Abstract
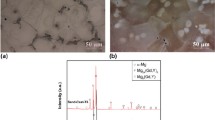
The fatigue crack growth behavior of Al−Si−Mg sand cast alloys has been investigated with reference to the effects of solidification structure and aging condition. Fatigue crack growth tests have been carried out under constant load amplitude and a stress ratio of R=0.1 using CT specimens. The amount of pores in the matrix was limited by performing HIP treatment. The pores tended to promote deflection of fatigue cracks, which decreased the fatigue crack growth rate at low ΔK regions and increased the number of cycles until final fatigue fracture. Refining and spheroidizing of eutectic Si particles increased the fatigue crack growth rates over a wide range of ΔK up to larger ΔK values. The difference of aging conditions significantly affected the da/dN-ΔKeff relationship.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. H. Rendigs,Proc. ICAA5-Part4/Supplement SF2M and INPG, Grenoble, France, (1996).
S. Kumai, J. Hu, Y. Higo, and S. Nunomura,J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 45, 198 (1995).
S. W. Han, U. J. Lee, and S. W. Kim,Metals and Materials Int. 8, 443 (2002).
M. H. Jacobes,Phil. Mag. 26, 1 (1972).
W. F. Smith,Metall. Trans. 4, 2435 (1973).
S. F. Orbin, D. S. Wilkinson, and J. D. Embury,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 207, 1 (1996).
C. E. Richards and W. F. Deans,The Measurement of Crack Length and Shape during Fracture and Fatigue, p. 28, Eng. Materials Advisory Services LTD (1980).
S. W. Han, S. Kumai, and A. Sato,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 332, 56 (2002).
S. Suresh,Metall. Trans. A 14, 2375 (1983).
S. Suresh and C. F. Shih,Int. J. Fract. 30, 249 (1986).
B. Skallerud,Eng. Fract. Mech. 44, 857 (1993).
G. Eisenmeier, B. Holzwarth, H. W. Höppel, and H. Mughrabi,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 319–321, 578 (2001).
M. Kubota, Y. Ochi, A. Ishii, and R. Shibata,Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. A 61, 14 (1995).
Y. Kuroki, T. Tanaka, T. Sato, and A. Kamio,J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 50, 116 (2000).
F. T. Lee, J. F. Major, and F. H. Samul,Metall. Mater. Trans. A 26, 1553 (1995).
M. Schaefer and R. A. Fournelle,Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27, 1293 (1996).
Q. G. Wang and C. H. Caceres,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 241, 72 (1998).
S. Kumai, S. Aoki, S. W. Han, and A. Sato,Mater. Trans. JIM 40, 685 (1999).
G. R. Irwin,Proc. 7th Sagamoro OMG Conf. IV, p. 60, Syracuse Univ., NY, USA (1960).
C. H. Caceres, J. R. Griffiths, and P. Reiner,Acta mater. 44, 15 (1996).
S. Suresh, A. K. Vasudevan, and P. E. Bretz,Metall. Trans. A 15, 369 (1984).
E. Hornborgen and K. H. ZumGahr,Acta metall. 24, 581 (1976).
J. D. Embury,Metall. Trans. 16, 2191 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, SW., Kim, SW. Fatigue crack growth behaviors in Al−Si−Mg sand cast alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 10, 13–18 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027358
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027358