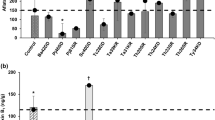
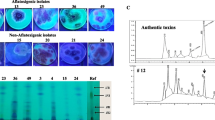
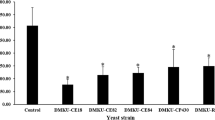
Abstract
Wheat (Triticum aestivum) is an agricultural product invaded by various fungi during harvest and storage resulting in a huge amount of loss and damage. An effective way to prevent this loss is to inhibit the growth of mycotoxin-producing fungi and to degrade mycotoxins without using chemicals and losing nutritional value. The use of specific microorganisms is an effective way of bio-detoxification. In this study, the effect of Candida albicans (103, 105, and 107 colony forming units (CFU)/mL) on the growth of Aspergillus parasiticus (102 and 104 spores/g) in laboratory culture medium and wheat grain samples was investigated. The results revealed that C. albicans significantly reduced the growth rate of the fungus compared to the control sample. Furthermore, C. albicans reduced the level of aflatoxins of types B1 and G1 and total aflatoxin in culture medium and wheat grain samples. It should be noted that in all concentrations and conditions, no growth of aflatoxins of types B2 and G2 was observed. According to our results, C. albicans has inhibitory effects on A. parasiticus and can therefore be introduced as a bio-alternative in wheat grain preservation.
Graphical abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi M, Jahed Khaniki G, Shariatifar N, Molaee-Aghaee E (2020) Investigation of aflatoxins level in some packaged and bulk legumes collected from Tehran market of Iran. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1789614
Bata Á, Lásztity R (1999) Detoxification of mycotoxin-contaminated food and feed by microorganisms. Trends Food Sci Technol 10(7):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-2244(99)00050-3
Bzducha-Wróbel A, Bryła M, Gientka I, Błażejak S, Janowicz M (2019) Candida utilis ATCC 9950 cell walls and β(1,3)/(1,6)-glucan preparations produced using agro-waste as a mycotoxins trap. Toxins 11(4):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040192
Caldas ED, Silva SC, Oliveira JN (2002) Aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in food and the risks to human health. Rev Saúde Pública 36(3):319–323
Calistru C, Mclean M, Berjak P (1997) In vitro studies on the potential for biological control of Aspergillus flavus and Fusarium moniliforme by Trichoderma species. Mycopathologia 137(2):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006802423729
Chang PK, Hua SST, Sarreal SBL, Li RW (2015) Suppression of aflatoxin biosynthesis in Aspergillus flavus by 2-phenylethanol is associated with stimulated growth and decreased degradation of branched-chain amino acids. Toxins 7(10):3887–3902. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7103887
Corassin C, Bovo F, Rosim R, Oliveira C (2013) Efficiency of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and lactic acid bacteria strains to bind aflatoxin M1 in UHT skim milk. Food Control 31(1):80–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.09.033
Da Cruz P, Jales De Matos C, Mangueira Nascimento Y, Fechine Tavares J, Leite De Souza E, Magalhães HIF (2021) Efficacy of potentially probiotic fruit-derived Lactobacillus fermentum, L. paracasei and L. plantarum to remove aflatoxin M1 in vitro. Toxins 13(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010004
De Alencar ER, Faroni LRDA, Soares NDFF, Da Silva WA, Da Silva Carvalho MC (2012) Efficacy of ozone as a fungicidal and detoxifying agent of aflatoxins in peanuts. J Sci Food Agric 92(4):899–905. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4668
Deepak MB, Jhanvi SP, Anuappaiah KA (2015) Aflatoxin binding and detoxification by non-saccharomyces yeast–a new vista for decontamination. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 4(5):310–317
El-Shiekh HH, Mahdy HM, El-Aaser MM (2007) Bioremediation of aflatoxins by some reference fungal strains. Pol J Microbiol 56:215–223
FAO (2004) Worldwide regulations for mycotoxins in food and feed in 2003. FAO Food and Nutrition Paper. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy
Faraj MK, Smith JE, Harran G (1993) Aflatoxin biodegradation: effects of temperature and microbes. Mycol Res 97(11):1388–1392. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(09)80174-3
Fochesato AS, Cristofolini A, Poloni VL, Magnoli A, Merkis CI, Dogi CA, Cavaglieri LR (2020) Culture medium and gastrointestinal environment positively influence the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RC016 cell wall polysaccharide profile and aflatoxin B1 bioadsorption. LWT 126:109306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109306
Ghanbari R, Molaee Aghaee E, Rezaie S, Jahed Khaniki G, Alimohammadi M, Soleimani M, Noorbakhsh F (2018) The inhibitory effect of lactic acid bacteria on aflatoxin production and expression of aflR gene in Aspergillus parasiticus. J Food Saf 38:12413. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12413
