Abstract
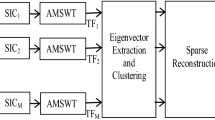
According to the theory of single channel blind source separation (SCBSS), the algorithm based on virtual channel expansion must be established in a known source number, and most algorithms can only separate two source signals. When separating multiple source signals, the performance will deteriorate sharply. Since the existing methods of this kind use only a single algorithm for virtual channel expansion, they cannot retain all the source signals’ valuable information and effectively separate the multiple source signals. From the perspective of making the constructed virtual multi-channel signal contain enough information of the source signals as much as possible, this paper proposes a SCBSS algorithm based on improved wavelet packet and variational mode decomposition (IWP-VMD-SCBSS). Firstly, the source number is estimated according to the interval sampling method and the minimum description length (MDL) criterion. Secondly, the signal reconstruction method based on improved wavelet packet decomposition (IWPD) is used to reconstruct multiple purer virtual signals. Then the virtual signals are combined with the first intrinsic mode function (IMF) of two-level variational mode decomposition (VMD) and the original single-channel observed signal to constitute a virtual multi-channel signal. Finally, the joint approximate diagonalization of eigen-matrices (JADE) algorithm is used to process the virtual multi-channel observed signal to achieve BSS and obtain estimated source signals. The simulation results indicate that the IWP-VMD-SCBSS algorithm can achieve a lower symbol error rate (SER) than existing algorithms and lower computational complexity. It can solve the SCBSS problem of multiple communication signals effectively under an unknown source number.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated or analyzed and material during this current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The codes during this current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Wei, L. L., Liu, Y. S., & Cheng, D. F. (2018). A novel partial discharge ultra-high frequency signal de-noising method based on a single channel blind source separation algorithm. Electronics Newsweekly, 11(3), 509–516.
Pang, L. H., & Deng, X. R. (2016). A SCBSS methodology for time-frequency overlapped signals using non-negative matrix factorization. International Journal of Electronics, 104(4), 624–634.
Wu, C. L., Liu, Z., Wang, X., Jiang, W. L., & Ru, X. H. (2016). Single-channel blind source separation of co-frequency overlapped GMSK signals under constant-modulus constraints. IEEE Communications Letters, 20(3), 486–489.
Zhao, M. C., Yao, X. J., Wang, J., & Dong, S. H. (2021). Single-channel blind source separation of spatial aliasing signal based on Stacked-TCN. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 43(9), 2628–2636.
Al-Tmeme, A., Woo, W. L., Dlay, S. S., & Gao, B. (2018). Single channel informed signal separation using artificial-stereophonic mixtures and exemplar-guided matrix factor deconvolution. International Journal Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 32(9), 1259–1281.
Sun, L. H., Xie, K. L., Gu, T., Chen, J., & Yang, Z. (2019). Joint dictionary learning using a new optimization method for single-channel blind source separation. Speech Communication, 106, 85–94.
Tengtrairat, N., & Woo, W. L. (2015). Single-channel separation using underdetermined blind autoregressive model and least absolute deviation. Neurocomputing, 147(1), 412–425.
He, P. J., She, T. T., Li, W. H., & Yuan, W. B. (2018). Single channel blind source separation on the instantaneous mixed signal of multiple dynamic sources. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 113, 22–35.
Lian, J. J., Wang, X. Q., Ma, B., & Liu, D. M. (2018). Improvement to the sources selection to identify the low frequency noise induced by flood discharge. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 110, 139–151.
Oliveira, D. R. D., Lima, M. A. A., Silva, L. R. M., Ferreira, D. D., & Duque, C. A. (2021). Second order blind identification algorithm with exact model order estimation for harmonic and interharmonic decomposition with reduced complexity. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 125, 106415.
Jiang, X., Geng, D. Y., & Zhang, Y. Y. (2019). BCG signal de-noising method research based on EMD-ICA. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 38(2), 139–148.
Xie, Y., Xie, K., & Xie, S. (2019). Underdetermined blind source separation for heart sound using higher-order statistics and sparse representation. IEEE Access, 7, 87606–87616.
Gao, B., Woo, W. L., & Dlay, S. S. (2011). Single-channel source separation using EMD-subband variable regularized sparse features. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(4), 961–976.
Pang, L. H., & Tang, B. (2017). Wavelet-FastICA-based separation method for single-channel and time-frequency overlapped signal in electromagnetic surveillance. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology., 11(2), 187–201.
Prasanna Kumar, M. K., & Kumaraswamy, R. (2017). Single-channel speech separation using combined EMD and speech-specific information. International Journal of Speech Technology., 20(4), 1037–1047.
Zhang, Y. N., Qi, S. B., & Zhou, L. (2018). Single channel blind source separation for wind turbine aeroacoustics signals based on variational mode decomposition. IEEE Access, 6(1), 73952–73964.
