chosen from available databases and compared to the results obtained via conventional frequency ICA and BEMD-ICA-based separation for convolutive mixtures. Simulation results show that the proposed method of BSS outperforms the BEMD-ICA separation technique for convolutive mixtures and conventional frequency ICA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Adali, D.-V. Calhoun, Complex ICA of brain imaging data. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 24(5), 136–139 (2007)
A. Adib, E. Moreau, D. Aboutajdine, Source separation contrasts using a reference signal. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(3), 312–315 (2004)
M.-U.B. Altaf, T. Gautama, T. Tanaka, D.-P. Mandic, Rotation invariant complex empirical mode decomposition, in Proceeding of ICASSP07 (2007), pp. 1009–1012
J. Anemüler, B. Kollmeier, Amplitude modulation decorrelation for convolutive blind source separation, in Proceeding of ICA (2000), pp. 215–220
J. Anemüller, T.J. Sejnowski, S. Makeig, Complex independent component analysis of frequency-domain electroencephalographic data. Neural Netw. 16(9), 1311–1323 (2003)
I. Bekkerman, J. Tabrikian, Target detection and localization using mimo radars and sonars. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(10), 3873–3883 (2006)
E. Bingham, A. Hyvärinen, A fast fixed-point algorithm for independent component analysis of complex valued signals. Int. J. Neural Syst. 10(1), 1–8 (2000)
A.-O. Boudraa, J.-C. Cexus, EMD-based signal filtering. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 56(6), 2196–2202 (2007)
J.-F. Cardoso, Higher-order contrasts for independent component analysis. Neural Comput. 11(1), 157–192 (1999)
M. Castella, J.-C. Pesquet, A.-P. Petropulu, A family of frequency and time domain contrasts for blind separation of convolutive mixtures of temporally dependent signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(1), 107–120 (2005)
J.C. Cexus, A.O. Boudraa, Non-stationary signals analysis by Teager–Huang Transform (THT), in Proceeding of EUSIPCO (2006)
R. Chai, G. Naik, T.-N. Nguyen, S. Ling, Y. Tran, A. Craig, H. Nguyen, Driver fatigue classification with independent component by entropy rate bound minimization analysis in an EEG-based system. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. (2016). doi:10.1109/JBHI.2016.2532354
H. Chunming, G. Huadong, W. Changlin, F. Dian, A novel method to reduce speckle in SAR images. Int J Remote Sens. 23(23), 5095–5101 (2002)
M.-A. Colominas, G. Schlotthauer, M.-E. Torres, Improve complete ensemble EMD: a suitable tool for biomedical signal processing. Biomed. Signal Process Control. 14, 19–29 (2014)
P. Comon, E. Moreau, Blind mimo equalization and joint diagonalization criteria, inProceeding of ICASSP (2001)
S. Cruces-Alvarez, A. Cichocki, L. Castedo-Ribas, An iterative inversion approach to blind source separation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 11(6), 1423–1437 (2000)
L. De Lathauwer, B. De Moor, On the blind separation of non-circular sources, in Proceeding of EUSIPCO (2002)
Y. Deville, Panorama des applications biomédicales des méthodes de séparation aveugle de sources, in Proceeding of GRETSI (2003), pp. 31–34
L.-E. Di Persia, D.-H. Milone, Using multiple frequency bins for stabilization of FD-ICA algorithms. Signal Process. 119(c), 162–168 (2016)
S.-C. Douglas, Fixed-point algorithms for the blind separation of arbitrary complex-valued non-Gaussian signal mixtures. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2007(1), 83–83 (2007)
L. Du, B. Wang, Y. Li, H. Liu, Robust classification scheme for airplane targets with low resolution radar based on EMD-CLEAN feature extraction method. IEEE Sens. J. 13(12), 4648–4662 (2013)
D. Farina, C. Févotte, C. Doncarli, R. Merletti, Blind separation of linear instantaneous mixtures of nonstationary surface myoelectric signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(9), 1555–1567 (2004)
C. Févotte, R. Gribonval, E. Vincent, BSS EVAL toolbox user guide, IRISA (2005), http://www.irisa.fr/metiss/bss_eval
P. Flandrin, G. Rilling, P. Gonçalves, Empirical mode decomposition as a filter bank. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(2), 112–114 (2004)
G.-S. Fu, R. Phlypo, M. Anderson, X.-L. Li, T. Adali, Blind source separation by entropy rate minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(16), 4245–4255 (2014)
J. Guo, Y. Deng, A time-frequency algorithm for noisy ICA, in Geo-Informatics in Resource Management and Sustainable Ecosystem. Communications in Computer and Information Science ed. by F. Bian, Y. Xie (2016), pp. 357–365
Y. Guo, S. Huang, Y. Li, G.-R. Naik, Edge effect elimination in single-mixture blind source separation. Circuits Syst Signal Process. 32(5), 2317–2334 (2013)
Y. Guo, G.-R. Naik, H. Nguyen, Single channel blind source separation based local mean decomposition for Biomedical applications, in Proceeding of 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc (2013) pp. 6812–6815
N.-E. Huang, Z. Shen, S.R. Long, M.C. Wu, H.H. Shih, Q. Zheng, N.C. Yen, C.C. Tung, H.H. Liu, The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and nonstationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454(1971), 903–995 (1998)
A. Hyvärinen, J. Karhunen, E. Oja, Independent Component Analysis (Wiley, New York, 2001)
E.-T. Jaynes, Information theory and statistical mechanics. Phys. Rev. 106(4), 620–630 (1957)
C. Jutten, M. Babaie-Zadeh, Source separation: principles, current advances and applications, in Proceeding of IAR Annual Meet (2006)
