Abstract
The objective of this work was to obtain a resistance gene analog from the TcLr35 wheat line. The 5’ and 3’ ends of the resistance gene homology fragment S2A2 from TcLr35 were obtained by rapid amplification cDNA ends (RACE), and a 3476-bp full length cDNA was obtained using gene specific primers based on the spliced sequence. Its deduced 866 amino acid sequence has the characteristic NBS-LRR domains of plant resistance gene products and includes a coiled-coil (CC) region typical of monocots. The genomic DNA sequence shows the presence of three exons and two short introns upstream of the predicted stop codon. BLASTp analysis indicates a considerable identity of S2A2 with a cloned barley NBS-LRR resistance gene homology sequence and a lower similarity with wheat leaf rust resistance genes Lr1, Lr21, Lr34, and Lr10. The S2A2 gene appeared not to be induced by Puccinia triticina and was a constitutive gene with low abundance in the wheat leaf tissue by semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alliffe MA & Lagudah ES, 2004. Molecular genetics of disease resistance in cereals. Ann Botany 94, 765–773.
Bai J, Pennill LA, Ning J, Lee SW, Ramalingam J, Webb CA, Zhao B, Sun Q, Nelson JC, Leach JE & Hulber SH, 2002. Diversity in nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes in cereals. Genome Res 12, 1871–1884.
Calenge F, Linden Van der CG, Schouten E, Arkel GV & Durel CD, 2005. Resistance gene analogues identified through the NBS-profiling method map close to major genes and QTL for disease resistance in apple. Theor Appl Genet 110, 660–668.
Cloutier S, McCallum BD, Loutrec C, Banks TW, Wicker T, Feuillet C, Keller B & Jordan MC, 2007. Leaf rust resistance gene Lr1, isolated from bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a member of the large psr567 gene family. Plant Mol Biol 65, 93–106.
Dangl JL & Jones JDG, 2001. Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411, 826–833.
Dildirligi M & Gill KS, 2004. Identification and analysis of expressed resistance gene sequences in wheat. Plant Mol Biol 48, 575–608.
Feuillet C, Travella S, Stein N, Albar L, Nublat A & Keller B, 2003. Map-based isolation of the leaf rust disease resistance gene Lr10 from the hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 15253–15258.
Gennaro A, Koebner R & Ceoloni C, 2009. A candidate for Lr19, an exotic gene conditioning leaf rust resistance in wheat. Funct Integr Genomics 9, 325–334.
Hammond-Kosack KE & Parker JE, 2003. Deciphering plant-pathogen communications: free perspectives for molecular resistance breeding. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14, 177–193.
He LM, Du CG, Covaleda L, Xu ZY, Robinson AF, Yu JZ, Kohel RJ & Zhang HB, 2004. Cloning, characterization, and evolution of the NBS-LRR-encoding resistance gene analogue family in polyploidy cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L). Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17, 1234–1241.
Huang L, Steven A, Wanlong L, Fellers JP, Trick HN & Gill BS, 2003. Map-based cloning of leaf rust resistance gene Lr21 from the large and polyploid genome of bread wheat. Genetics 164, 655–664.
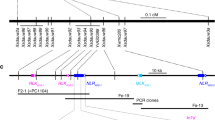
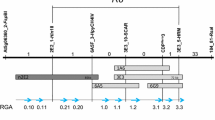
Julia G, 1999. Development of a molecular marker for rust resistance genes Sr39 and Lr35 in wheat breeding lines. Electron J Biotech 2, 35–40.
Kerber ER & Dyck PL, 1990. Transfer to hexaploid wheat of linked genes for adult-plant leaf rust and seeding stem rust resistance from an amphiploid of Aegilops speltoides x Triti-cum monococcum. Genome 33, 530–537.
Kolmer JA, Jin Y & Long DL, 2007. Wheat leaf and stem rust in the United States. Aust J Agric Res 58, 631–638.
Krattinger SG, Lagudah ES, Spielmeyer W, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, McFadden H, Selter LL & Keller B, 2009. A multi-pathogen resistance QTL in wheat is controlled by a single gene. Science 323, 1360–1363.
Linden C, Wouters D, Mihalka V, Kochieva E & Smulders V, 2004. Efficient targeting of plant disease resistance loci using NBS-profiling. Theor Appl Genet 109, 384–393.
Lukasik E & Takken FFW, 2009. STANDing strong, resistance proteins instigators of plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12, 1–10.
McHale L, Tan X, Koehl P & Michelmore RW, 2006. Plant NBS-LRR proteins: adaptable guards. Genome Biol 7, 212.
Meyers BC, Dickerman AW, Michelmore RW, Sivaramakrishnan S, Sobral BW & Young ND, 1999. Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding superfamily. Plant J 20, 317–332.
McIntosh RA, Wellings CR & Park RF, 1995. Wheat rusts: an atlas of resistance genes. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Pan Q, Wendel J & Fluhr R, 2000. Divergent evolution of plant NBS-LRR resistance gene homologues in dicot and cereal genomes. J Mol Evol 50, 203–213.
Seyfarth R, Feuillet C, Schachermayr G, Winzeler M & Keller B, 1999. Development of a molecular marker for the adult plant leaf rust resistance gene Lr35 in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 99, 554–560.
Tanhuanpaa P, 2004. Identification and mapping of resistance gene analogs and a white rust resistance locus in Brassica rapa ssp. Oleifera. Theor Appl Genet 108, 1039–1046.
Tian Y, Fan L, Thurau T, Jung C & Cai D, 2004. The absence of TIR-type resistance gene analogues in the sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) genome. J Mol Evol 58, 40–53.
Wang HY, Yang WX & Liu DQ, 2006. Isolation and characterization of NBS-LRR resistance gene homology sequences from wheat. Sci Agric Sinica 39, 1558–1564.
Xu Q, Wen X & Deng XX, 2005. Isolation of TIR and non TIR NBS-LRR resistance gene analogues and identification of molecular markers linked to a powdery mildew resistance locus in chestnut rose (Rosa roxburghii Tratt). Theor Appl Genet 111, 819–830.
Yu YG, Buss GR & Maroof MA, 1996. Isolation of a superfamily of candidate disease-resistance genes in soybean based on a conserved nucleotide-binding site. Proc Natl Sci USA 93, 11751–11756.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H.Y., Liu, D.Q. & Yang, W.X. A wheat disease resistance gene analog of the NBS-LRR class: identification and analysis. J Plant Dis Prot 118, 63–68 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356383
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356383