Abstract
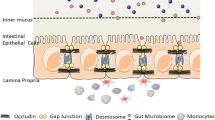
The gastrointestinal epithelium forms the boundary between the body and external environment. It effectively provides a selective permeable barrier that limits the permeation of luminal noxious molecules, such as pathogens, toxins, and antigens, while allowing the appropriate absorption of nutrients and water. This selective permeable barrier is achieved by intercellular tight junction (TJ) structures, which regulate paracellular permeability. Disruption of the intestinal TJ barrier, followed by permeation of luminal noxious molecules, induces a perturbation of the mucosal immune system and inflammation, and can act as a trigger for the development of intestinal and systemic diseases. In this context, much effort has been taken to understand the roles of extracellular factors, including cytokines, pathogens, and food factors, for the regulation of the intestinal TJ barrier. Here, I discuss the regulation of the intestinal TJ barrier together with its implications for the pathogenesis of diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AJ:
-
Adherens junction
- ALD:
-
Alcoholic liver disease
- AMPK:
-
AMP activated protein kinase
- BBDP:
-
Biobreeding diabetes-prone
- BiCM:
-
Conditioned medium of Bifidobacterium infantis
- BT-IgSF:
-
Brain- and testis-specific immunoglobulin superfamily
- C10:
-
Capric acid
- C12:
-
Lauric acid
- CAR:
-
Coxsacki and adenovirus receptor
- CD:
-
Crohn’s disease
- CHO:
-
Chinese hamster ovary
- CPE:
-
Clostridium perfringen enterotoxin
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- DSS:
-
Dextran sodium sulfate
- ECN:
-
Escherichia coli Nissle1917
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EHEC:
-
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- EPEC:
-
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- ESAM:
-
Endothelial selective adhesion molecule
- EspF:
-
Escherichia coli secreted protein F
- GPCR:
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- HA/P:
-
Hemagglutinin/protease
- HS/R:
-
Hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- IBS:
-
Irritative bowel syndrome
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- Ig:
-
Immunoglobulin
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- JAM:
-
Junctional adhesion molecule
- LA:
-
Linolec acid
- LCFA:
-
Long chain fatty acid
- LIGHT:
-
Lymphotoxin-like inducible protein
- L. plantarum :
-
Lactobacillus plantarum
- L. rhamnosus :
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus
- MAGUK:
-
Membrane-associated guanylate kinase homolog
- MAP:
-
Mitochondrial-associated protein
- MCFA:
-
Medium chain fatty acid
- MEK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MLC:
-
Myosin light chain
- MLCK:
-
Myosin light chain kinase
- NFκB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- PAR:
-
Proteinase activated receptor
- PDZ:
-
Post-synaptic density 95/Drosophila discs large/zona-occludens 1
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase
- PK:
-
Protein kinase
- PKA:
-
cAMP-dependent kinase
- PP:
-
Protein phosphatase
- PPAR:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- PTP:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase
- ROCK:
-
Rho-associated kinase
- SCFA:
-
Short chain fatty acid
- SH:
-
Src homology
- T1D:
-
Type I diabetes
- TER:
-
Transepithelial electrical resistance
- TGF:
-
Transforming growth factor
- TJ:
-
Tight junction
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- TNFR:
-
TNF-α receptor
- TPN:
-
Total parenteral nutrition
- VDR:
-
Vitamin D receptor
- ZO:
-
Zonula occludens
- ZOT:
-
Zonula occludens toxin
References
Ferraris RP, Diamond J (1997) Regulation of intestinal sugar transport. Physiol Rev 77:257–302
Broer S (2008) Amino acid transport across mammalian intestinal and renal epithelia. Physiol Rev 88:249–286
Kiela PR, Ghishan FK (2009) Ion transport in the intestine. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 25:87–91
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M (2001) Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:285–293
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2006) Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol 68:403–429
Oda H, Takeichi M (2011) Evolution: structural and functional diversity of cadherin at the adherens junction. J Cell Biol 193:1137–1146
Baum B, Georgiou M (2011) Dynamics of adherens junctions in epithelial establishment, maintenance, and remodeling. J Cell Biol 192:907–917
Turner JR (2009) Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9:799–809
Nusrat A, Turner JR, Madara JL (2000) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions. IV. Regulation of tight junctions by extracellular stimuli: nutrients, cytokines, and immune cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279:G851–G857
Clayburgh DR, Shen L, Turner JR (2004) A porous defense: the leaky epithelial barrier in intestinal disease. Lab Invest 84:282–291
Farhadi A, Banan A, Fields J, Keshavarzian A (2003) Intestinal barrier: an interface between health and disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:479–497
Capaldo CT, Nusrat A (2009) Cytokine regulation of tight junctions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:864–871
Amasheh M, Andres S, Amasheh S, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2009) Barrier effects of nutritional factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:267–273
Mullin JM, Skrovanek SM, Valenzano MC (2009) Modification of tight junction structure and permeability by nutritional means. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:99–112
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123:1777–1788
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol 141:1539–1550
Martin-Padura I, Lostaglio S, Schneemann M, Williams L, Romano M, Fruscella P, Panzeri C, Stoppacciaro A, Ruco L, Villa A, Simmons D, Dejana E (1998) Junctional adhesion molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that distributes at intercellular junctions and modulates monocyte transmigration. J Cell Biol 142:117–127
Ikenouchi J, Furuse M, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Tsukita S (2005) Tricellulin constitutes a novel barrier at tricellular contacts of epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 171:939–945
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE (2003) Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 81:1–44
Madara JL, Moore R, Carlson S (1987) Alteration of intestinal tight junction structure and permeability by cytoskeletal contraction. Am J Physiol 253:C854–C861
Turner JR, Rill BK, Carlson SL, Carnes D, Kerner R, Mrsny RJ, Madara JL (1997) Physiological regulation of epithelial tight junctions is associated with myosin light-chain phosphorylation. Am J Physiol 273:C1378–C1385
Walsh SV, Hopkins AM, Chen J, Narumiya S, Parkos CA, Nusrat A (2001) Rho kinase regulates tight junction function and is necessary for tight junction assembly in polarized intestinal epithelia. Gastroenterology 121:566–579
Al-Sadi R, Khatib K, Guo S, Ye D, Youssef M, Ma T (2011) Occludin regulates macromolecule flux across the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300:G1054–G1064
Furuse M, Itoh M, Hirase T, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S (1994) Direct association of occludin with ZO-1 and its possible involvement in the localization of occludin at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 127:1617–1626
Wong V, Gumbiner BM (1997) A synthetic peptide corresponding to the extracellular domain of occludin perturbs the tight junction permeability barrier. J Cell Biol 136:399–409
Saitou M, Fujimoto K, Doi Y, Itoh M, Fujimoto T, Furuse M, Takano H, Noda T, Tsukita S (1998) Occludin-deficient embryonic stem cells can differentiate into polarized epithelial cells bearing tight junctions. J Cell Biol 141:397–408
Schulzke JD, Gitter AH, Mankertz J, Spiegel S, Seidler U, Amasheh S, Saitou M, Tsukita S, Fromm M (2005) Epithelial transport and barrier function in occludin-deficient mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1669:34–42
