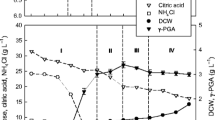
Abstract
Bacillus stearothermophilus BR219, a phenol-resistant thermophile, can convert phenol to the specialty chemical catechol. The growth kinetics of this organism were studied in batch, continuous, and im-mobilized-cell culture. Batch growth was insensitive to pH between 6.0 and 8.0, but little growth occurred at 5.5. In continuous culture on a dilute medium supplemented with 10 mM phenol, several steady states were achieved between dilution rates of 0.25 and 1.3 h-1. Phenol degradation was found to be uncoupled from growth. Immobilized cells grew rapidly in a rich medium, but cell viability plummeted following a switch to a dilute medium supplemented with 5 mM phenol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sonnleitner, B. (1983),Microbial Activities, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 69.
Sonnleitner, B. and Fiechter, A. (1983),Trends Biotechnol. 1, 74.
Berquist, P. L., Love, D. R., Croft, J. E., Streiff, M. B., Daniel, R. M., and Morgan, W. H. (1987), inBiotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews, vol. 5, Russekk, G. E., ed., Intercept, Dorset, p. 199.
Gurujeyalakshmi, G. and Oriel, P. (1988),App. Environ. Microbiol. 55, 500.
Gurujeyalakshmi, G. and Oriel, P. (1989),Biotechnol. Lett. 11, 689.
Oriel, P. and Gurujeyalakshmi, G. (1989),U.S. Patent #4,894,337.
Buswell, J. A. (1975),J. Bacteriol. 124, 1077.
Barnett, J. A. and Ingram, M. (1955),J. Appl. Bacteriol. 18, 131.
Worden, R. M. (1986), “Dynamics of a Biological Fixed Film for Phenol Degradation, Part II: Development of an Active-Biomass Assay for Biological Fixed Films,” Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of Tennessee.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewaters. 14th Ed. (1975), American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C., p. 580.
National Research Council (1928),International Critical Tables, vol. 3, McGraw-Hill, New York, p. 257.
Atkinson, B. and Mavituna, F. (1983),Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology Handbook, Nature Press, New York, p. 265.
Oriel, P. J. (1990),Personal Communication, Michigan State University.
Sontakke, S., Beaumier, D., Beaulieu, C., Greer, C., and Samson, R. (1989),Proc. Int. Conf. on Physiochem. and Biolog. Detoxific. of Hazardous Wastes, vol. 2, May 3–5, 1988, Atlantic City, NJ, Technomic Pub. Co., Lancaster, p. 619.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Worden, R.M., Subramanian, R., Bly, M.J. et al. growth kinetics ofbacillus stearothermophilus BR219. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 28, 267–275 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02922606
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02922606