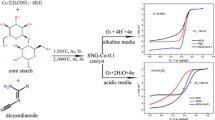
Abstract
Because of the low energy requirement and the environmentally safe byproducts, the capacitive deionization water desalination technology has attracted the attention of many researchers. The important requirements for electrode materials are good electrical conductivity, high surface area, good chemical stability and high specific capacitance. In this study, metallic nanoparticles that are encapsulated in a graphite shell (Cd-doped Co/C NPs) are introduced as the new electrode material for the capacitive deionization process because they have higher specific capacitance than the pristine carbonaceous materials. Cd-doped Co/C NPs perform better than graphene and the activated carbon. The introduced nanoparticles were synthesized using a simple sol-gel technique. A typical sol-gel composed of cadmium acetate, cobalt acetate and poly(vinyl alcohol) was prepared based on the polycondensation property of the acetates. The physiochemical characterizations that were used confirmed that the drying, grinding and calcination in an Ar atmosphere of the prepared gel produced the Cd-doped Co nanoparticles, which were encapsulated in a thin graphite layer. Overall, the present study suggests a new method to effectively use the encapsulated bimetallic nanostructures in the capacitive deionization technology.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
A. D. Khawaji, I. K. Kutubkhanah and J. M. Wie, “Advances in seawater desalination technologies”, Desalination 221(1), 47–69 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.067
T. Welgemoed and C. Schutte, “Capacitive deionization technology™: an alternative desalination solution”, Desalination 183(1), 327–340 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.02.054
H. Li, L. Pan, C. Nie, Y. Liu and Z. Sun, “Reduced graphene oxide and activated carbon composites for capacitive deionization”, J. Mater. Chem. 22(31), 15556–15561 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2jm32207b
J. K. Edzwald and J. Haarhoff, “Seawater pretreatment for reverse osmosis: chemistry, contaminants, and coagulation”, Water Res. 45(17), 5428–5440 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.014
R. Semiat, “Energy issues in desalination processes”, Environ. Sci. Technol. 42(22), 8193–8201 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/es801330u
A. Subramani, M. Badruzzaman, J. Oppenheimer and J. G. Jacangelo, “Energy minimization strategies and renewable energy utilization for desalination: a review”, Water Res. 45(5), 1907–1920 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.12.032
Y. Oren, “Capacitive deionization (CDI) for desalination and water treatment—past, present and future (a review)”, Desalination 228(1), 10–29 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.08.005
L. Zou, L. Li, H. Song and G. Morris, “Using mesoporous carbon electrodes for brackish water desalination”, Water Res. 42(8), 2340–2348 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.12.022
I. Villar, S. Roldan, V. Ruiz, M. Granda, C. Blanco, R. Menéndez and R. Santamaría, “Capacitive Deionization of NaCl Solutions with Modified Activated Carbon Electrodes”, Energy Fuels. 24(6), 3329–3333 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ef901453q
Y. J. Kim and J. H. Choi, “Enhanced desalination efficiency in capacitive deionization with an ion-selective membrane”, Sep. Purif. Technol. 71(1), 70–75 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.10.026
L. Zou, G. Morris and D. Qi, “Using activated carbon electrode in electrosorptive deionisation of brackish water”, Desalination 225(1), 329–340 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.07.014
C. J. Gabelich, T. D. Tran and I. H. Suffet, “Electrosorption of inorganic salts from aqueous solution using carbon aerogels”, Environ. Sci. Technol. 36(13), 3010–3019 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/es0112745
P. Xu, J. E. Drewes, D. Heil and G. Wang, “Treatment of brackish produced water using carbon aerogel-based capacitive deionization technology”, Water Res. 42(10), 2605–2617 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.01.011
L. Pan, X. Wang, Y. Gao, Y. Zhang, Y. Chen and Z. Sun, “Electrosorption of anions with carbon nanotube and nanofibre composite film electrodes”, Desalination 244(1), 139–143 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.05.019
L. Li, L. Zou, H. Song and G. Morris, “Ordered mesoporous carbons synthesized by a modified sol—gel process for electrosorptive removal of sodium chloride”, Carbon 47(3), 775–781 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2008.11.012
H. Li, L. Zou, L. Pan and Z. Sun, “Using graphene nano-flakes as electrodes to remove ferric ions by capacitive deionization”, Sep. Purif. Technol. 75(1), 8–14 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2010.07.003