Saitou M, Furuse M, Sasaki H, Schulzke JD, Fromm M, Takano H, Noda T, Tsukita S (2000) Complex phenotype of mice lacking occludin, a component of tight junction strands. Mol Biol Cell 11:4131–4142
Sakakibara A, Furuse M, Saitou M, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Tsukita S (1997) Possible involvement of phosphorylation of occludin in tight junction formation. J Cell Biol 137:1393–1401
Rao R (2009) Occludin phosphorylation in regulation of epithelial tight junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:62–68
Jain S, Suzuki T, Seth A, Samak G, Rao R (2011) Protein kinase Czeta phosphorylates occludin and promotes assembly of epithelial tight junctions. Biochem J 437:289–299
Suzuki T, Elias BC, Seth A, Shen L, Turner JR, Giorgianni F, Desiderio D, Guntaka R, Rao R (2009) PKC eta regulates occludin phosphorylation and epithelial tight junction integrity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:61–66
Dorfel MJ, Westphal JK, Huber O (2009) Differential phosphorylation of occludin and tricellulin by CK2 and CK1. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:69–73
McKenzie JA, Riento K, Ridley AJ (2006) Casein kinase I epsilon associates with and phosphorylates the tight junction protein occludin. FEBS Lett 580:2388–2394
Smales C, Ellis M, Baumber R, Hussain N, Desmond H, Staddon JM (2003) Occludin phosphorylation: identification of an occludin kinase in brain and cell extracts as CK2. FEBS Lett 545:161–166
Wong V (1997) Phosphorylation of occludin correlates with occludin localization and function at the tight junction. Am J Physiol 273:C1859–C1867
Seth A, Sheth P, Elias BC, Rao R (2007) Protein phosphatases 2A and 1 interact with occludin and negatively regulate the assembly of tight junctions in the CACO-2 cell monolayer. J Biol Chem 282:11487–11498
Nunbhakdi-Craig V, Machleidt T, Ogris E, Bellotto D, White CL 3rd, Sontag E (2002) Protein phosphatase 2A associates with and regulates atypical PKC and the epithelial tight junction complex. J Cell Biol 158:967–978
Elias BC, Suzuki T, Seth A, Giorgianni F, Kale G, Shen L, Turner JR, Naren A, Desiderio DM, Rao R (2008) Phosphorylation of Y398 and Y402 in occludin prevents its interaction with ZO-1 and destabilizes its assembly at the tight junctions. J Biol Chem 284:1559–1569
Rao RK, Basuroy S, Rao VU, Karnaky KJ Jr, Gupta A (2002) Tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation of occludin-ZO-1 and E-cadherin-beta-catenin complexes from the cytoskeleton by oxidative stress. Biochem J 368:471–481
Kale G, Naren AP, Sheth P, Rao RK (2003) Tyrosine phosphorylation of occludin attenuates its interactions with ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:324–329
Suzuki T, Seth A, Rao R (2008) Role of phospholipase Cgamma-induced activation of protein kinase Cepsilon (PKCepsilon) and PKCbetaI in epidermal growth factor-mediated protection of tight junctions from acetaldehyde in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Biol Chem 283:3574–3583
Atkinson KJ, Rao RK (2001) Role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in acetaldehyde-induced disruption of epithelial tight junctions. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 280:G1280–G1288
Tsukita S, Furuse M (2000) Pores in the wall: claudins constitute tight junction strands containing aqueous pores. J Cell Biol 149:13–16
Furuse M, Hata M, Furuse K, Yoshida Y, Haratake A, Sugitani Y, Noda T, Kubo A, Tsukita S (2002) Claudin-based tight junctions are crucial for the mammalian epidermal barrier: a lesson from claudin-1-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 156:1099–1111
Tamura A, Hayashi H, Imasato M, Yamazaki Y, Hagiwara A, Wada M, Noda T, Watanabe M, Suzuki Y, Tsukita S (2011) Loss of claudin-15, but not claudin-2, causes Na+ deficiency and glucose malabsorption in mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology 140:913–923
Miyamoto T, Morita K, Takemoto D, Takeuchi K, Kitano Y, Miyakawa T, Nakayama K, Okamura Y, Sasaki H, Miyachi Y, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2005) Tight junctions in Schwann cells of peripheral myelinated axons: a lesson from claudin-19-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 169:527–538
Weber S, Hoffmann K, Jeck N, Saar K, Boeswald M, Kuwertz-Broeking E, Meij II, Knoers NV, Cochat P, Sulakova T, Bonzel KE, Soergel M, Manz F, Schaerer K, Seyberth HW, Reis A, Konrad M (2000) Familial hypomagnesaemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis maps to chromosome 3q27 and is associated with mutations in the PCLN-1 gene. Eur J Hum Genet 8:414–422
Gow A, Southwood CM, Li JS, Pariali M, Riordan GP, Brodie SE, Danias J, Bronstein JM, Kachar B, Lazzarini RA (1999) CNS myelin and sertoli cell tight junction strands are absent in Osp/claudin-11 null mice. Cell 99:649–659
Morita K, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999) Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 147:185–194
Holmes JL, Van Itallie CM, Rasmussen JE, Anderson JM (2006) Claudin profiling in the mouse during postnatal intestinal development and along the gastrointestinal tract reveals complex expression patterns. In. Gene expr patterns 6:581–588
Inai T, Kobayashi J, Shibata Y (1999) Claudin-1 contributes to the epithelial barrier function in MDCK cells. Eur J Cell Biol 78:849–855
Amasheh S, Meiri N, Gitter AH, Schoneberg T, Mankertz J, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (2002) Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 115:4969–4976
Colegio OR, Van Itallie CM, McCrea HJ, Rahner C, Anderson JM (2002) Claudins create charge-selective channels in the paracellular pathway between epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C142–C147
Hou J, Gomes AS, Paul DL, Goodenough DA (2006) Study of claudin function by RNA interference. J Biol Chem 281:36117–36123
Milatz S, Krug SM, Rosenthal R, Gunzel D, Muller D, Schulzke JD, Amasheh S, Fromm M (2010) Claudin-3 acts as a sealing component of the tight junction for ions of either charge and uncharged solutes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1798:2048–2057
Yu AS, Enck AH, Lencer WI, Schneeberger EE (2003) Claudin-8 expression in Madin–Darby canine kidney cells augments the paracellular barrier to cation permeation. J Biol Chem 278:17350–17359
Alexandre MD, Jeansonne BG, Renegar RH, Tatum R, Chen YH (2007) The first extracellular domain of claudin-7 affects paracellular Cl- permeability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:87–91
Amasheh S, Schmidt T, Mahn M, Florian P, Mankertz J, Tavalali S, Gitter AH, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (2005) Contribution of claudin-5 to barrier properties in tight junctions of epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 321:89–96
Van Itallie C, Rahner C, Anderson JM (2001) Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J Clin Invest 107:1319–1327
Krause G, Winkler L, Piehl C, Blasig I, Piontek J, Muller SL (2009) Structure and function of extracellular claudin domains. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:34–43
Fujita H, Chiba H, Yokozaki H, Sakai N, Sugimoto K, Wada T, Kojima T, Yamashita T, Sawada N (2006) Differential expression and subcellular localization of claudin-7, -8, -12, -13, and -15 along the mouse intestine. J Histochem Cytochem 54:933–944
Fujibe M, Chiba H, Kojima T, Soma T, Wada T, Yamashita T, Sawada N (2004) Thr203 of claudin-1, a putative phosphorylation site for MAP kinase, is required to promote the barrier function of tight junctions. Exp Cell Res 295:36–47
Soma T, Chiba H, Kato-Mori Y, Wada T, Yamashita T, Kojima T, Sawada N (2004) Thr(207) of claudin-5 is involved in size-selective loosening of the endothelial barrier by cyclic AMP. Exp Cell Res 300:202–212
D’Souza T, Agarwal R, Morin PJ (2005) Phosphorylation of claudin-3 at threonine 192 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates tight junction barrier function in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem 280:26233–26240
Tanaka M, Kamata R, Sakai R (2005) EphA2 phosphorylates the cytoplasmic tail of claudin-4 and mediates paracellular permeability. J Biol Chem 280:42375–42382
Van Itallie CM, Gambling TM, Carson JL, Anderson JM (2005) Palmitoylation of claudins is required for efficient tight-junction localization. J Cell Sci 118:1427–1436
