Abstract
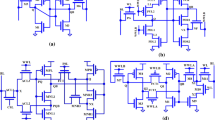
As the VLSI technology is heading toward deep subnanometer range, the NBTI effect has emerged as a major reliability issue for the state-of-the-art CMOS as well as FinFET-based circuits. NBTI causes an incremental deviation in the threshold voltage of PMOS and hence causes variation in timing of digital circuits. Further, NBTI may increase the delay of circuits which are lying in the critical path of a system. This timing mismatch is a serious concern for synchronous clock-based circuits such as dynamic logic gates employed in a register file which itself lies in the critical path of a microprocessor. This is a critical reliability issue for microprocessors and microcontrollers which are used in electronic systems with high lifetime such as sensors. This paper has introduced a reliable FinFET-based low-power 32-word \(\times \) 32-bit register file which is designed using 32-nm BSIM-IMG technology. In this paper, the impact of NBTI on the different modules of FinFET-based register file has been studied. This analysis reveals that the domino OR gate bit-line is responsible for much of the NBTI degradation in a register file. Hence, a novel aging-aware domino bit-line has been proposed here which is capable of maintaining a constant performance under NBTI degradation. This proposed domino bit-line is further used to design a novel register file which is capable of maintaining a constant performance for a lifetime of more than 10 years.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.N. Bhoj, N.K. Jha, Design of logic gates and flip-flops in high-performance FinFET technology. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 21(11), 1975–1988 (2013)
A. Cortex, A72 processor user manual (2016)
R. Fernandez, R. Rodrguez, M. Nafra, X. Aymerich, B. Kaczer, G. Groeseneken, FinFET and MOSFET preliminary comparison of gate oxide reliability. Microelectron. Reliab. 46(9), 1608–1611 (2006)
N. Gong et al., Tm-rf: Aging-aware power-efficient register file design for modern microprocessors. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 23(7), 1196–1209 (2015)
S. Khandelwal, Y.S. Chauhan, D.D. Lu, S. Venugopalan, M.A.U. Karim, A.B. Sachid, B.Y. Nguyen, O. Rozeau, O. Faynot, A.M. Niknejad et al., BSIM-IMG: A compact model for ultrathin-body SOI MOSFETs with back-gate control. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59(8), 2019–2026 (2012)
S. Khan, I. Agbo, S. Hamdioui, H. Kukner, B. Kaczer, P. Raghavan, and F. Catthoor, Bias temperature instability analysis of FinFET based SRAM cells, in Proceedings of the Conference on Design, Automation & Test in Europe (European Design and Automation Association, 2014), p. 31
M.H. Kaffashian, R. Lotfi, K. Mafinezhad, H. Mahmoodi, Impact of NBTI on performance of domino logic circuits in nano-scale CMOS. Microelectron. J. 42(12), 1327–1334 (2011)
Z. Lu, J.G. Fossum, Short-channel effects in independent-gate FinFETs. Electron Device Lett. IEEE 28(2), 145–147 (2007)
V. Mahor, M. Pattanaik, A state-of-the-art current mirror-based reliable wide fan-in FinFET domino OR gate design. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. (2017). doi:10.1007/s00034-017-0571-0
M. Makabe, T. Kubota, T. Kitano, Bias-temperature degradation of pMOSFETs: Mechanism and suppression, in Reliability Physics Symposium, Proceedings. 38th Annual 2000 IEEE International (IEEE, 2000), pp. 205–209
C. Ma et al., A unified FinFET reliability model including high K gate stack dynamic threshold voltage, hot carrier injection, and negative bias temperature instability, in IEEE International Symposium on Quality of Electronic Design (ISQED) (2009), pp. 7–12
H. Mostafa, M. Anis, M. Elmasry, NBTI and process variations compensation circuits using adaptive body bias. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 25(3), 460–467 (2012)
M. Masahara et al., Demonstration, analysis, and device design considerations for independent DG MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 52(9), 2046–2053 (2005)
F. Oboril, M.B. Tahoori, Exploiting instruction set encoding for aging-aware microprocessor design. ACM Trans. Design Autom. Electron. Syst. (TODAES) 21(1), 5 (2015)
D. Rossi et al., Reliable power gating with NBTI aging benefits. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 24(8), 2735–2744 (2016)
B.S. Reniwal, V. Vijayvargiya, S.K. Vishvakarma, D. Dwivedi, Ultra-fast current mode sense amplifier for small iCELL SRAM in FinFET with improved offset tolerance. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(9), 3066–3085 (2016)
S.S. Rathod, A.K. Saxena, S. Dasgupta, Analysis of double-gate FinFET-based address decoder for radiation-induced single-event-transients. Circuits Devices Syst. IET 6(4), 218–226 (2012)
M. Rostami, K. Mohanram, Dual-independent-gate FinFETs for low power logic circuits. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Design Integr. Circuits Syst. 30(3), 337–349 (2011)
T. Sakurai, A. Richard, Newton. Alpha-power law MOSFET model and its applications to CMOS inverter delay and other formulas. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 25(2), 584–594 (1990)
Synopsys, Hspice users manual: Simulation and analysis (2016)
B. Tudor et. al., MOSRA: An efficient and versatile mos aging modeling and reliability analysis solution for 45nm and below, in 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT) (IEEE, 2010)
T. Yang et al. 14.7 In-situ techniques for In-Field sensing of NBTI degradation in an SRAM register file, in 2015 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC) (IEEE, 2015)
Y. Zhang, S. Chen, L. Peng, S. Chen, Mitigating nbti degradation on FinFET GPUs through exploiting device heterogeneity, in IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI) (IEEE, 2014), pp. 577–582
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the help and support received from the ABV-IIITM research project “SMDP-C2SD,” Deity, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahor, V., Pattanaik, M. An Aging-Aware Reliable FinFET-Based Low-Power 32-Word \(\times \) 32-bit Register File. Circuits Syst Signal Process 36, 4789–4808 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0638-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0638-y