Abstract
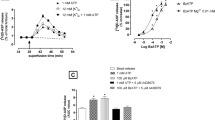
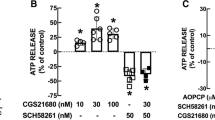
We previously reported that the activation of histamine H3 receptors (H3Rs) selectively counteracts the facilitatory action of adenosine A2A receptors (A2ARs) on GABA release from rat globus pallidus (GP) isolated nerve terminals (synaptosomes). In this work, we examined the mechanisms likely to underlie this functional interaction. Three possibilities were explored: (a) changes in receptor affinity for agonists induced by physical A2AR/H3R interaction, (b) opposite actions of A2ARs and H3Rs on depolarization-induced Ca2+ entry, and (c) an A2AR/H3R interaction at the level of adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) formation. In GP synaptosomal membranes, H3R activation with immepip reduced A2AR affinity for the agonist 2-p-(2-carboxyethyl)phenethylamino-5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine hydrochloride hydrate (CGS-21680) (Ki control 4.53 nM; + immepip 9.32 nM), whereas A2AR activation increased H3R affinity for immepip (Ki control 0.63 nM; + CGS-21680 0.26 nM). Neither A2AR activation nor H3R stimulation modified calcium entry through voltage-gated calcium channels in GP synaptosomes, as evaluated by microfluorometry. A2AR-mediated facilitation of depolarization-evoked [2,3-3H]-γ-aminobutyric acid ([3H]-GABA) release from GP synaptosomes (130.4 ± 3.6% of control values) was prevented by the PKA inhibitor H-89 and mimicked by the adenylyl cyclase activator forskolin or by 8-Bromo-cAMP, a membrane permeant cAMP analogue (169.5 ± 17.3 and 149.5 ± 14.5% of controls). H3R activation failed to reduce the facilitation of [3H]-GABA release induced by 8-Bromo-cAMP. In GP slices, A2AR activation stimulated cAMP accumulation (290% of basal) and this effect was reduced (− 75%) by H3R activation. These results indicate that in striato-pallidal nerve terminals, A2ARs and H3Rs interact at the level of cAMP formation to modulate PKA activity and thus GABA release.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A2AR:
-
Adenosine A2A receptor
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- GP:
-
Globus pallidus
- H3R:
-
Histamine H3 receptor
References
Stockwell J, Jakova E, Cayabyab FS (2017) Adenosine A1 and A2A receptors in the brain: current research and their role in neurodegeneration. Molecules 22:676
Burnstock G (2006) Historical review: ATP as a neurotransmitter. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:166–176
Wall MJ, Dale N (2007) Auto-inhibition of rat parallel fibre-Purkinje cell synapses by activity-dependent adenosine release. J Physiol 581:553–565
Fredholm BB, IJzerman AP, Jacobson KA, Linden J, Müller CE (2011) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors-an update. Pharmacol Rev 63:1–34
Bolam JP, Hanley JJ, Booth PA, Bevan MD (2000) Synaptic organisation of the basal ganglia. J Anat 196:527–542
Chan CS, Surmeier DJ, Yung WH (2005) Striatal information signaling and integration in globus pallidus: timing matters. Neurosignals 14:281–289
Bogenpohl JW, Ritter SL, Hall RA, Smith Y (2012) Adenosine A2A receptor in the monkey basal ganglia: ultrastructural localization and colocalization with the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in the striatum. J Comp Neurol 520:570–589
Fredholm BB, IJzerman AP, Jacobson KA, Klotz K-N, Linden J (2001) International Union of Pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 53:527–552
Mayfield R, Suzuki F, Zahniser NR (1993) Adenosine A2A receptor modulation of electrically evoked endogenous GABA release from slices of rat globus pallidus. J Neurochem 60:2334–2337
Dayne Mayfield R, Larson G, Orona RA, Zahniser NR (1996) Opposing actions of adenosine A2a and dopamine D2 receptor activation on GABA release in the basal ganglia: evidence for an A2a/D2 receptor interaction in globus pallidus. Synapse 22:132–138
