Abstract
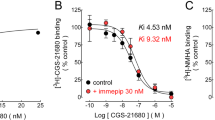
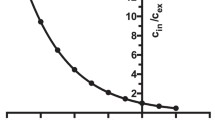
Human cerebral cortical slices and synaptosomes, guinea-pig cerebral cortical slices and human right atrial appendages were used to study the effects of SB-216641, a preferential h5-HT1B receptor ligand, and of BRL-15572, a preferential h5-HT1D receptor ligand, on the presynaptic h5-HT1B and h5-HT1B-like autoreceptors in the human and guinea-pig brain preparations, respectively, and on the presynaptic h5-HT1D heteroreceptors in the human atrium. The brain preparations, preincubated with [3H]serotonin ([3H]5-HT), and the segments of atrial appendages, preincubated with [3H]noradrenaline, were superfused with modified Krebs’ solution and tritium overflow was evoked electrically (human and guinea-pig cerebral cortex slices and human atrial appendages) or by high K+ (human cerebral cortex synaptosomes). The electrically evoked tritium overflow from guinea-pig cerebral cortex slices was reduced by the 5-HT receptor agonist 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT). This effect was not modified by BRL-15572 (2μM; concentration 154 times higher than its Ki at h5-HT1D receptors) but was antagonized by SB-216641 (0.1μM; concentration 100 times higher than its Ki at h5-HT1B receptors; apparent pA2 8.45). SB-216641 (0.1μM) by itself facilitated, whereas BRL-15572 (2μM) did not affect, the evoked overflow. In human cerebral cortex slices SB-216641 (0.1μM) also facilitated, and BRL-15572 (2μM) again failed to affect, the electrically evoked tritium overflow. In human cerebral cortical synaptosomes, 5-CT reduced the K+-evoked tritium overflow. This response was unaffected by BRL-15572 (300nM) but antagonized by SB-216641 (15nM; drug concentrations 23 and 15 times higher than their Ki at h5-HT1D and h5-HT1B receptors, respectively). Both drugs, given alone, did not modify the K+-evoked tritium overflow. In human atrial appendages, the electrically evoked tritium overflow was inhibited by 5-HT in a manner susceptible to antagonism by BRL-15572 (300nM; 23 times Ki at h5-HT1D receptors) but not by SB-216641 (30nM; 30 times Ki at h5-HT1B receptors). Both drugs by themselves did not change the electrically evoked tritium overflow. In conclusion, SB-216641 behaves as a preferential antagonist at native human 5-HT1B receptors and BRL-15572 as a preferential antagonist at native human 5-HT1D receptors. These compounds are clearly useful tools for the differentiation between human 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors in functional studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 March 1997 / Accepted: 18 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlicker, E., Fink, K., Molderings, G. et al. Effects of selective h5-HT1B (SB-216641) and h5-HT1D (BRL-15572) receptor ligands on guinea-pig and human 5-HT auto- and heteroreceptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 356, 321–327 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005057
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005057