Cunningham SA, Arrate MP, Rodriguez JM, Bjercke RJ, Vanderslice P, Morris AP, Brock TA (2000) A novel protein with homology to the junctional adhesion molecule. Characterization of leukocyte interactions. J Biol Chem 275:34750–34756
Arrate MP, Rodriguez JM, Tran TM, Brock TA, Cunningham SA (2001) Cloning of human junctional adhesion molecule 3 (JAM3) and its identification as the JAM2 counter-receptor. J Biol Chem 276:45826–45832
Hirabayashi S, Tajima M, Yao I, Nishimura W, Mori H, Hata Y (2003) JAM4, a junctional cell adhesion molecule interacting with a tight junction protein, MAGI-1. Mol Cell Biol 23:4267–4282
Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G, Kurt-Jones EA, Krithivas A, Hong JS, Horwitz MS, Crowell RL, Finberg RW (1997) Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science 275:1320–1323
Hirata K, Ishida T, Penta K, Rezaee M, Yang E, Wohlgemuth J, Quertermous T (2001) Cloning of an immunoglobulin family adhesion molecule selectively expressed by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 276:16223–16231
Suzu S, Hayashi Y, Harumi T, Nomaguchi K, Yamada M, Hayasawa H, Motoyoshi K (2002) Molecular cloning of a novel immunoglobulin superfamily gene preferentially expressed by brain and testis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296:1215–1221
Bazzoni G (2003) The JAM family of junctional adhesion molecules. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:525–530
Liu Y, Nusrat A, Schnell FJ, Reaves TA, Walsh S, Pochet M, Parkos CA (2000) Human junction adhesion molecule regulates tight junction resealing in epithelia. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 13):2363–2374
Laukoetter MG, Nava P, Lee WY, Severson EA, Capaldo CT, Babbin BA, Williams IR, Koval M, Peatman E, Campbell JA, Dermody TS, Nusrat A, Parkos CA (2007) JAM-A regulates permeability and inflammation in the intestine in vivo. J Exp Med 204:3067–3076
Cohen CJ, Shieh JT, Pickles RJ, Okegawa T, Hsieh JT, Bergelson JM (2001) The coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor is a transmembrane component of the tight junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:15191–15196
Westphal JK, Dorfel MJ, Krug SM, Cording JD, Piontek J, Blasig IE, Tauber R, Fromm M, Huber O (2010) Tricellulin forms homomeric and heteromeric tight junctional complexes. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:2057–2068
Krug SM, Amasheh S, Richter JF, Milatz S, Gunzel D, Westphal JK, Huber O, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (2009) Tricellulin forms a barrier to macromolecules in tricellular tight junctions without affecting ion permeability. Mol Biol Cell 20:3713–3724
Ikenouchi J, Sasaki H, Tsukita S, Furuse M (2008) Loss of occludin affects tricellular localization of tricellulin. Mol Biol Cell 19:4687–4693
Gumbiner B, Lowenkopf T, Apatira D (1991) Identification of a 160-kDa polypeptide that binds to the tight junction protein ZO-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3460–3464
Willott E, Balda MS, Fanning AS, Jameson B, Van Itallie C, Anderson JM (1993) The tight junction protein ZO-1 is homologous to the Drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor protein of septate junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7834–7838
Haskins J, Gu L, Wittchen ES, Hibbard J, Stevenson BR (1998) ZO-3, a novel member of the MAGUK protein family found at the tight junction, interacts with ZO-1 and occludin. J Cell Biol 141:199–208
Fanning AS, Ma TY, Anderson JM (2002) Isolation and functional characterization of the actin binding region in the tight junction protein ZO-1. FASEB J 16:1835–1837
Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K, Kubota K, Saitou M, Tsukita S (1999) Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3, with the COOH termini of claudins. J Cell Biol 147:1351–1363
Bazzoni G, Martinez-Estrada OM, Orsenigo F, Cordenonsi M, Citi S, Dejana E (2000) Interaction of junctional adhesion molecule with the tight junction components ZO-1, cingulin, and occludin. J Biol Chem 275:20520–20526
Alexandre MD, Lu Q, Chen YH (2005) Overexpression of claudin-7 decreases the paracellular Cl-conductance and increases the paracellular Na+ conductance in LLC-PK1 cells. J Cell Sci 118:2683–2693
Wittchen ES, Haskins J, Stevenson BR (2000) Exogenous expression of the amino-terminal half of the tight junction protein ZO-3 perturbs junctional complex assembly. J Cell Biol 151:825–836
Balda MS, Matter K (2000) The tight junction protein ZO-1 and an interacting transcription factor regulate ErbB-2 expression. EMBO J 19:2024–2033
Umeda K, Matsui T, Nakayama M, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2004) Establishment and characterization of cultured epithelial cells lacking expression of ZO-1. J Biol Chem 279:44785–44794
Cordenonsi M, D’Atri F, Hammar E, Parry DA, Kendrick-Jones J, Shore D, Citi S (1999) Cingulin contains globular and coiled-coil domains and interacts with ZO-1, ZO-2, ZO-3, and myosin. J Cell Biol 147:1569–1582
Cordenonsi M, Turco F, D’Atri F, Hammar E, Martinucci G, Meggio F, Citi S (1999) Xenopus laevis occludin. Identification of in vitro phosphorylation sites by protein kinase CK2 and association with cingulin. Eur J Biochem 264:374–384
Guillemot L, Hammar E, Kaister C, Ritz J, Caille D, Jond L, Bauer C, Meda P, Citi S (2004) Disruption of the cingulin gene does not prevent tight junction formation but alters gene expression. J Cell Sci 117:5245–5256
Niessner M, Volk BA (1995) Altered Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in the intestinal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease as assessed by quantitative reversed transcribed polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Clin Exp Immunol 101:428–435
Stallmach A, Giese T, Schmidt C, Ludwig B, Mueller-Molaian I, Meuer SC (2004) Cytokine/chemokine transcript profiles reflect mucosal inflammation in Crohn’s disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 19:308–315
Bruewer M, Luegering A, Kucharzik T, Parkos CA, Madara JL, Hopkins AM, Nusrat A (2003) Proinflammatory cytokines disrupt epithelial barrier function by apoptosis-independent mechanisms. J Immunol 171:6164–6172
Bruewer M, Utech M, Ivanov AI, Hopkins AM, Parkos CA, Nusrat A (2005) Interferon-gamma induces internalization of epithelial tight junction proteins via a macropinocytosis-like process. FASEB J 19:923–933
Sandborn WJ, Hanauer SB (1999) Antitumor necrosis factor therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a review of agents, pharmacology, clinical results, and safety. Inflamm Bowel Dis 5:119–133
Ricart E, Panaccione R, Loftus EV, Tremaine WJ, Sandborn WJ (1999) Successful management of Crohn’s disease of the ileoanal pouch with infliximab. Gastroenterology 117:429–432
Murch SH, Braegger CP, Walker-Smith JA, MacDonald TT (1993) Location of tumour necrosis factor alpha by immunohistochemistry in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 34:1705–1709
Braegger CP, Nicholls S, Murch SH, Stephens S, MacDonald TT (1992) Tumour necrosis factor alpha in stool as a marker of intestinal inflammation. Lancet 339:89–91
Schulzke JD, Bojarski C, Zeissig S, Heller F, Gitter AH, Fromm M (2006) Disrupted barrier function through epithelial cell apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1072:288–299
Ma TY, Iwamoto GK, Hoa NT, Akotia V, Pedram A, Boivin MA, Said HM (2004) TNF-alpha-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability requires NF-kappa B activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G367–G376
Ma TY, Boivin MA, Ye D, Pedram A, Said HM (2005) Mechanism of TNF-{alpha} modulation of Caco-2 intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier: role of myosin light-chain kinase protein expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288:G422–G430
Graham WV, Wang F, Clayburgh DR, Cheng JX, Yoon B, Wang Y, Lin A, Turner JR (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-induced long myosin light chain kinase transcription is regulated by differentiation-dependent signaling events. Characterization of the human long myosin light chain kinase promoter. J Biol Chem 281:26205–26215
