Summary
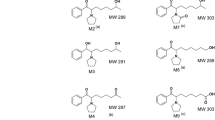
The urinary recovery (p.o.) and pharmacokinetics (i.v. and p.o.) of two compounds from the 1-hydroxyalkyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one series. 1-(2′-hydroxyethyl)-2-ethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one (CP102) and 1-(3′-hydroxypropyl)-2-ethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one (CP106) were studied in the rat. The pharmacokinetics of the 1-carboxyethyl metabolite (CP110) of CP106 was also studied (i.v.). CP102 was not metabolised to any considerable extent with 68.4±12.2% of the administered dose recovered unchanged in rat urine. In contrast. CP106 undergoes extensive phase I metabolism to form the 1-carboxyalkyl metabolite which accounted for 56.4±11% of the administered dose with 22.0±1.0% as unchanged drug. Intravenous and oral pharmacokinetics of CP102 and CP106 were studied in the rat at 450 μmoles/kg. The AUCs of CP102 and CP106 after bolus i.v. infusion were 458±38 and 171±20 μmoles/l.h. The AUC values after bolus oral administration were 318±46 and 77±18 μmoles/l.h, respectively, with corresponding bioavailabilities (F) of 0.69 and 0.45. The Cmax of CP102 and CP106 were 142±25 and 70±15 μmoles/l with Tmax values of 0.75±0.15 and 0.50±0.10 h, respectively. The CL, MRT and Vdss of CP102 was 1.00±0.09 l/kg/h, 0.92±0.04 h and 0.91±0.05 l/kg, respectively. The corresponding pharmacokinetic parameters for CP106 were 2.64±0.20 l/kg/h, 0.42±0.12 h and 1.12±0.26 l/kg, respectively. Renal clearance (CLR) of CP102 and CP106 were 1.00±0.18 l/kg and 1.27±0.31 l/kg respectively. The pharmacokinetics of CP110, which was conducted by the i.v. route only at a dose of 450 μmoles/kg, had an AUC of 289±46 μmoles/l.h, CL of 1.56±0.29 l/kg/h, MRT of 0.25±0.09 h and Vdss of 0.40±0.13 l/kg, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh S., Hider R.C. (1994): Therapeutic iron-chelating agents. In: Rice-Evans C.A., Burdon R.H. (Eds). Free Radical Damage and its Control. Amsterdam, Elsevier, pp. 189–213.
Hider R.C., Singh S., Porter J.B., Huehns E.R. (1990): The development of hydroxypyridin-4-ones as orally active iron chelators. Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 612, 327–338.
Pippard M.J., Letsky E.A., Callender S.T., Weatherall D.J. (1978): Prevention of iron loading in transfusion-dependent thalassaemia. Lancet, i, 1178–1180.
Propper R.D., Cooper B., Rufo R., et al. (1977): Continuous subcutaneous administration of desferrioxamine in thalassaemia major. N. Engl. J. Med., 297, 418–423.
Lee P., Mohammed N., Marshall L., et al. (1993): Intravenous infusion pharmacokinetics of desferrioxamine in thalassaemic patients. Drug Metab. Dispos., 21, 640–644.
Hider R.C., Porter J.B., Singh S. (1994): The design of therapeutically useful iron chelators. In: Bergeron R.J., Brittenham G.M. (Eds), The Development of Iron Chelators for Clinical Use, Florida, CRC Press, pp. 353–371.
Porter J.B., Huehns E.R., Hider R.C. (1989): The development of iron chelating drugs. Ballieres Clin. Haematol., 2, 257–292.
Kontoghiorghes G.J., Aldouri M.A., Hoffbrand A.V., et al. (1987): Effective chelation of iron in β-thalassaemia with the oral iron chelator 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one. BMJ, 295, 1509–1512.
Oliveri N.F., Koren G., Hermann C., et al. (1990): Comparison of oral iron chelator L1 and desferrioxamine in iron-loaded patients. Lancet, 336, 1275.
Agarwal M.B., Gupta S.S., Visvanathan C., et al. (1992): Longterm assessment of efficacy and safety of L1, an oral iron chelator in transfusion dependent thalassaemia: Indian trial. Br. J. Haematol., 82, 460–466.
Tondury P., Kontoghiorghes G.J., Ridolfi-Luthy A., et al. (1990): L1 (1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one) for oral iron chelation in patients with β-thalassaemia major. Br. J. Haematol., 76, 550.
Porter J.B., Abeysinghe R.D., Barra C., et al. (1991): Oral efficacy and metabolism of 1,2-diethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one in thalassaemia major (Abstract). Blood, 78, 2071.
Singh S., Epemolu R.O., Dobbin P.S., et al. (1992): Urinary metabolic profiles in man and rat of 1,2-dimethyl- and 1,2-diethyl substituted 3-hydroxypyridin-4-ones. Drug Metab. Dispos., 20, 25.
Singh S., Epemolu R.O., Ackerman R., Porter J.B., Hider R.C. (1992): Development of 3-hydroxypyridin-4-ones which do not undergo extensive phase II metabolism, 3rd NIH-Sponsored Symposium on The Development of Iron Chelators for Clinical Use, Gainsville, FL, Abstract # 52.
Singh S. (1994): Therapeutically useful iron chelators, Chem. Ind., 452–455.
Dobbin P.S., Hider R.C., Hall A.D., et al. (1993): Synthesis, physiochemical properties and biological evaluation of N-substituted 2-alkyl-3-hydroxy-4-(1H)-pyridinones: orally active iron chelators with clinical potential. J. Med. Chem., 36, 2448–2458.
Jin Y., Singh S., Epemolu R.O., et al. (1993): CP102; a potent orally active iron chelator. Proceedings of the European Iron Club Meeting, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Choudhury, R., Epemolu, R.O. et al. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of 1-(2′-hydroxyethyl)- and 1-(3′-hydroxypropyl)-2-ethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-ones in the rat. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 21, 33–41 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190276
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190276