Abstract
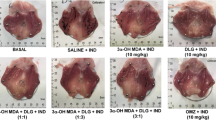
It has been suggested that oxygen-derived free radicals play an important role in the pathophysiology of acute gastric ulceration induced by NSAIDs and ischemia-reperfusion. Taurine is hypothetized to exert its protective effect on NSAIDs-induced gastric injury by its antioxidant properties. Protective effect of taurine on indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal lesion and its protection mechanism were investigated. Intragastric administration of 25 mg/kg of indomethacin induced hemorrhagic lesions on the glandular stomach in rats. Pretreatment with 0.25 or 0.5 g/kg of taurine one day before or for 3 days significantly reduced the gastric lesion formation and inhibited the elevation of lipid peroxide level, in gastric mucosa. The luminol-dependent chemiluminescence of rat peritoneal neutrophils increased immediately after treatment of FMLP or indomethacin. Taurine (5–20 mM) inhibited chemiluminescence of neutrophils activated by FMLP. Human neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes) significantly adhered to the confluent monolayer of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) after coincubation with indomethacin. This neutrophil adhesion induced by indomethacin to HUVEC was prevented by taurine in a dose-dependent manner. These results indicate that the protective effect of taurine against NSAIDs-induced gastric mucosal injury is due to its antioxidant effect, which inhibits lipid peroxidation and neutrophil activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Aruoma, O. I., Halliwell, B., Hoey, B. M. and Butler, J. The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors.Biochem. J., 256, 251–255 (1988).
Ashey, S. W., Sonnenschein, L. A. and Cheung, L. Y. Focal gastric mucosal blood flow at the site of aspirin-induced ulceration.Am. J. Surg., 149, 53–59 (1985).
Ayene, I. S., Dodia, C. and Fisher, A. B. Role of oyygen in oxidation of lipid and protein during ischemia/reperfusion in isolated perfused rat lung.Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 296, 183–189 (1992).
Banks, M. A., Porter, D. W., Martin, W. G. and Castranova, V. Effects of in vitro ozone exposure on peroxidative damage, membrane leakage, and taurine content of rat alveolar macrophages.Toxicol. Appl. Pharm., 105, 55–65 (1990).
Cantin, A. M. Taurine modulation of hypochlorous a-cid-induced lung epithelial cell injuryin vitro.J. Clin. Invest., 93, 606–614 (1994).
Dahlgren, C. Effect of different inhibitors on the intracellularly and extracellularly generated chemiluminescence induced by formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Cellular response in the presence of mannitol, benzoate, taurine, indomethacin and NDGA.J. Biolum. Chemilum., 6, 29–34 (1991).
Gimbrone, M. A. Jr., Brock, A. F. and Schafer, A. Leukotriene B4 stimulates polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesion to cultured vascular endothelial cells.J. Clin. Invest., 74, 1552–1555 (1984).
Giri, S. N. and Wang, Q. Taurine and niacin offer a novel therapeutic modality in prevention of chemically-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters, in: “Taurine”, Lombardini, J. B., ed., Plenum Press, New York, pp. 329–340 (1992).
Green, T. R., Fellman, J. H., Eicher, A. L. and Pratt, K. L. Antioxidant role and subcellular location of hypotaurine and taurine in human neutrophils.Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1073, 91–97 (1991).
Hirota, M., Inoue, M., Ando, Y. and Morino, Y. Inhibition of stress-induced gastric mucosal injury by a long acting superoxide dismutase that circulates bound to albumin.Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 280, 269–273 (1990).
Kitahora, T. and Guth, P. H. Effect of aspirin plus hydrochloric acid on the gastric mucosal microcirculation.Gastroenterology, 93, 810–817 (1987).
McGregor, P. E., Agrawal, D. K. and Edwards, J. D. Technique for assessment of leukocyte adherence to human umbilical vein endothelial cell monolayers.J. Pharm. Mol., 32, 73–77 (1994)
Naito, Y., Yoshikawa, T., Kaneko, T., Iinuma, S., Nishimura, S., Takahashi, S. and Kondo, M. Role of oxygen radicals in indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal microvascular injury in rats.J. Clin. Gastroenterol, 17, S99-S103 (1993).
Pasantes-Morales, H. and Cruz, C. Protective effect of taurine and zinc on peroxidation-induced damage in photoreceptor outer segments.J. Neuros. Res., 11, 303–311 (1984).
Pasantes-Morales, H. and Cruz, C. Taurine, and hypotaurine inhibit light-induced lipid peroxidation and protect rod outer segment structure.Brain Res., 330, 154–157 (1985).
Schuller-levis, G., Quinn, M. R., Wright, C. and Park, E. Taurine protects against oxidant-induced lung injury: possible mechanisms of action, in: “Taurine in health and disease” Huxtable, R. J. and Michalk, D. V. ed., Plenum Press, New York. pp. 31–39 (1994)
Takeuchi, K., Ueshima, K., Hironaka, Y., Fujioka, Y., Matsumoto, J., Okabe, S. Oxygen free radicals and lipid peroxidation in the pathogenesis of gastric mucosal lesions induced by indomethacin in rats.Digestion, 49, 175–184 (1991).
Trachtman, H., Futterweit, S. and Bienkowski, R. S. Taurine prevents glucose-induced lipid peroxidation and increases collagen production in cultured rat mesangial cells.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 191, 759–765 (1993).
Vaananen, P. M., Meddings, J. B. and Wallace, J. L. Role of oxygen-derived free radicals in indomethacin-induced gastric injury.Am. J. Physiol., 261, G470-G475 (1991).
Wallace, J. L., Keenan, C. M. and Granger, D. N. Gastric ulceration induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is a neutrophil-dependent process.J. Physiol., 259, G462-G467 (1990).
Wallace, J. L. and Granger, D. N. Pathogenesis of NSAID gastropathy: are neutrophils the culprits?TIPS, 13, 129–131 (1992).
Wang, Q., Hyde, D. M. and Giri, S. N. Abatement of bleomycin-induced increases in vascular permeability, inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrotic lesions in hamster lungs by combined treatment with taurine and niacin.Lab. Invest., 67, 234–242 (1992).
Yoshida, N., Takemura, T., Neil Granger, D., Anderson, D. C., Wolf, R. E., McIntire, L. V. and Kvietys, P. R. Molecular determinants of aspirin-induced neutrophil adherence to endothelial cells.Gastroenterology, 105, 715–724 (1993).
Yoshikawa, T., Ueda, S., Naito, Y., Takahashi, S., Oyamada, H., Morita, Y., Yoneta, T. and Kondo, M. Role of oxygen-derived free radicals in gastric mucosal injury induced by ischemia or ischemia-reperfusion in rats.Free Rad. Res. Comms., 7, 285–291 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, M., Kim, H.K., Kim, W.B. et al. Protective effect of taurine on indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury. Arch. Pharm. Res. 19, 85–90 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976839
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976839