Dong, S. J., Tang, B. P., & Zhang, Y. (2012). A repeated single channel mechanical signal blind separation method based on morphological filtering and singular value decomposition. Measurement, 45(8), 2052–2063.
Liu, X., Guan, Y. L., Koh, S. N., Liu, Z., & Wang, P. (2018). Low-complexity single-channel blind separation of co-frequency coded signals. IEEE Communications Letters, 22(5), 990–993.
Yang, Y., Zhang, D. L., & Peng, H. (2018). Single-channel blind source separation for paired carrier multiple access signals. IET Signal Processing, 12(1), 37–41.
Zhu, H., Zhang, S., & Zhao, H. (2016). Single-channel source separation of multi-component radar signal with the same generalized period using ICA. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 35(1), 353–363.
Fu, W. H., Yang, X. N., & Liu, N. A. (2008). Robust algorithm for communication signal blind separation fourth-order-cumulant-based. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 30(8), 1853–1856.
Al-Tmeme, A., Woo, W. L., Dlay, S. S., & Gao, B. (2017). Underdetermined convolutive source separation using GEM-MU with variational approximated optimum model order NMF2D. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing., 25(1), 31–45.
He, P. J., Qi, M., Liu, G. Y., Yu, Z. J., & Fu, Q. (2019). An adaptive single channel EMD-TNMF blind source separation algorithm for both instantaneous and convolutive mixed signal. Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering., 658(1), 012003.
Parathai, P., Tengtrairat, N., & Woo, W. L. (2019). Single-channel signal separation using spectral basis correlation with sparse nonnegative tensor factorization. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 38, 5786–5816.
He, J., Chen, W., & Song, Y. X. (2020). Single channel blind source separation under deep recurrent neural network. Wireless Personal Communications, 115(2), 1277–1289.
Zhou, H. J., Jiao, L. C., Zheng, S. J., Yang, L. F., Shen, W. G., & Yang, X. N. (2020). Generative adversarial network-based electromagnetic signal classification: A semi-supervised learning framework. China Communications, 17(10), 157–169.
Yue, G., Li, X., Chen, S. Y., & Li, X. L. (2021). An automatic ocular artifacts removal approach for multi-channel EEG data based on NMF and EMD. Journal of Neural Engineering, 18(5), 6012–6017.
Liu, X. L., Wang, H., & Huang, Y. M. (2021). A SCBSS signal de-noising method of integrating EEMD and ESMD for dynamic deflection of bridges using GBSAR. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 14, 2845–2856.
Shang, H. K., Lo, K. L., & Li, F. (2017). Partial discharge feature extraction based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and sample entropy. Entropy, 19(9), 439–456.
Song, H. L., Dong, H. B., Yuan, Z. W., Zhu, J., Zhang, H. Y., & Huang, Y. J. (2019). An EEMD-based electromagnetic induction method for nondestructive testing of buried metal conductors. IEEE Access, 7(1), 142261–142271.
Zhao, L. H., Hong, G., Wang, Z. L., Chen, W. W., & Long, W. (2021). Research on fault vibration signal features of GIS disconnector based on EEMD and kurtosis criterion. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 16(5), 677–686.
Dragomiretskiy, K., & Zosso, D. (2014). Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 62(3), 531–544.
Bhattacharjee, A., Fattah, S. A., Zhu, W. P., & Ahmad, M. O. (2018). VMD-RiM: Rician modeling of temporal feature variation extracted from variational mode decomposed EEGs signal for automatic sleep apnea detection. IEEE Access, 6(1), 77440–77453.
Ma, Z. Q., Li, Y. C., Liu, Z., & Guang, C. J. (2016). Rolling bearings’ fault feature extraction based on variational mode decomposition and Teager energy operator. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 35(13), 134–139.
Wang, R., Xu, L., & Liu, F. K. (2020). Bearing fault diagnosis based on improved VMD and DCNN. Journal of Vibro-Engineering, 22(5), 1055–1068.
Zhao, Z. J., & Huang, Y. B. (2017). Single-channel blind-source separation algorithm based on wavelet packet decomposition. Communications Technology, 50(3), 425–429.
Wu, Y., Li, X. K., & Cao, Z. M. (2020). Source number estimation based on a novel multi-view meta-hierarchical classification framework. Measurement Science and Technology., 31(6), 14–29.
Dong, Z., Hu, J. P., Du, B. L., & He, Y. Z. (2017). Improvement of source number estimation method for single channel signal. PLoS ONE, 11(10), e0164654.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the anonymous reviewers who read the drafts and provided many helpful suggestions.
Funding
This work is sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (19ZR1454000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wensheng Zhao and Weihong Fu wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Fu, W. A single-channel blind source separation algorithm based on improved wavelet packet and variational mode decomposition. Telecommun Syst (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-024-01115-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-024-01115-8