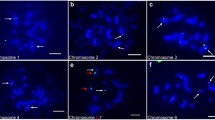
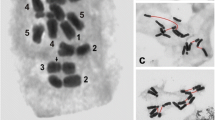
Abstract
The present study is a rare example of a detailed characterization of chromosomal aberrations by identification of individual chromosomes (or chromosome arms) involved in their formation in plant cells by using fluorescentin situ hybridization (FISH). In addition, the first application of more than 2 DNA probes in FISH experiments in order to analyse chromosomal aberrations in plant cells is presented. Simultaneous FISH with 5S and 25S rDNA and, after reprobing of preparations, telomeric and centromeric DNA sequences as probes, were used to compare the cytogenetic effects of 2 chemical mutagens: N-nitroso-N-methylurea (MNU) and maleic hydrazide (MH) on root tip meristem cells ofHordeum vulgare (2n = 14). The micronucleus (MN) test combined with FISH allowed the quantitative analysis of the involvement of specific chromosome fragments in micronuclei formation and thus enabled the possible origin of mutagen-induced micronuclei to be explained. Terminal deletions were most frequently caused by MH and MNU. The analysis of the frequency of micronuclei with signals of the investigated DNA probes showed differences between the frequency of MH- and MNU-induced micronuclei with specific signals. The micronuclei with 2 signals, telomeric DNA and rDNA (5S and/or 25S rDNA), were the most frequently observed in the case of both mutagens, but with a higher frequency after treatment with MH (46%) than MNU (37%). Also, 10% of MH-induced micronuclei were characterized by the presence of only telomere DNA sequences, whereas there were almost 3-fold more in the case of MNU-induced micronuclei (28%). Additionally, by using FISH with the same probes, an attempt was made to identify the origin of chromosome fragments in mitotic anaphase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams SP, Leitch IL, Bennett MD, Leitch AR, 2000.Aloe L.-a second plant family without (TTTAGGG)n telomeres. Chromosoma 109: 201–205.
Andersson H, Kihlman BA, 1987. Localization of chemically induced chromosomal aberrations in three different karyotypes ofVicia faba. Hereditas 107: 15–25.
Aragon-Alcaide L, Miller T, Schwarzacher T, Reader S, Moore G, 1996. A cereal centromeric sequence. Chromosoma 105: 261–268.
Dias VM, Manelli-Oliveira R, Machado-Santelli GM, 2005. Using fluorescence for improvement of the quantitative analysis of micronucleus in cell culture. Mutation Res 565: 173–179.
Fajkus J, Sykorova E, Leitch AR, 2005. Telomeres in evolution and evolution in telomeres. Chromosome Res 13: 469–479.
Gerlach WL, Dyer TA, 1980. Sequence organization of the repeating units in the nucleus in wheat which contain 5S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 4851–4865.
Hasterok R, Jenkins G, Langdon T, Jones RN, 2002a. The nature and destiny of translocated B-chromosome-specific satellite DNA of rye. Chromosome Res 10: 83–86.
Hasterok R, Langdon T, Taylor S, Jenkins G, 2002b. Combinatorial labeling of DNA probes enables multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization in plants. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 40: 319–323.
Heslop-Harrison JS, Harrison GE, Leitch IJ, 1992. Reprobing of DNA:DNAin situ hybridization preparations. Trends Genet 8: 372–373.
Jovtchev G, Menke M, Schubert I, 2001. The comet assay detects adaptation to MNU-induced DNA damage in barley. Mutation Res 493: 95–100.
Jovtchev G, Stergios M, Schubert I, 2002. A comparison of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced chromatid aberrations and micronuclei in barley meristems using FISH techniques. Mutation Res 517: 47–51.
Kanaya N, Gill BS, Grover IS, Murin A, Osiecka R, Sandhu SS, Andersson HC, 1994.Vicia faba chromosomal aberration assay. Mutation Res 310: 231–247.