Ye D, Ma I, Ma TY (2006) Molecular mechanism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G496–G504
Mankertz J, Amasheh M, Krug SM, Fromm A, Amasheh S, Hillenbrand B, Tavalali S, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2009) TNFalpha up-regulates claudin-2 expression in epithelial HT-29/B6 cells via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling. Cell Tissue Res 336:67–77
Reinecker HC, Steffen M, Witthoeft T, Pflueger I, Schreiber S, MacDermott RP, Raedler A (1993) Enhanced secretion of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 beta by isolated lamina propria mononuclear cells from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Clin Exp Immunol 94:174–181
Wang F, Graham WV, Wang Y, Witkowski ED, Schwarz BT, Turner JR (2005) Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha synergize to induce intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by up-regulating myosin light chain kinase expression. Am J Pathol 166:409–419
Wang F, Schwarz BT, Graham WV, Wang Y, Su L, Clayburgh DR, Abraham C, Turner JR (2006) IFN-gamma-induced TNFR2 expression is required for TNF-dependent intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction. Gastroenterology 131:1153–1163
Schwarz BT, Wang F, Shen L, Clayburgh DR, Su L, Wang Y, Fu YX, Turner JR (2007) LIGHT signals directly to intestinal epithelia to cause barrier dysfunction via cytoskeletal and endocytic mechanisms. Gastroenterology 132:2383–2394
Dinarello CA (1994) The interleukin-1 family: 10 years of discovery. FASEB J 8:1314–1325
Carty E, De Brabander M, Feakins RM, Rampton DS (2000) Measurement of in vivo rectal mucosal cytokine and eicosanoid production in ulcerative colitis using filter paper. Gut 46:487–492
Barksby HE, Lea SR, Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ (2007) The expanding family of interleukin-1 cytokines and their role in destructive inflammatory disorders. Clin Exp Immunol 149:217–225
Dinarello CA (2003) Anti-cytokine therapeutics and infections. Vaccine 21(Suppl 2):S24–S34
Al-Sadi RM, Ma TY (2007) IL-1beta causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. J Immunol 178:4641–4649
Al-Sadi R, Ye D, Dokladny K, Ma TY (2008) Mechanism of IL-1beta-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. J Immunol 180:5653–5661
Al-Sadi R, Ye D, Said HM, Ma TY (2010) IL-1beta-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability is mediated by MEKK-1 activation of canonical NF-kappaB pathway. Am J Pathol 177:2310–2322
Oliphant CJ, Barlow JL, McKenzie AN (2011) Insights into the initiation of type 2 immune responses. Immunology 134:378–385
Okoye IS, Wilson MS (2011) CD4+ T helper 2 cells-microbial triggers, differentiation requirements and effector functions. Immunology 134:368–377
Wisner DM, Harris LR 3rd, Green CL, Poritz LS (2008) Opposing regulation of the tight junction protein claudin-2 by interferon-gamma and interleukin-4. J Surg Res 144:1–7
Colgan SP, Resnick MB, Parkos CA, Delp-Archer C, McGuirk D, Bacarra AE, Weller PF, Madara JL (1994) IL-4 directly modulates function of a model human intestinal epithelium. J Immunol 153:2122–2129
Ceponis PJ, Botelho F, Richards CD, McKay DM (2000) Interleukins 4 and 13 increase intestinal epithelial permeability by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Lack of evidence for STAT 6 involvement. J Biol Chem 275:29132–29137
Tilg H, Dinarello CA, Mier JW (1997) IL-6 and APPs: anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive mediators. Immunol Today 18:428–432
Alonzi T, Fattori E, Lazzaro D, Costa P, Probert L, Kollias G, De Benedetti F, Poli V, Ciliberto G (1998) Interleukin 6 is required for the development of collagen-induced arthritis. J Exp Med 187:461–468
Louis E, Belaiche J, van Kemseke C, Franchimont D, de Groote D, Gueenen V, Mary JY (1997) A high serum concentration of interleukin-6 is predictive of relapse in quiescent Crohn’s disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:939–944
Kusugami K, Fukatsu A, Tanimoto M, Shinoda M, Haruta J, Kuroiwa A, Ina K, Kanayama K, Ando T, Matsuura T et al (1995) Elevation of interleukin-6 in inflammatory bowel disease is macrophage- and epithelial cell-dependent. Dig Dis Sci 40:949–959
Suzuki T, Yoshinaga N, Tanabe S (2011) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) regulates claudin-2 expression and tight junction permeability in intestinal epithelium. J Biol Chem 286:31263–31271
Yang R, Han X, Uchiyama T, Watkins SK, Yaguchi A, Delude RL, Fink MP (2003) IL-6 is essential for development of gut barrier dysfunction after hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285:G621–G629
Ouyang W, Rutz S, Crellin NK, Valdez PA, Hymowitz SG (2011) Regulation and functions of the IL-10 family of cytokines in inflammation and disease. Annu Rev Immunol 29:71–109
Saraiva M, O’Garra A (2010) The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol 10:170–181
Kucharzik T, Lugering N, Pauels HG, Domschke W, Stoll R (1998) IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13 down-regulate monocyte-chemoattracting protein-1 (MCP-1) production in activated intestinal epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol 111:152–157
Madsen KL, Malfair D, Gray D, Doyle JS, Jewell LD, Fedorak RN (1999) Interleukin-10 gene-deficient mice develop a primary intestinal permeability defect in response to enteric microflora. Inflamm Bowel Dis 5:262–270
Madsen KL, Lewis SA, Tavernini MM, Hibbard J, Fedorak RN (1997) Interleukin 10 prevents cytokine-induced disruption of T84 monolayer barrier integrity and limits chloride secretion. Gastroenterology 113:151–159
Duran B (2005) The effects of long-term total parenteral nutrition on gut mucosal immunity in children with short bowel syndrome: a systematic review. BMC Nurs 4:2
Wildhaber BE, Yang H, Spencer AU, Drongowski RA, Teitelbaum DH (2005) Lack of enteral nutrition–effects on the intestinal immune system. J Surg Res 123:8–16
Kansagra K, Stoll B, Rognerud C, Niinikoski H, Ou CN, Harvey R, Burrin D (2003) Total parenteral nutrition adversely affects gut barrier function in neonatal piglets. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285:G1162–G1170
Sun X, Yang H, Nose K, Nose S, Haxhija EQ, Koga H, Feng Y, Teitelbaum DH (2008) Decline in intestinal mucosal IL-10 expression and decreased intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of total parenteral nutrition. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G139–G147
Heller F, Florian P, Bojarski C, Richter J, Christ M, Hillenbrand B, Mankertz J, Gitter AH, Burgel N, Fromm M, Zeitz M, Fuss I, Strober W, Schulzke JD (2005) Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions, apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology 129:550–564
Fuss IJ, Heller F, Boirivant M, Leon F, Yoshida M, Fichtner-Feigl S, Yang Z, Exley M, Kitani A, Blumberg RS, Mannon P, Strober W (2004) Nonclassical CD1d-restricted NK T cells that produce IL-13 characterize an atypical Th2 response in ulcerative colitis. J Clin Invest 113:1490–1497
Prasad S, Mingrino R, Kaukinen K, Hayes KL, Powell RM, MacDonald TT, Collins JE (2005) Inflammatory processes have differential effects on claudins 2, 3 and 4 in colonic epithelial cells. Lab Invest 85:1139–1162
Weber CR, Raleigh DR, Su L, Shen L, Sullivan EA, Wang Y, Turner JR (2010) Epithelial myosin light chain kinase activation induces mucosal interleukin-13 expression to alter tight junction ion selectivity. J Biol Chem 285:12037–12046
Pappu R, Ramirez-Carrozzi V, Sambandam A (2011) The interleukin-17 cytokine family: critical players in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Immunology 134:8–16
Chang SH, Dong C (2011) Signaling of interleukin-17 family cytokines in immunity and inflammation. Cell Signal 23:1069–1075
Cosmi L, Liotta F, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Annunziato F (2011) Th17 cells: new players in asthma pathogenesis. Allergy 66:989–998
Kinugasa T, Sakaguchi T, Gu X, Reinecker HC (2000) Claudins regulate the intestinal barrier in response to immune mediators. Gastroenterology 118:1001–1011