Ghanbari R, Rezaie S, Noorbakhsh F, Khaniki GJ, Soleimani M, MolaeeAghaee EM (2019) Biocontrol effect of Kluyveromyces lactis on aflatoxin expression and production in Aspergillus parasiticus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 366(10):114. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnz114
Guan S, Zhao L, Ma Q, Zhou T, Wang N, Hu X, Ji C (2010) In vitro efficacy of Myxococcus fulvus ANSM068 to biotransform aflatoxin B1. Int J Mol Sci 11(10):4063–4079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11104063
Hernandez-Mendoza A, Guzman-De-Peña D, Garcia HS (2009) Key role of teichoic acids on aflatoxin B1 binding by probiotic bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 107(2):395–403. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04217.x
Hua SST, Baker JL, Flores-Espiritu M (1999) Interactions of saprophytic yeasts with a Aspergillus flavus. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(6):2738–2740
Hua SST, Brandl MT, Hernlem B, Eng JG, Sarreal SBL (2011) Fluorescent viability stains to probe the metabolic status of aflatoxigenic fungus in dual culture of Aspergillus flavus and Pichia anomala. Mycopathologia 171(2):133–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-010-9352-z
ISIRI (2002) Food and feed-mycotoxins: maximum tolerated level, 1st edn. Institute of standards and industrial research of Iran (ISIRI )Tehran, Iran, pp 3–20
Ismail A, Levin RE, Riaz M, Akhtar S, Gong YY, De Oliveira CAF (2017) Effect of different microbial concentrations on binding of aflatoxin M1 and stability testing. Food Control 73:492–496
Jouany JP, Yiannikouris A, Bertin G (2005) The chemical bonds between mycotoxins and cell wall components of Saccharomyces cerevisiae have been identified. Arch Zootech 8:26–50
Kamkar A, Tooriyan F, Jafari M, Bagherzade M, Saadatjou S, MolaeeAghaee E (2014) antioxidant activity of methanol and ethanol extracts of Satureja hortensis L. in soybean oil. J Food Qual Hazards Control 1(4):113–119
Kong Q, Chi C, Yu J, Shan S, Li Q, Guan B, Nierman WC, Bennett JW (2014) The inhibitory effect of Bacillus megaterium on aflatoxin and cyclopiazonic acid biosynthetic pathway gene expression in Aspergillus flavus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(11):5161–5172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5632-8
Kusumaningtyas E, Widiastuti R, Maryam R (2006) Reduction of aflatoxin B1 in chicken feed by using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Rhizopus oligosporus and their combination. Mycopathologia 162(4):307–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-006-0047-4
La Penna M, Nesci A, Etcheverry M (2004) In vitro studies on the potential for biological control on Aspergillus section Flavi by Kluyveromyces spp. Lett Appl Microbiol 38(4):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765x.2003.01467.x
Lahtinen SJ, Haskard CA, Ouwehand AC, Salminen SJ, Ahokas JT (2004) Binding of aflatoxin B1 to cell wall components of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG. Food Addit Contam 21(2):158–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030310001639521
Lu L, Xie M, Wei D (2022) Biological detoxification of mycotoxins: current status and future advances. Int J Mol Sci 23(3):1064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031064
Masoud W, Kaltoft CH (2006) The effects of yeasts involved in the fermentation of Coffea arabica in East Africa on growth and ochratoxin A (OTA) production by Aspergillus ochraceus. Int J Food Microbiol 106(2):229–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.06.015
Mccormick SP (2013) Microbial detoxification of mycotoxins. J Chem Ecol 39(7):907–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-013-0321-0
Milani J, Seyed Nazari SS, Bamyar E, Maleki G (2018) Effect of bread making process on aflatoxin level changes. J Chem Health Risks 4(4):16. https://doi.org/10.22034/JCHR.2018.544078
Mingorance-Cazorla L, Clemente-Jimenez JM, Martínez-Rodríguez S, Las Heras-Vázquez FJ, Rodríguez-Vico F (2003) Contribution of different natural yeasts to the aroma of two alcoholic beverages. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19(3):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023662409828
Mohammadi Kouchesfahani M, Alimohammadi M, Jahed Khaniki G, Nabizadeh Nodehi R, Aghamohseni Z, Moazeni M, Rezaie S (2015) Antifungal effects of ozonated water on Aspergillus parasiticus: a new approach to prevent wheat contamination. J Food Saf 35:295–302. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12159
Molaee Aghaee E, Kamkar A, Akhondzadeh Basti A, Khanjari A, Kontominas MG (2016) Antimicrobial effect of garlic essential oil (Allium sativum L.) in combination with chitosan biodegradable coating films. J Med Plants 15:141–150