C. Jutten, P. Comon, Séparation de sources-Tome 2 : au-delà de l’aveugle et applications, Chap. 13, ed. by Y. Deville. Hermès–Lavoisier (2007)
A. Kachenoura, L. Albera, L. Senhadji, Blind source separation in biomedical engineering. IRBM 28(1), 20–34 (2007)
K. Kokkinakis, V. Zarzoso, A.-K. Nandi, Blind separation of acoustic mixtures based on linear prediction analysis, in Proceeding of the 4th ICA2003 (2003), pp. 343–348
A. Krause, M. Olson, The Basics of S-PLUS (Statistics and Computing), 4th edn. (Springer-Verlag, New York, 2005)
X. Li, T. Adali, Independent component analysis by entropy bound minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(10), 5151–5164 (2010)
X.-L. Li, T. Adalı, Complex independent component analysis by entropy bound minimization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 57(7), 1417–1430 (2010)
W. Li, H. Z. Yang, Blind source separation in underdetermined model based on local mean decomposition and AMUSE algorithm, in Proceeding of CCC (2014), pp. 7206–7211
B. Mijović, M. De Vos, I. Gligorijević, J. Taelman, S. Van Huffel, Source separation from single-channel recordings by combining empirical-mode decomposition and independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57(9), 2188–2196 (2010)
B. Mijovic, M. De Vos, I. Gligorijevic, S. Van Huffel, Combining EMD with ICA for extracting independent sources from single channel and two-channel data, in Proceeding of 32nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS (2010)
G.-R. Naik, A.-H. Al-Timemy, H.-T. Nguyen, Transradial amputee gesture classification using an optimal number of sEMG sensors: an approach using ICA clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 24(8), 837–846 (2016)
G.-R. Naik, K.-K. Dinesh, Estimation of independent and dependent components of non-invasive EMG using fast ICA: validation in recognising complex gestures. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 14(12), 1105–1111 (2011)
G.-R. Naik, K.-K. Dinesh, P. Marimuthu, Signal processing evaluation of myoelectric sensor placement in low-level gestures: sensitivity analysis using independent component analysis. Expert Syst. 31(1), 91–99 (2014)
G.-R. Naik, S.-E. Selvan, H.-T. Nguyen, Single-channel EMG classification with ensemble empirical mode decomposition based ICA for diagnosing neuromuscular disorders. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 24(7), 734–743 (2016)
NOIZEUS database, http://ecs.utdallas.edu/loizou/speech/noizeus/
M. Novey, T. Adali, Complex ICA by negentropy maximization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 19(4), 596–609 (2008)
D. Nuzillard, A. Bijaoui, Blind source separation and analysis of multispectral astronomical images. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 147(1), 129–138 (2000)
E. Ollila, V. Koivunen, Complex ICA using generalized uncorrelating transform. Signal Process. 89(4), 365–377 (2009)
L. Parra, C. Spence, Convolutive blind source separation of non-stationary sources. Proc. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 8(3), 320–327 (2000)
G. Pendharkar, G.-R. Naik, H.T. Nguyen, Using blind source separation on accelerometry data to analyze and distinguish the toe walking gait from normal gait in ITW children. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 13, 41–49 (2014)
D.-T. Pham, P. Garat, Blind separation of mixture of independent sources through aquasi-maximum likelihood approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(7), 1712–1725 (1997)
N. Rehman, D.-P. Mandic, Multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A. 466, 1291–1302 (2010)
G. Rilling, P. Flandrin, P. Gonçalves, J.M. Lilly, Bivariate empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 14(12), 936–939 (2007)
P. Smaragdis, Blind separation of convolved mixtures in the frequency domain. Neurocomputing 22(1–3), 21–34 (1998)
J.-S. Smith, The local mean decomposition and its application to EEG perception data. J. R. Soc. Interface 2(5), 443–454 (2005)
A.-K. Takahata, E.-Z. Nadalin, R. Ferrari, L.-T. Duarte, R. Suyama, R.-R. Lopes, J.M.-T. Romano, M. Tygel, Unsupervised processing of geophysical signals: a review of some key aspects of blind deconvolution and blind source separation. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 29(4), 27–35 (2012)
T. Tanaka, D.P. Mandic, Complex empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 14(2), 101–104 (2007)
TIMIT database, https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/ldc93s1
M.E. Torres, M.A. Colominas, G. Schlotthauer, P. Flandrin, A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise, in Proceeding of 36th ICASSP (2011)
J. Traa, P. Smaragdis, Multichannel source separation and tracking with RANSAC and directional statistics. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 22(12), 2233–2243 (2014)
Z. Wu, N.E. Huang, Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 1(1), 1–41 (2009)
H.-C. Wu, J.-C. Principe, Simultaneous diagonalization in the frequency domain (SDIF) for source separation, in Proceeding of ICA (1999), pp. 245–250
P. Xie, SL. Grant, A fast and efficient frequency-domain method for convolutive blind source separation, Proceeding of Region 5 Conference, IEEE (2008)
M.-H. Yeh, The complex bidimensional empirical mode decomposition. Signal Process. 92(2), 523–541 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kemiha, M., Kacha, A. Complex Blind Source Separation. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 4670–4687 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0539-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0539-0