Harris RC, Chung E, Coffey RJ (2003) EGF receptor ligands. Exp Cell Res 284:2–13
Booth BW, Smith GH (2007) Roles of transforming growth factor-alpha in mammary development and disease. Growth Factors 25:227–235
Forsyth CB, Banan A, Farhadi A, Fields JZ, Tang Y, Shaikh M, Zhang LJ, Engen PA, Keshavarzian A (2007) Regulation of oxidant-induced intestinal permeability by metalloprotease-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:84–97
Rao R, Baker RD, Baker SS (1999) Inhibition of oxidant-induced barrier disruption and protein tyrosine phosphorylation in Caco-2 cell monolayers by epidermal growth factor. Biochem Pharmacol 57:685–695
Howe KL, Reardon C, Wang A, Nazli A, McKay DM (2005) Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of epithelial tight junction proteins enhances barrier function and blocks enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7-induced increased permeability. Am J Pathol 167:1587–1597
Hering NA, Andres S, Fromm A, van Tol EA, Amasheh M, Mankertz J, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2011) Transforming growth factor-beta, a whey protein component, strengthens the intestinal barrier by upregulating claudin-4 in HT-29/B6 cells. J Nutr 141:783–789
Roche JK, Martins CA, Cosme R, Fayer R, Guerrant RL (2000) Transforming growth factor beta1 ameliorates intestinal epithelial barrier disruption by Cryptosporidium parvum in vitro in the absence of mucosal T lymphocytes. Infect Immun 68:5635–5644
Rao R (2008) Oxidative stress-induced disruption of epithelial and endothelial tight junctions. Front Biosci 13:7210–7226
Basuroy S, Seth A, Elias B, Naren AP, Rao R (2006) MAPK interacts with occludin and mediates EGF-induced prevention of tight junction disruption by hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J 393:69–77
Banan A, Fields JZ, Talmage DA, Zhang L, Keshavarzian A (2002) PKC-zeta is required in EGF protection of microtubules and intestinal barrier integrity against oxidant injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282:G794–G808
Banan A, Fields JZ, Talmage DA, Zhang Y, Keshavarzian A (2001) PKC-beta1 mediates EGF protection of microtubules and barrier of intestinal monolayers against oxidants. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G833–G847
Banan A, Keshavarzian A, Zhang L, Shaikh M, Forsyth CB, Tang Y, Fields JZ (2007) NF-kappaB activation as a key mechanism in ethanol-induced disruption of the F-actin cytoskeleton and monolayer barrier integrity in intestinal epithelium. Alcohol 41:447–460
Samak G, Aggarwal S, Rao RK (2011) ERK is involved in EGF-mediated protection of tight junctions, but not adherens junctions, in acetaldehyde-treated Caco-2 cell monolayers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301:G50–G59
Baudry B, Fasano A, Ketley J, Kaper JB (1992) Cloning of a gene (zot) encoding a new toxin produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun 60:428–434
Fasano A, Baudry B, Pumplin DW, Wasserman SS, Tall BD, Ketley JM, Kaper JB (1991) Vibrio cholerae produces a second enterotoxin, which affects intestinal tight junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:5242–5246
Di Pierro M, Lu R, Uzzau S, Wang W, Margaretten K, Pazzani C, Maimone F, Fasano A (2001) Zonula occludens toxin structure-function analysis. Identification of the fragment biologically active on tight junctions and of the zonulin receptor binding domain. J Biol Chem 276:19160–19165
Goldblum SE, Rai U, Tripathi A, Thakar M, De Leo L, Di Toro N, Not T, Ramachandran R, Puche AC, Hollenberg MD, Fasano A (2011) The active Zot domain (aa 288–293) increases ZO-1 and myosin 1C serine/threonine phosphorylation, alters interaction between ZO-1 and its binding partners, and induces tight junction disassembly through proteinase activated receptor 2 activation. FASEB J 25:144–158
Mel SF, Fullner KJ, Wimer-Mackin S, Lencer WI, Mekalanos JJ (2000) Association of protease activity in Vibrio cholerae vaccine strains with decreases in transcellular epithelial resistance of polarized T84 intestinal epithelial cells. Infect Immun 68:6487–6492
Wu Z, Nybom P, Magnusson KE (2000) Distinct effects of Vibrio cholerae haemagglutinin/protease on the structure and localization of the tight junction-associated proteins occludin and ZO-1. Cell Microbiol 2:11–17
Muza-Moons MM, Schneeberger EE, Hecht GA (2004) Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection leads to appearance of aberrant tight junctions strands in the lateral membrane of intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol 6:783–793
Philpott DJ, McKay DM, Sherman PM, Perdue MH (1996) Infection of T84 cells with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli alters barrier and transport functions. Am J Physiol 270:G634–G645
Shifflett DE, Clayburgh DR, Koutsouris A, Turner JR, Hecht GA (2005) Enteropathogenic E. coli disrupts tight junction barrier function and structure in vivo. Lab Invest 85:1308–1324
Simonovic I, Rosenberg J, Koutsouris A, Hecht G (2000) Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli dephosphorylates and dissociates occludin from intestinal epithelial tight junctions. Cell Microbiol 2:305–315
Spitz J, Yuhan R, Koutsouris A, Blatt C, Alverdy J, Hecht G (1995) Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli adherence to intestinal epithelial monolayers diminishes barrier function. Am J Physiol 268:G374–G379
Tomson FL, Koutsouris A, Viswanathan VK, Turner JR, Savkovic SD, Hecht G (2004) Differing roles of protein kinase C-zeta in disruption of tight junction barrier by enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Gastroenterology 127:859–869
Dean P, Kenny B (2004) Intestinal barrier dysfunction by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is mediated by two effector molecules and a bacterial surface protein. Mol Microbiol 54:665–675
Philpott DJ, McKay DM, Mak W, Perdue MH, Sherman PM (1998) Signal transduction pathways involved in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-induced alterations in T84 epithelial permeability. Infect Immun 66:1680–1687
Brynestad S, Granum PE (2002) Clostridium perfringens and foodborne infections. Int J Food Microbiol 74:195–202
McClane BA, Wnek AP, Hulkower KI, Hanna PC (1988) Divalent cation involvement in the action of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Early events in enterotoxin action are divalent cation-independent. J Biol Chem 263:2423–2435
Hanna PC, Mietzner TA, Schoolnik GK, McClane BA (1991) Localization of the receptor-binding region of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin utilizing cloned toxin fragments and synthetic peptides. The 30 C-terminal amino acids define a functional binding region. J Biol Chem 266:11037–11043
Hanna PC, Wieckowski EU, Mietzner TA, McClane BA (1992) Mapping of functional regions of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun 60:2110–2114
Katahira J, Sugiyama H, Inoue N, Horiguchi Y, Matsuda M, Sugimoto N (1997) Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin utilizes two structurally related membrane proteins as functional receptors in vivo. J Biol Chem 272:26652–26658
Katahira J, Inoue N, Horiguchi Y, Matsuda M, Sugimoto N (1997) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of the receptor for Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. J Cell Biol 136:1239–1247
Sonoda N, Furuse M, Sasaki H, Yonemura S, Katahira J, Horiguchi Y, Tsukita S (1999) Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fragment removes specific claudins from tight junction strands: evidence for direct involvement of claudins in tight junction barrier. J Cell Biol 147:195–204
Takahashi A, Kondoh M, Masuyama A, Fujii M, Mizuguchi H, Horiguchi Y, Watanabe Y (2005) Role of C-terminal regions of the C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin in its interaction with claudin-4. J Controlled Release 108:56–62
Singh U, Van Itallie CM, Mitic LL, Anderson JM, McClane BA (2000) CaCo-2 cells treated with Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin form multiple large complex species, one of which contains the tight junction protein occludin. J Biol Chem 275:18407–18417