Moradi M, Rohani M, Fani SR, Mosavian MTH, Probst C, Khodaygan P (2020) Biocontrol potential of native yeast strains against Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin production in pistachio. Food Addit Contam Part A 37(11):1963–1973. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2020.1811901
Muñoz R, Arena ME, Silva J, González SN (2010) Inhibition of mycotoxin-producing Aspergillus nomius vsc 23 by lactic acid bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Braz J Microbiol 41(4):1019–1026
Niknejad F, Zaini F, Faramarzi M, Amini M, Kordbacheh P, Mahmoudi M, Safara M (2012) Candida parapsilosis as a potent biocontrol agent against growth and aflatoxin production by Aspergillus species. Iran J Public Health 41(10):72–80
Noroozi R, Sadeghi E, Rouhi M, Safajoo S, Razmjoo F, Paimard G, Moradi L (2020) Fates of aflatoxin B1 from wheat flour to Iranian traditional cookies: managing procedures to aflatoxin B1 reduction during traditional processing. Food Sci Nutr 8(11):6014–6022. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1888
Nout MJR (1989) Effect of Rhizopus and Neurospora spp. on growth of Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus and accumulation of aflatoxin B1 in groundnut. Mycological Res 93(4):518–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(89)80046-2
Oluwafemi F, Kumar M, Bandyopadhyay R, Ogunbanwo T, Ayanwande KB (2010) Bio-detoxification of aflatoxin B1 in artificially contaminated maize grains using lactic acid bacteria. Toxin Rev 29(3):115–122. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569543.2010.512556
Paster N, Droby S, Chalutz E, Menasherov M, Nitzan R, Wilson CL (1993) Evaluation of the potential of the yeast Pichia guilliermondii as a biocontrol agent against Aspergillus flavus and fungi of stored soya beans. Mycol Res 97(10):1201–1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(09)81285-9
Safaei P, Aghaee EM, Khaniki GJ, Afshari SAK, Rezaie S (2019) A simple and accurate PCR method for detection of genetically modified rice. Environ Health Sci 17:847–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00401-x
Shetty PH, Hald B, Jespersen L (2007) Surface binding of aflatoxin B1 by Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with potential decontaminating abilities in indigenous fermented foods. Int J Food Microbiol 113:41–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.07.013
Škrbić B, Živančev J, Đurišić-Mladenović N, Godula M (2012) Principal mycotoxins in wheat flour from the Serbian market: levels and assessment of the exposure by wheat-based products. Food Control 25(1):389–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.10.059
Tacconi C, Cucina M, Zadra C, Gigliotti G, Pezzolla D (2019) Plant nutrients recovery from aflatoxin B1 contaminated corn through co-composting. J Environ Chem Eng 7(2):103046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103046
Udomkun P, Wiredu AN, Nagle M, Muller J, Vanlauwe B, Bandyopadhyay R (2017) Innovative technologies to manage aflatoxins in foods and feeds and the profitability of application—a review. Food Control 76:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.01.008
Whipps JM, Lumsden RD (1991) Biological control of Pythium species. Biocontrol Sci Technol 1(2):75–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/09583159109355188
WHO (1993) Some naturally occurring substances: food items and constituents, heterocyclic aromatic amines and mycotoxins. World Health Organization, Geneva
Yiannikouris A, Poughon L, Cameleyre X, Dussap CG, Francois J, Bertin G, Jouany JP (2003) A novel technique to evaluate interactions between Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall and mycotoxins: application to zearalenone. Biotechnol Lett 25(10):783–789. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1023576520932
Yiannikouris A, Andre G, Poughon L, Francois J, Dussap CG, Jeminet G, Bertin G, Jouany JP (2006) Chemical and conformational study of the interactions involved in mycotoxin complexation with β-d-glucans. Biomacromol 7:1147–1155. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm050968t
Zoghia A, Khosravi-Darani K, Sohrabvandib S (2014) Surface binding of toxins and heavy metals by probiotics. Mini Rev Med Chem 14(1):84–98. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557513666131211105554
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aghamohseni, Z., Rezaie, S., Jahed Khaniki, G. et al. Antifungal activity and detoxification by Candida albicans against Aspergillus parasiticus and aflatoxin production. J Consum Prot Food Saf 17, 377–386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-022-01381-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-022-01381-1