Kirsch-Volders M, Elhajouji A, Cundari E, Hummelen PV, 1997. The in vitro micronucleus test: a multi-endpoint assay to detect simultaneously mitotic delay, apoptosis, chromosome breakage, chromosome loss and non-disjunction, Mutation Res 392: 19–30.
Leitch IJ, Heslop-Harrison S, 1993. Physical mapping of five sites of 18S-5.8S-26S rRNA genes in barley byin situ hybridization. Barley Genet Newsletter 21: 54–56.
Maluszynska J, Maluszynski M, 1983. The influence of MNUA and MH on the cell cycle and DNA contents in meristematic cells of barley. Acta Biologica 11: 227–237.
Maluszynska J, Heslop-Harrison JS, 1991. Localization of tandemly repeated DNA sequencesin Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 1: 159–166.
Maluszynska J, Juchimiuk J, Wolny E, 2003. Chromosomal aberrations inCrepis capillaris cells detected by FISH. Folia Histochem et Cytobiol 41: 101–104.
Mann SK, Brat SV, Mhach S, 1975. Effect of maleic hydrazide onmitosis, ActaBotanica Indica 2: 44–48.
Marcano L, Carruya A, Del Campo A, Montiel X, 2004. Cytotoxity and mode of action of maleic hydrazide in root tips ofAllium cepa. Environ Res 94: 221–226.
Marshall RR, Murphy M, Kirkland DJ, Bentley KB, 1996. Fluorescencein situ hybridization with chromosome-specific centromeric probes: a sensitive method to detect aneuploidy. Mutation Res 372: 233–245.
Natarajan AT, Boei JJWA, 2003. Formation of chromosome aberrations: insight from FISH. Mutation Res 544: 299–304.
Norppa H, Falck GCM, 2003. What do human micronuclei contain? Mutagenesis 18: 221–233.
Schubert I, 1992. Telomeric polymorphism inVicia faba. Biol Zentralbl 111: 164–168.
Schubert I, Shi F, Fuchs J, Endo TR, 1998. An efficient screening for terminal deletions and translocations of barley chromosomes added to common wheat. The Plant J 14: 104–108.
Schubert I, Pecinka A, Meister A, Schubert V, Klatte M, Jovtchev G, 2004. DNA damage processing and aberration formation in plants. Cytogenet Genome Res 104: 489–495.
Schuler MG, Rupa DS, Eastmond DA, 1997. A critical evaluation of centromeric labeling to distinguish micronuclei induced by chromosomal loss and breakage in vitro. Mutation Res 393: 81–95.
Siroky J, Zluvova J, Riha K, Shippen DE, Vyskot B, 2003. Rearrangements of ribosomal DNA clusters in late generation telomerase-deficientArabidopsis. Chromosoma 112: 116–123.
Sugihara T, Sawada S, Hakura A, Hori Y, Uchida K, Sagami F, 2000. A staining procedure for micronucleus test using methylene blue and acridine orange specimens that are supravitally stained with possible long-term storage. Mutation Res 470: 103–108.
Taketa S, Harrison GE, Heslop-Harrison JS, 1999. Comparative physical mapping of the 5S and 18S-25S rDNA in nine wildHordeum species and cytotypes. Theor Appl Genet 98: 1–9.
Unfriend I, Gruendler P, 1990. Nucleotide sequence of the 5.8S and 25S rRNA genes and of the internal transcribed spacers fromArabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acid Res 18: 4011.
Weiss H, Maluszynska J, 2000. Chromosomal rearrangement in autotetraploid plants ofArabidopsis thaliana. Hereditas 133: 255–261.
Weiss H, Maluszynska J, 2001. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of polyploidization in the anther tapetum of diploid and autotetraploidArabidopsis thaliana plants. Annals of Botany 87: 729–735.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juchimiuk, J., Hering, B. & Maluszynska, J. Multicolour FISH in an analysis of chromosome aberrations induced by N-nitroso-N-methylurea and maleic hydrazide in barley cells. J Appl Genet 48, 99–106 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03194666
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03194666