Peng X, Yan H, You Z, Wang P, Wang S (2004) Effects of enteral supplementation with glutamine granules on intestinal mucosal barrier function in severe burned patients. Burns 30:135–139
Ding LA, Li JS (2003) Effects of glutamine on intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation in TPN-rats with endotoxemia. World J Gastroenterol 9:1327–1332
Li J, Langkamp-Henken B, Suzuki K, Stahlgren LH (1994) Glutamine prevents parenteral nutrition-induced increases in intestinal permeability. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 18:303–307
Foitzik T, Stufler M, Hotz HG, Klinnert J, Wagner J, Warshaw AL, Schulzke JD, Fromm M, Buhr HJ (1997) Glutamine stabilizes intestinal permeability and reduces pancreatic infection in acute experimental pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg 1:40–46 (discussion 46–47)
Li N, Lewis P, Samuelson D, Liboni K, Neu J (2004) Glutamine regulates Caco-2 cell tight junction proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287:G726–G733
Li N, Neu J (2009) Glutamine deprivation alters intestinal tight junctions via a PI3-K/Akt mediated pathway in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr 139:710–714
Seth A, Basuroy S, Sheth P, Rao RK (2004) l-Glutamine ameliorates acetaldehyde-induced increase in paracellular permeability in Caco-2 cell monolayer. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287:G510–G517
Basuroy S, Sheth P, Mansbach CM, Rao RK (2005) Acetaldehyde disrupts tight junctions and adherens junctions in human colonic mucosa: protection by EGF and l-glutamine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289:G367–G375
Watanabe J, Fukumoto K, Fukushi E, Sonoyama K, Kawabata J (2004) Isolation of tryptophan as an inhibitor of ovalbumin permeation and analysis of its suppressive effect on oral sensitization. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:59–65
Isobe N, Suzuki M, Oda M, Tanabe S (2008) Enzyme-modified cheese exerts inhibitory effects on allergen permeation in rats suffering from indomethacin-induced intestinal inflammation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72:1740–1745
Tanabe S (2012) Short peptide modules for enhancing intestinal barrier function. Curr Pharm Des 18:776–781
Yasumatsu H, Tanabe S (2010) The casein peptide Asn-Pro-Trp-Asp-Gln enforces the intestinal tight junction partly by increasing occludin expression in Caco-2 cells. Br J Nutr 104:951–956
Usami M, Muraki K, Iwamoto M, Ohata A, Matsushita E, Miki A (2001) Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) on tight junction permeability in intestinal monolayer cells. Clin Nutr 20:351–359
Usami M, Komurasaki T, Hanada A, Kinoshita K, Ohata A (2003) Effect of gamma-linolenic acid or docosahexaenoic acid on tight junction permeability in intestinal monolayer cells and their mechanism by protein kinase C activation and/or eicosanoid formation. Nutrition 19:150–156
Willemsen LE, Koetsier MA, Balvers M, Beermann C, Stahl B, van Tol EA (2008) Polyunsaturated fatty acids support epithelial barrier integrity and reduce IL-4 mediated permeability in vitro. Eur J Nutr 47:183–191
Anderberg EK, Lindmark T, Artursson P (1993) Sodium caprate elicits dilatations in human intestinal tight junctions and enhances drug absorption by the paracellular route. Pharm Res 10:857–864
Lindmark T, Nikkila T, Artursson P (1995) Mechanisms of absorption enhancement by medium chain fatty acids in intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:958–964
Soderholm JD, Oman H, Blomquist L, Veen J, Lindmark T, Olaison G (1998) Reversible increase in tight junction permeability to macromolecules in rat ileal mucosa in vitro by sodium caprate, a constituent of milk fat. Dig Dis Sci 43:1547–1552
Mortensen PB, Clausen MR (1996) Short-chain fatty acids in the human colon: relation to gastrointestinal health and disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl 216:132–148
Topping DL, Clifton PM (2001) Short-chain fatty acids and human colonic function: roles of resistant starch and nonstarch polysaccharides. Physiol Rev 81:1031–1064
Mariadason JM, Barkla DH, Gibson PR (1997) Effect of short-chain fatty acids on paracellular permeability in Caco-2 intestinal epithelium model. Am J Physiol 272:G705–G712
Kinoshita M, Suzuki Y, Saito Y (2002) Butyrate reduces colonic paracellular permeability by enhancing PPARgamma activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:827–831
Peng L, Li ZR, Green RS, Holzman IR, Lin J (2009) Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Nutr 139:1619–1625
Suzuki T, Yoshida S, Hara H (2008) Physiological concentrations of short-chain fatty acids immediately suppress colonic epithelial permeability. Br J Nutr 100:297–305
Le Poul E, Loison C, Struyf S, Springael JY, Lannoy V, Decobecq ME, Brezillon S, Dupriez V, Vassart G, Van Damme J, Parmentier M, Detheux M (2003) Functional characterization of human receptors for short chain fatty acids and their role in polymorphonuclear cell activation. J Biol Chem 278:25481–25489
Brown AJ, Goldsworthy SM, Barnes AA, Eilert MM, Tcheang L, Daniels D, Muir AI, Wigglesworth MJ, Kinghorn I, Fraser NJ, Pike NB, Strum JC, Steplewski KM, Murdock PR, Holder JC, Marshall FH, Szekeres PG, Wilson S, Ignar DM, Foord SM, Wise A, Dowell SJ (2003) The Orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J Biol Chem 278:11312–11319
Karaki S, Mitsui R, Hayashi H, Kato I, Sugiya H, Iwanaga T, Furness JB, Kuwahara A (2006) Short-chain fatty acid receptor, GPR43, is expressed by enteroendocrine cells and mucosal mast cells in rat intestine. Cell Tissue Res 324:353–360
Karaki S, Tazoe H, Hayashi H, Kashiwabara H, Tooyama K, Suzuki Y, Kuwahara A (2008) Expression of the short-chain fatty acid receptor, GPR43, in the human colon. J Mol Histol 39:135–142
Rowe A (1997) Retinoid X receptors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29:275–278
Dusso AS, Brown AJ (1998) Mechanism of vitamin D action and its regulation. Am J Kidney Dis 32:S13–S24
Maciel AA, Oria RB, Braga-Neto MB, Braga AB, Carvalho EB, Lucena HB, Brito GA, Guerrant RL, Lima AA (2007) Role of retinol in protecting epithelial cell damage induced by Clostridium difficile toxin A. Toxicon 50:1027–1040
Kong J, Zhang Z, Musch MW, Ning G, Sun J, Hart J, Bissonnette M, Li YC (2008) Novel role of the vitamin D receptor in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G208–G216
Kandaswami C, Middleton E Jr (1994) Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of plant flavonoids. Adv Exp Med Biol 366:351–376
Hamalainen M, Nieminen R, Vuorela P, Heinonen M, Moilanen E (2007) Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids: genistein, kaempferol, quercetin, and daidzein inhibit STAT-1 and NF-kappaB activations, whereas flavone, isorhamnetin, naringenin, and pelargonidin inhibit only NF-kappaB activation along with their inhibitory effect on iNOS expression and NO production in activated macrophages. Mediat Inflamm 2007:45673
Suzuki T, Hara H (2009) Quercetin enhances intestinal barrier function through the assembly of zonula occludens-2, occludin, and claudin-1 and the expression of claudin-4 in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr 139:965–974
Suzuki T, Tanabe S, Hara H (2011) Kaempferol enhances intestinal barrier function through the cytoskeletal association and expression of tight junction proteins in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr 141:87–94
Amasheh M, Schlichter S, Amasheh S, Mankertz J, Zeitz M, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2008) Quercetin enhances epithelial barrier function and increases claudin-4 expression in Caco-2 cells. J Nutr 138:1067–1073
Sheth P, Seth A, Atkinson KJ, Gheyi T, Kale G, Giorgianni F, Desiderio DM, Li C, Naren A, Rao R (2007) Acetaldehyde dissociates the PTP1B-E-cadherin-beta-catenin complex in Caco-2 cell monolayers by a phosphorylation-dependent mechanism. Biochem J 402:291–300
Watson JL, Ansari S, Cameron H, Wang A, Akhtar M, McKay DM (2004) Green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin gallate blocks epithelial barrier dysfunction provoked by IFN-gamma but not by IL-4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 287:G954–G961