J. Yang, L. Zou, H. Song and Z. Hao, “Development of novel MnO2/nanoporous carbon composite electrodes in capacitive deionization technology”, Desalination 276(1), 199–206 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.03.044
Z. Wang, L. Yue, Z.-T. Liu, Z.-H. Liu and Z. Hao, “Functional graphene nanocomposite as an electrode for the capacitive removal of FeCl3 from water”, J. Mater. Chem. 22(28), 14101–14107 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2jm32175k
D. Zhang, X. Wen, L. Y. Shi, T. Yan and J. Zhang, “Enhanced capacitive deionization of graphene/mesoporous carbon composites”, Nanoscale 4(17), 5440–5446 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2nr31154b
J. Yang, L. Zou and H. Song, “Preparing MnO2/PSS/CNTs composite electrodes by layer-by-layer deposition of MnO2 in the membrane capacitive deionisation”, Desalination 286, 108–114 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.013
M. T. Z. Myint and J. Dutta, “Fabrication of zinc oxide nanorods modified activated carbon cloth electrode for desalination of brackish water using capacitive deionization approach”, Desalination 305, 24–30 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2012.08.010
M.-W. Ryoo and G. Seo, “Improvement in capacitive deionization function of activated carbon cloth by titania modification”, Water Res. 37(7), 1527–1534 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00531-6
M. W. Ryoo, J. H. Kim and G. Seo, “Role of titania incorporated on activated carbon cloth for capacitive deionization of NaCl solution”, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 264(2), 414–419 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00375-8
N. A. Barakat, K. A. Khalil and H. Y. Kim, “Toward facile synthesizing of diamond nanostructures via nanotechnological approach: Lonsdaleite carbon nanofibers by electrospinning”, Mater. Res. Bull. 47(9), 2140–2147 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.06.012
N. A. M. Barakat, B. Kim, S. J. Park, Y. Jo, M.-H. Jung and H. Y. Kim, “Cobalt nanofibers encapsulated in a graphite shell by an electrospinning process”, J. Mater. Chem. 19(39), 7371–7378 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b904669k
N. A. M. Barakat, A. G. El-Deen, G. Shin, M. Park and H. Y. Kim, “Novel Cd-doped Co/C nanoparticles for electrochemical supercapacitors”, Mater. Lett. 99, 168-171 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.03.034
S. Park and R. S. Ruoff, “Chemical methods for the production of graphenes”, Nat. Nanotechnol. 4(4), 217–224 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.58
Y. Xu, H. Bai, G. Lu, C. Li and G. Shi, “Flexible graphene films via the filtration of water-soluble noncovalent functionalized graphene sheets”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(18), 5856–5857 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja800745y
W. S. Hummers Jr and R. E. Offeman, “Preparation of graphitic oxide”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80(6), 1339–1339 (1958). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja01539a017
A. Yousef, N. A. M. Barakat, T. Amna, A. R. Unnithan, S. S. Al-Deyab and H. Yong Kim, “Influence of CdO-doping on the photoluminescence properties of ZnO nanofibers: effective visible light photocatalyst for waste water treatment”, J. Lumin. 132(7), 1668–1677 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2012.02.031
N. A. M. Barakat, M. F. Abadir, K. T. Nam, A. M. Hamza, S. S. Al-Deyab, W. I. Baek and H. Y. Kim, “Synthesis and film formation of iron-cobalt nanofibers encapsulated in graphite shell: magnetic, electric and optical properties study”, J. Mater. Chem. 21(29), 10957–10964 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c1jm00052g
N. A. M. Barakat, K. A. Khalil, I. H. Mahmoud, M. A. Kanjwal, F. A. Sheikh and H. Y. Kim, “CoNi Bimetallic Nanofibers by Electrospinning: Nickel-Based Soft Magnetic Material with Improved Magnetic Properties”, J. Phys. Chem. C 114(37), 15589–15593 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp1041074
N. A. M. Barakat, B. Kim and H. Y. Kim, “Production of Smooth and Pure Nickel Metal Nanofibers by the Electrospinning Technique: Nanofibers Possess Splendid Magnetic Properties”, J. Phys. Chem. C 113(2), 531–536 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp805692r
B. Malecka, “Thermal decomposition of Cd (CH3COO)2·H2O studied by a coupled TG-DTA-MS method”, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 78(2), 535–544 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/B:JTAN.0000046117.25037.5a
T. Wanjun and C. Donghua, “Mechanism of thermal decomposition of cobalt acetate tetrahydrate”, Chem. Pap. 61(4), 329–332 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.2478/s11696-007-0042-3.