Shindou T, Nonaka H, Richardson PJ, Mori A, Kase H, Ichimura M (2002) Presynaptic adenosine A2A receptors enhance GABAergic synaptic transmission via a cyclic AMP dependent mechanism in the rat globus pallidus. Br J Pharmacol 136:296–302
Floran B, Gonzalez B, Floran L, Erlij D, Aceves J (2005) Interactions between adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors in the control of [3H]GABA release in the globus pallidus of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 520:43–50
Diao HL, Xue Y, Han XH, Wang SY, Liu C, Chen WF, Chen L (2017) Adenosine A2A receptor modulates the activity of globus pallidus neurons in rat. Front Physiol 8:897
Panula P, Pirvola U, Auvinen S, Airaksinen MS (1989) Histamine-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat brain. Neuroscience 28:585–610
Pillot C, Heron A, Cochois V, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Ligneau X, Schwartz JC, Arrang JM (2002) A detailed mapping of the histamine H3 receptor and its gene transcripts in rat brain. Neuroscience 114:173–193
Morales-Figueroa GE, Márquez-Gómez R, González-Pantoja R, Escamilla-Sánchez J, Arias-Montaño JA (2014) Histamine H3 receptor activation counteracts adenosine A2A receptor-mediated enhancement of depolarization-evoked [3H]-GABA release from rat globus pallidus synaptosomes. ACS Chem Neurosci 5:637–645
Morales-Figueroa GE, González-Pantoja R, Escamilla-Sánchez J, Arias-Montaño JA (2017) Functional interaction between histamine H3 receptors and adenosine A2A receptors in rat striato-pallidal nerve terminals. 46th Annual Meeting, European Histamine Research Society. Inflamm Res 66 (Suppl. 1), S21
Osorio-Espinoza A, Alatorre A, Ramos-Jimenez J, Garduño-Torres B, García-Ramírez M, Querejeta E, Arias-Montaño JA (2011) Pre-synaptic histamine H3 receptors modulate glutamatergic transmission in rat globus pallidus. Neuroscience 176:20–31
Cheng Y, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (KI) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108
Flores-Clemente C, Osorio-Espinoza A, Escamilla-Sánchez J, Leurs R, Arias JM, Arias-Montaño JA (2013) A single-point mutation (Ala280Val) in the third intracellular loop alters the signalling properties of the human histamine H3 receptor stably expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Br J Pharmacol 170:127–135
Alexander SPH, Christopoulos A, Davenport AP, Kelly E, Marrion NV, Peters JA (2017) The concise guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2017/2018: G protein-coupled receptors. Br J Pharmacol 174:S17–S129
Shindou T, Mori A, Kase H, Ichimura M (2001) Adenosine A2A receptor enhances GABAA-mediated IPSCs in the rat globus pallidus. J Physiol 532:423–434
Ferrada C, Ferré S, Casadó V, Cortés A, Justinova Z, Barnes C, Canela EI, Goldberg SR, Leurs R, Lluis C, Franco R (2008) Interactions between histamine H3 and dopamine D2 receptors and the implications for striatal function. Neuropharmacology 55:190–197
Ferrada C, Moreno E, Casadó V, Bongers G, Cortés A, Mallol J, Canela EI, Leurs R, Ferré S, Lluís C, Franco R (2009) Marked changes in signal transduction upon heteromerization of dopamine D1 and histamine H3 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 157:64–75
Márquez-Gómez R, Robins MT, Gutiérrez-Rodelo C, Arias JM, Olivares-Reyes JA, van Rijn RM, Arias-Montaño JA (2018) Functional histamine H3 and adenosine A2A receptor heteromers in recombinant cells and rat striatum. Pharmacol Res 129:515–525
Nguyen MD, Lee ST, Ross AE, Ryals M, Choudhry VI, Venton BJ (2014) Characterization of spontaneous, transient adenosine release in the caudate-putamen and prefrontal cortex. PLoS One 9:e87165
Lee ST, Venton BJ (2018) Regional variations of spontaneous, transient adenosine release in brain slices. ACS Chem Neurosci 9:505–513
Takeshita Y, Watanabe T, Sakata T, Munakata M, Ishibashi H, Akaike N (1998) Histamine modulates high-voltage-activated calcium channels in neurons dissociated from the rat tuberomammillary nucleus. Neuroscience 87:797–805