Sanders ME (2003) Probiotics: considerations for human health. Nutr Rev 61:91–99
Ukena SN, Singh A, Dringenberg U, Engelhardt R, Seidler U, Hansen W, Bleich A, Bruder D, Franzke A, Rogler G, Suerbaum S, Buer J, Gunzer F, Westendorf AM (2007) Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 inhibits leaky gut by enhancing mucosal integrity. PLoS One 2:e1308
Garrido-Mesa N, Utrilla P, Comalada M, Zorrilla P, Garrido-Mesa J, Zarzuelo A, Rodriguez-Cabezas ME, Galvez J (2011) The association of minocycline and the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 results in an additive beneficial effect in a DSS model of reactivated colitis in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 82:1891–1900
Zyrek AA, Cichon C, Helms S, Enders C, Sonnenborn U, Schmidt MA (2007) Molecular mechanisms underlying the probiotic effects of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 involve ZO-2 and PKCzeta redistribution resulting in tight junction and epithelial barrier repair. Cell Microbiol 9:804–816
Resta-Lenert S, Barrett KE (2003) Live probiotics protect intestinal epithelial cells from the effects of infection with enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC). Gut 52:988–997
Resta-Lenert S, Barrett KE (2006) Probiotics and commensals reverse TNF-alpha- and IFN-gamma-induced dysfunction in human intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 130:731–746
Mennigen R, Nolte K, Rijcken E, Utech M, Loeffler B, Senninger N, Bruewer M (2009) Probiotic mixture VSL#3 protects the epithelial barrier by maintaining tight junction protein expression and preventing apoptosis in a murine model of colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296:G1140–G1149
Dai C, Zhao DH, Jiang M (2012) VSL#3 probiotics regulate the intestinal epithelial barrier in vivo and in vitro via the p38 and ERK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med 29:202–208
Chen HQ, Yang J, Zhang M, Zhou YK, Shen TY, Chu ZX, Hang XM, Jiang YQ, Qin HL (2010) Lactobacillus plantarum ameliorates colonic epithelial barrier dysfunction by modulating the apical junctional complex and PepT1 in IL-10 knockout mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299:G1287–G1297
Ko JS, Yang HR, Chang JY, Seo JK (2007) Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits epithelial barrier dysfunction and interleukin-8 secretion induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. World J Gastroenterol 13:1962–1965
Karczewski J, Troost FJ, Konings I, Dekker J, Kleerebezem M, Brummer RJ, Wells JM (2010) Regulation of human epithelial tight junction proteins by Lactobacillus plantarum in vivo and protective effects on the epithelial barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298:G851–G859
Cario E, Gerken G, Podolsky DK (2004) Toll-like receptor 2 enhances ZO-1-associated intestinal epithelial barrier integrity via protein kinase C. Gastroenterology 127:224–238
Miyauchi E, Morita H, Tanabe S (2009) Lactobacillus rhamnosus alleviates intestinal barrier dysfunction in part by increasing expression of zonula occludens-1 and myosin light-chain kinase in vivo. J Dairy Res 92:2400–2408
Donato KA, Gareau MG, Wang YJ, Sherman PM (2010) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG attenuates interferon-{gamma} and tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced barrier dysfunction and pro-inflammatory signalling. Microbiology 156:3288–3297
Johnson-Henry KC, Donato KA, Shen-Tu G, Gordanpour M, Sherman PM (2008) Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG prevents enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7-induced changes in epithelial barrier function. Infect Immun 76:1340–1348
Yan F, Cao H, Cover TL, Whitehead R, Washington MK, Polk DB (2007) Soluble proteins produced by probiotic bacteria regulate intestinal epithelial cell survival and growth. Gastroenterology 132:562–575
Seth A, Yan F, Polk DB, Rao RK (2008) Probiotics ameliorate the hydrogen peroxide-induced epithelial barrier disruption by a PKC- and MAP kinase-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G1060–G1069
Yan F, Cao H, Cover TL, Washington MK, Shi Y, Liu L, Chaturvedi R, Peek RM Jr, Wilson KT, Polk DB (2011) Colon-specific delivery of a probiotic-derived soluble protein ameliorates intestinal inflammation in mice through an EGFR-dependent mechanism. J Clin Invest 121:2242–2253
Ewaschuk JB, Diaz H, Meddings L, Diederichs B, Dmytrash A, Backer J, Looijer-van Langen M, Madsen KL (2008) Secreted bioactive factors from Bifidobacterium infantis enhance epithelial cell barrier function. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G1025–G1034
Keshavarzian A, Farhadi A, Forsyth CB, Rangan J, Jakate S, Shaikh M, Banan A, Fields JZ (2009) Evidence that chronic alcohol exposure promotes intestinal oxidative stress, intestinal hyperpermeability and endotoxemia prior to development of alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. J Hepatol 50:538–547
Ferrier L, Berard F, Debrauwer L, Chabo C, Langella P, Bueno L, Fioramonti J (2006) Impairment of the intestinal barrier by ethanol involves enteric microflora and mast cell activation in rodents. Am J Pathol 168:1148–1154
Tamai H, Kato S, Horie Y, Ohki E, Yokoyama H, Ishii H (2000) Effect of acute ethanol administration on the intestinal absorption of endotoxin in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:390–394
Ma TY, Nguyen D, Bui V, Nguyen H, Hoa N (1999) Ethanol modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol 276:G965–G974
Visapaa JP, Jokelainen K, Nosova T, Salaspuro M (1998) Inhibition of intracolonic acetaldehyde production and alcoholic fermentation in rats by ciprofloxacin. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:1161–1164
Rao RK (1998) Acetaldehyde-induced increase in paracellular permeability in Caco-2 cell monolayer. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:1724–1730
Soderholm JD, Peterson KH, Olaison G, Franzen LE, Westrom B, Magnusson KE, Sjodahl R (1999) Epithelial permeability to proteins in the noninflamed ileum of Crohn’s disease? Gastroenterology 117:65–72
Hollander D, Vadheim CM, Brettholz E, Petersen GM, Delahunty T, Rotter JI (1986) Increased intestinal permeability in patients with Crohn’s disease and their relatives. A possible etiologic factor. Ann Intern Med 105:883–885
Suenaert P, Bulteel V, Lemmens L, Noman M, Geypens B, Van Assche G, Geboes K, Ceuppens JL, Rutgeerts P (2002) Anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment restores the gut barrier in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 97:2000–2004
Zeissig S, Burgel N, Gunzel D, Richter J, Mankertz J, Wahnschaffe U, Kroesen AJ, Zeitz M, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2007) Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5 and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction in active Crohn’s disease. Gut 56:61–72
Vetrano S, Rescigno M, Cera MR, Correale C, Rumio C, Doni A, Fantini M, Sturm A, Borroni E, Repici A, Locati M, Malesci A, Dejana E, Danese S (2008) Unique role of junctional adhesion molecule-a in maintaining mucosal homeostasis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 135:173–184
Blair SA, Kane SV, Clayburgh DR, Turner JR (2006) Epithelial myosin light chain kinase expression and activity are upregulated in inflammatory bowel disease. Lab Invest 86:191–201
Smecuol E, Bai JC, Vazquez H, Kogan Z, Cabanne A, Niveloni S, Pedreira S, Boerr L, Maurino E, Meddings JB (1997) Gastrointestinal permeability in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 112:1129–1136
Schulzke JD, Bentzel CJ, Schulzke I, Riecken EO, Fromm M (1998) Epithelial tight junction structure in the jejunum of children with acute and treated celiac sprue. Pediatr Res 43:435–441
van Elburg RM, Uil JJ, Mulder CJ, Heymans HS (1993) Intestinal permeability in patients with coeliac disease and relatives of patients with coeliac disease. Gut 34:354–357
Lammers KM, Lu R, Brownley J, Lu B, Gerard C, Thomas K, Rallabhandi P, Shea-Donohue T, Tamiz A, Alkan S, Netzel-Arnett S, Antalis T, Vogel SN, Fasano A (2008) Gliadin induces an increase in intestinal permeability and zonulin release by binding to the chemokine receptor CXCR3. Gastroenterology 135(194–204):e193