N. McIntyre and M. Cook, “X-ray photoelectron studies on some oxides and hydroxides of cobalt, nickel, and copper”, Anal. Chem. 47(13), 2208–2213 (1975). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ac60363a034
G. Hota, S. Idage and K. C. Khilar, “Characterization of nano-sized CdS-Ag2S core-shell nanoparticles using XPS technique”, Colloids Surf. A 293(1), 5–12 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.06.036
A. Gulino, F. Castelli, P. Dapporto, P. Rossi and I. Fragalá, “Synthesis and characterization of thin films of cadmium oxide”, Chem. Mater. 14(2), 704–709 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cm011175q
J. Chang, R. S. Mane, D. Ham, W. Lee, B. W. Cho, J. K. Lee and S. H. Han, “Electrochemical capacitive properties of cadmium oxide films”, Electrochim. Acta 53(2), 695–699 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.07.056
Pierre Delhaes, “Graphite and Precursors (World of Carbon)”, CRC Press, Edition 1 (2001).
S. Stankovich, D. A. Dikin, R. D. Piner, K. A. Kohlhaas, A. Kleinhammes, Y. Jia, Y. Wu, S. B. T. Nguyen and R. S. Ruoff, “Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide”, Carbon 45(7), 1558–1565 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2007.02.034
Y. Zhu, S. Murali, W. Cai, X. Li, J. W. Suk, J. R. Potts and R. S. Ruoff, “Graphene and graphene oxide: synthesis, properties, and applications”, Adv. Mater. 22(35), 3906–3924 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adma.201001068
S. Stankovich, R. D. Piner, X. Chen, N. Wu, S. T. Nguyen and R. S. Ruoff, “Stable aqueous dispersions of graphitic nanoplatelets via the reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide in the presence of poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate)”, J. Mater. Chem. 16(2), 155–158 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b512799h
C. F. Chang, Q. D. Truong and J. R. Chen, “Graphene sheets synthesized by ionic-liquid-assisted electrolysis for application in water purification”, Appl. Surf. Sci. 264, 329–334 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.10.022
A. B. Bourlinos, D. Gournis, D. Petridis, T. Szabó, A. Szeri and I. Dékány, “Graphite oxide: chemical reduction to graphite and surface modification with primary aliphatic amines and amino acids”, Langmuir 19(15), 6050–6055 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/la026525h
F. Tuinstra and J. Koenig, “Characterization of graphite fiber surfaces with Raman spectroscopy”, J. Compos. Mater. 4(4), 492–499 (1970). http://jcm.sagepub.com/content/4/4/492
G. Wang, C. Pan, L. Wang, Q. Dong, C. Yu, Z. Zhao and J. Qiu, “Activated carbon nanofiber webs made by electrospinning for capacitive deionization”, Electrochim. Acta 69(1), 65–70 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.02.066
B. H. Park and J. H. Choi, “Improvement in the capacitance of a carbon electrode prepared using water-soluble polymer binder for a capacitive deionization application”, Electrochim. Acta 55(8), 2888–2893 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.12.084
J. Chmiola, G. Yushin, R. K. Dash, E. N. Hoffman, J. E. Fischer, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, “Double-layer capacitance of carbide derived carbons in sulfuric acid”, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 8(7), A357–A360 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1149/1.1921134
L. L. Zhang, T. Wei, W. Wang and X. Zhao, “Manganese oxide-carbon composite as supercapacitor electrode materials”, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 123(1), 260–267 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.04.008
J. Li, Q. M. Yang and I. Zhitomirsky, “Nickel foam-based manganese dioxide-carbon nanotube composite electrodes for electrochemical supercapacitors”, J. Power Sources 185(2), 1569–1574 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.07.057
A.G. El-Deen, N.A. Barakat, K.A. Khalil and H.Y. Kim, ‘Development of Multi-Channel Carbon Nanofibers as Effective Electrosorptive Electrodes for a Capacitive Deionization Process’, Journal of Materials Chemistry A 1(36), 11001–11010 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C3TA12450A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
To view a copy of this licence, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Barakat, N.A.M., Khalil, K.A., El-Deen, A.G. et al. Development of Cd-doped Co Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Graphite Shell as Novel Electrode Material for the Capacitive Deionization Technology. Nano-Micro Lett. 5, 303–313 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03353762
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03353762