Molina-Hernandez A, Nunez A, Sierra JJ, Arias-Montano JA (2001) Histamine H3 receptor activation inhibits glutamate release from rat striatal synaptosomes. Neuropharmacology 41:928–934
De Waard M, Hering J, Weiss N, Feltz A (2005) How do G proteins directly control neuronal Ca2+ channel function? Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:427–436
Gubitz AK, Widdowson L, Kurokawa M, Kirkpatrick KA, Richardson PJ (1996) Dual signalling by the adenosine A2a receptor involves activation of both N- and P-type calcium channels by different G proteins and protein kinases in the same striatal nerve terminals. J Neurochem 67:374–381
Cunha RA, Ribeiro JA (2000) Purinergic modulation of [3H]GABA release from rat hippocampal nerve terminals. Neuropharmacology 39:1156–1167
Arias-Montano J-A, Floran B, Garcia M, Aceves J, Young J-M (2001) Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of depolarization-induced, dopamine D1 receptor-dependent release of [3H]-gamma-aminobutyric acid from rat striatal slices. Br J Pharmacol 133:165–171
Arias-Montano J-A, Floran B, Floran L, Aceves J, Young J-M (2007) Dopamine D1 receptor facilitation of depolarization-induced release of gamma-amino-butyric acid in rat striatum is mediated by the cAMP/PKA pathway and involves P/Q-type calcium channels. Synapse 61:310–319
Oliveira L, Costa AC, Noronha-Matos JB, Silva I, Cavalcante WL, Timóteo MA, Corrado AP, Dal Belo CA, Ambiel CR, Alves-do-Prado W, Correia-de-Sá P (2015) Amplification of neuromuscular transmission by methylprednisolone involves activation of presynaptic facilitatory adenosine A2A receptors and redistribution of synaptic vesicles. Neuropharmacology 89:64–76
Ibrisimovic E, Drobny H, Yang Q, Höfer T, Boehm S, Nanoff C, Schicker K (2012) Constitutive activity of the A2A adenosine receptor and compartmentalised cyclic AMP signalling fine-tune noradrenaline release. Purinergic Signal 8:677–692
Seino S, Shibasaki T (2005) PKA-dependent and PKA-independent pathways for cAMP-regulated exocytosis. Physiol Rev 85:1303–1342
Matsumoto JP, Almeida MG, Castilho-Martins EA, Costa MA, Fior-Chadi DR (2014) Protein kinase a mediates adenosine A2a receptor modulation of neurotransmitter release via synapsin I phosphorylation in cultured cells from medulla oblongata. Neurosci Res 85:1–11
Bouabid S, Zhou FM (2018) Cyclic AMP-producing chemogenetic activation of indirect pathway striatal projection neurons and the downstream effects on the globus pallidus and subthalamic nucleus in freely moving mice. J Neurochem 145:436–448
Acknowledgements
G.-E.M.-F. and N.R.R. held Conacyt pre-doctoral scholarships.
Funding
This study was supported by Cinvestav and Conacyt (grant 220448 to J.-A.A.-M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.-E.M.-F., E.J.G., and J.-A.A.-M. designed the study. G.-E.M.-F., J.E.-S., R.G.-P., U.G.-H., and N.R.-R. conducted experiments. G.-E.M.-F. and J.-A.A.-M. performed data analysis. G.-E.M.-F. and J.-A.A.-M. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they do not have any actual or potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures were approved by the Cinvestav Animal Care Committee and followed the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals issued by the National Institutes of Health (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978) and the Mexican Council for Animal Care (NOM-062-ZOO-1999).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morales-Figueroa, GE., Rivera-Ramírez, N., González-Pantoja, R. et al. Adenosine A2A and histamine H3 receptors interact at the cAMP/PKA pathway to modulate depolarization-evoked [3H]-GABA release from rat striato-pallidal terminals. Purinergic Signalling 15, 85–93 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-018-9638-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-018-9638-z