Lu R, Wang W, Uzzau S, Vigorito R, Zielke HR, Fasano A (2000) Affinity purification and partial characterization of the zonulin/zonula occludens toxin (Zot) receptor from human brain. J Neurochem 74:320–326
Wang W, Uzzau S, Goldblum SE, Fasano A (2000) Human zonulin, a potential modulator of intestinal tight junctions. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 24):4435–4440
Drago S, El Asmar R, Di Pierro M, Grazia Clemente M, Tripathi A, Sapone A, Thakar M, Iacono G, Carroccio A, D’Agate C, Not T, Zampini L, Catassi C, Fasano A (2006) Gliadin, zonulin and gut permeability: effects on celiac and non-celiac intestinal mucosa and intestinal cell lines. Scand J Gastroenterol 41:408–419
Szakal DN, Gyorffy H, Arato A, Cseh A, Molnar K, Papp M, Dezsofi A, Veres G (2010) Mucosal expression of claudins 2, 3 and 4 in proximal and distal part of duodenum in children with coeliac disease. Virchows Arch 456:245–250
Louka AS, Sollid LM (2003) HLA in coeliac disease: unravelling the complex genetics of a complex disorder. Tissue Antigens 61:105–117
Mooradian AD, Morley JE, Levine AS, Prigge WF, Gebhard RL (1986) Abnormal intestinal permeability to sugars in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 29:221–224
Bosi E, Molteni L, Radaelli MG, Folini L, Fermo I, Bazzigaluppi E, Piemonti L, Pastore MR, Paroni R (2006) Increased intestinal permeability precedes clinical onset of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 49:2824–2827
Vaarala O (2008) Leaking gut in type 1 diabetes. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24:701–706
Westerholm-Ormio M, Vaarala O, Pihkala P, Ilonen J, Savilahti E (2003) Immunologic activity in the small intestinal mucosa of pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 52:2287–2295
Watts T, Berti I, Sapone A, Gerarduzzi T, Not T, Zielke R, Fasano A (2005) Role of the intestinal tight junction modulator zonulin in the pathogenesis of type I diabetes in BB diabetic-prone rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2916–2921
Meddings JB, Jarand J, Urbanski SJ, Hardin J, Gall DG (1999) Increased gastrointestinal permeability is an early lesion in the spontaneously diabetic BB rat. Am J Physiol 276:G951–G957
Sapone A, de Magistris L, Pietzak M, Clemente MG, Tripathi A, Cucca F, Lampis R, Kryszak D, Carteni M, Generoso M, Iafusco D, Prisco F, Laghi F, Riegler G, Carratu R, Counts D, Fasano A (2006) Zonulin upregulation is associated with increased gut permeability in subjects with type 1 diabetes and their relatives. Diabetes 55:1443–1449
Rao RK, Seth A, Sheth P (2004) Recent Advances in Alcoholic Liver Disease I. Role of intestinal permeability and endotoxemia in alcoholic liver disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G881–G884
Keshavarzian A, Holmes EW, Patel M, Iber F, Fields JZ, Pethkar S (1999) Leaky gut in alcoholic cirrhosis: a possible mechanism for alcohol-induced liver damage. Am J Gastroenterol 94:200–207
Fujimoto M, Uemura M, Nakatani Y, Tsujita S, Hoppo K, Tamagawa T, Kitano H, Kikukawa M, Ann T, Ishii Y, Kojima H, Sakurai S, Tanaka R, Namisaki T, Noguchi R, Higashino T, Kikuchi E, Nishimura K, Takaya A, Fukui H (2000) Plasma endotoxin and serum cytokine levels in patients with alcoholic hepatitis: relation to severity of liver disturbance. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:48S–54S
Nanji AA, Jokelainen K, Fotouhinia M, Rahemtulla A, Thomas P, Tipoe GL, Su GL, Dannenberg AJ (2001) Increased severity of alcoholic liver injury in female rats: role of oxidative stress, endotoxin, and chemokines. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G1348–G1356
Mathurin P, Deng QG, Keshavarzian A, Choudhary S, Holmes EW, Tsukamoto H (2000) Exacerbation of alcoholic liver injury by enteral endotoxin in rats. Hepatology 32:1008–1017
Nanji AA, Khettry U, Sadrzadeh SM (1994) Lactobacillus feeding reduces endotoxemia and severity of experimental alcoholic liver (disease). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 205:243–247
Adachi Y, Moore LE, Bradford BU, Gao W, Thurman RG (1995) Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology 108:218–224
Bode C, Bode JC (2003) Effect of alcohol consumption on the gut. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17:575–592
Parlesak A, Schafer C, Schutz T, Bode JC, Bode C (2000) Increased intestinal permeability to macromolecules and endotoxemia in patients with chronic alcohol abuse in different stages of alcohol-induced liver disease. J Hepatol 32:742–747
Keshavarzian A, Fields JZ, Vaeth J, Holmes EW (1994) The differing effects of acute and chronic alcohol on gastric and intestinal permeability. Am J Gastroenterol 89:2205–2211
Camilleri M, Gorman H (2007) Intestinal permeability and irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19:545–552
Barbara G, Stanghellini V, De Giorgio R, Cremon C, Cottrell GS, Santini D, Pasquinelli G, Morselli-Labate AM, Grady EF, Bunnett NW, Collins SM, Corinaldesi R (2004) Activated mast cells in proximity to colonic nerves correlate with abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 126:693–702
Collins SM (2005) Dysregulation of peripheral cytokine production in irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol 100:2517–2518
Piche T, Barbara G, Aubert P, Bruley des Varannes S, Dainese R, Nano JL, Cremon C, Stanghellini V, De Giorgio R, Galmiche JP, Neunlist M. (2009) Impaired intestinal barrier integrity in the colon of patients with irritable bowel syndrome: involvement of soluble mediators. Gut 58:196–201
Alonso C, Guilarte M, Vicario M, Ramos L, Ramadan Z, Antolin M, Martinez C, Rezzi S, Saperas E, Kochhar S, Santos J, Malagelada JR (2008) Maladaptive intestinal epithelial responses to life stress may predispose healthy women to gut mucosal inflammation. Gastroenterology 135(163–172):e161
Mazzon E, Crisafulli C, Galuppo M, Cuzzocrea S (2009) Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in ileum tight junction alteration in mouse model of restraint stress. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297:G488–G505
Estienne M, Claustre J, Clain-Gardechaux G, Paquet A, Tache Y, Fioramonti J, Plaisancie P (2010) Maternal deprivation alters epithelial secretory cell lineages in rat duodenum: role of CRF-related peptides. Gut 59:744–751
Soderholm JD, Yang PC, Ceponis P, Vohra A, Riddell R, Sherman PM, Perdue MH (2002) Chronic stress induces mast cell-dependent bacterial adherence and initiates mucosal inflammation in rat intestine. Gastroenterology 123:1099–1108
Berin MC, Sicherer S (2011) Food allergy: mechanisms and therapeutics. Curr Opin Immunol 23:794–800
Ventura MT, Polimeno L, Amoruso AC, Gatti F, Annoscia E, Marinaro M, Di Leo E, Matino MG, Buquicchio R, Bonini S, Tursi A, Francavilla A (2006) Intestinal permeability in patients with adverse reactions to food. Dig Liver Dis 38:732–736
Andre C, Andre F, Colin L, Cavagna S (1987) Measurement of intestinal permeability to mannitol and lactulose as a means of diagnosing food allergy and evaluating therapeutic effectiveness of disodium cromoglycate. Ann Allergy 59:127–130
Brandt EB, Strait RT, Hershko D, Wang Q, Muntel EE, Scribner TA, Zimmermann N, Finkelman FD, Rothenberg ME (2003) Mast cells are required for experimental oral allergen-induced diarrhea. J Clin Invest 112:1666–1677
Moneret-Vautrin DA, de Korwin JD, Tisserant J, Grignon M, Claudot N (1984) Ultrastructural study of the mast cells of the human duodenal mucosa. Clin Allergy 14:471–481
Banan A, Zhang LJ, Farhadi A, Fields JZ, Shaikh M, Keshavarzian A (2004) PKC-beta1 isoform activation is required for EGF-induced NF-kappaB inactivation and IkappaBalpha stabilization and protection of F-actin assembly and barrier function in enterocyte monolayers. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C723–C738
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) 23780135 to T. Suzuki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, T. Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 631–659 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1070-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1070-x