Abstract
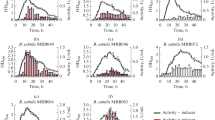
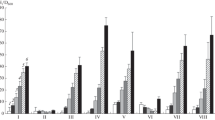
The formation of the exoenzymes, neutral and alkaline proteinase as well as α-amylase ofBacillus subtilis, is characterized by the same time course. The exoenzyme formation starts in the exponential phase of growth by an excess of C and N sources. We assume that carbon metabolism of pyruvate is responsible for the exoenzyme formation during this growth phase. The proteinase formation at the transient and/or stationary phase of growth is related to amino acid limitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Chaloupka J., Křečkova P.: Regulation of the formation of protease inBacillus megaterium. Folia.Microbiol.11, 82–88 (1966).
Chaloupka J., Severin A.I., Sastry K.J., Kučerová H., Strnadová M.: Differences in the regulation of exocellular proteinase synthesis during growth and sporogenesis ofBacillus megaterium.Can. J. Microbiol.28, 1214 (1982).
Drechsler H., Grunow R.: Transfer and expression of mutant pleiotropic genes for extracellular enzymes synthesis inBacillus subtilis.Molek. Genet. Mikrobiol. Virusol.2, 30–33 (1985).
Freese E., Heinze I., Galliers E.M.: Partial purine deprivation causes sporulation ofBacillus subtilis in the presence of excess ammonia, glucose and phosphate.J. Gen. Microbiol.115, 193–205 (1979).
Hageman J.H., Shankweiler G.W., Wall P.R., Franich G.W., McCowand G.A., Caublr S.M., Grajeda J., Quinbnes C.: Single chemically defined sporulation medium forB. subtilis: growth, sporulation and extracellular protease production.J. Bact.160, 438–441 (1984).
Hanlon G.W., Hodges N.A.: Bacitracin and protease production in relation to sporulation during exponential growth ofBacillus licheniformis on poorly utilized carbon and nitrogen sources.J. Bact.147, 427–431 (1981a).
Hanlon G.W., Hodges N.A.: Requirement for glucose during production of extracellular serine protease by cultures ofBacillus licheniformis.FEMS Microbiol.Letters11, 51–54 (1981b).
Kornberg H.L.: Formation and utilization of PEP in microbial carbohydrate transport.Curr. Top.Cell. Regul.18, 313–327 (1981).
Kučerová H., Váchová L., Chaloupka J.: Mutants ofBacillus megaterium with altered synthesis of an exocellular neutral proteinase.Folia Microbiol.29, 99–103 (1984).
Laishly E.J., Bernlohr R.W.: Regulation of arginine and proline catabolism inBacillus licheniformis.J.Bacteriol.96, 322–329 (1968).
Langner J.: Azocasein methods in proteinase in mammalian tissues and cells.Wissensch.Beitr. Martin-Luther-Univ.Halle14, 76–79 (1982).
Mandelstam J.: Bacterial sporulation: a problem in the biochemistry and genetic of a primitive developmental system.Proc. Roy. Soc. London Ser.B193, 89–106 (1976).
Priest F.G.: Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genusBacillus.Bacteriol. Rev.41, 711–753 (1977).
Riedel K.: Abhangigkeit der α-Amylasebildung beiBacillus subtilis vom Kohlenhydratstoff-wechsel.Z. Allg. Mikrobiol.21, 131–139 (1981).
Riedel K., Liebs P., Renneberg R.: Ar. electrochemical method for determination of cell respiration.J. Basic Microbiol.25, 51–59 (1985).
Schaeffer P.: Sporulation and the production of antibiotics, exoenzymes and exotoxins.Bacteriol. Rev.33, 48–71 (1969).
Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J.P.: Catabolite repression of bacterial sporulation.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci.54, 704–711 (1965).
Scheller F., Pfeiffer D., Kühn M., Hundertmark I., Quade A., Jänlhen M., Lange G., Holesch H., Dittmer H.: Glukosemessung in verdünntem Vollblut mit einer Enzymelektrode.Acta Biol. Med. Germ.39, 671–679 (1980).
Sekiguchi J., Okada H.: Regulation of α-amylase production in aBacillus subtilisMarburg strain.J. Ferment.Technol.50, 801–809 (1972).
Wambutt R., Riesenberg D., Krüger M., Schultze M.: Formation of extracellular α-amylase byBacillus subtilis in relation to guanosine polyphosphates.Z. Allg. Mikrobiol.24, 575–579 (1984).
Yoneda Y., Maruo B.: Mutation ofBocillus subtilis causing hyperproduction of α-amylase and protease and its synergetic effect.J. Bacteriol.124, 48–54 (1975).
Yoneda Y., Yamane K., Mamuo B.: Membrane mutation related to the production of extracellular α-amylase and protease inBacillus subtilis.Biochem. Biophys. Res.Commun.50, 765–770 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We wish to thank Dr. J. Chaloupka for valuable discussions. Special thanks as well go to Dr. M. Krüger (Institute of Technical Microbiology, Berlin) for analyzing the amino acids. Furthermore we thank J. Dorn and B. Brandt for excellent technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liebs, P., Riedel, K., Graba, J.P. et al. Formation of some extracellular enzymes during the exponential growth ofBacillus subtilis . Folia Microbiol 33, 88–95 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02928073
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02928073