Abstract
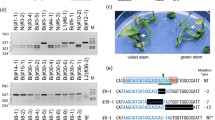
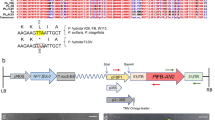
Chalcone synthase A is a key enzyme in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway. Expression ofchsA gene in transgenicPetunia hybrida resulted in flower color alterations and co-suppression of transgenes and endogenous genes. We fused the β-glucuronidase (uidA) gene to the C-terminal ofchsA gene, and transferred the fusion gene intoPetunia hybrida viaAgrobacterium tumefaciens. GUS histochemical staining analysis showed that co-suppression occurred specifically during the development of flowers and co-suppression required the mutual interaction of endogenous genes and transgenes. RNAin situ hybridization analysis suggested that co-suppression occurred in the entire plant, and RNA degradation occurred in the cytoplasm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Napoli, C., Lemieux, C., Jorgensen, R., Introduction of a chimeric chalone synthase gene into petunia results in reversible cosuppession of homologous genesin trans, The Plant Cell, 1990, 2: 279–289.
Van der Krol, A.R., Mur, L.A., Beld, M. M. et al., Flavonnoid genes in petunia: addition of a limited number of gene copies may lead to a suppression of gene expression, The Plant Cell, 1990, 2: 291–299.
Manika, P.B., Bhadra, U., Birchler, J., Cosuppression in Drosophila: gene silencing ofAlcohol dehydrogenase byWhite-Adh transgene isPolycomb dependent, Cell, 1997, 90: 479–498.
de Carvalho Niebel, F., Frendo, P., Van Montagu, M. et al., Post-transcriptional cosuppression of β-1,3-glucanase transgene expression in homozygous plants, EMBO J., 1992, 11: 2595–2602.
Van Blokland, R., Van der Geest, N., Mol, J. N. M. et al., Transgene-mediated suppression of chalcone synthase expression inPetunia hybrida results from an increase in RNA turnover, The Plant Cell, 1994, 6: 861–877.
Stam, M., Mol, J. N. M., Kooter, J. M., The silence of genes in transgenic plants, Annals of Bot., 1997, 79: 3–12.
Vaucheret, H., Beclin, C., Elmayan, T. et al., Transgene-induced gene silencing in plants, Plant J., 1998, 16(6): 651–659.
Shao, L., Li, Y., Yang, M. Z. et al., Transformation of Petunia hybrida with chalcone synthase A (chsA) resulting flower colour alteration and male sterility, Acta Botanica Sinica (in Chinese), 1996, 38(7): 517–524.
Koes, R. E., Spelt, C. E., Mol, J. N. M., The chalcone synthase multigene family of Petunia hybrida (V30): differential, light-regulated expression during flower development and UV light induction, Plant Mol. Biol., 1989, 12: 213–225.
Drews, G. N., Beals, T. P., Bul, A. Q. et al., Regional and cell-specific expression patterns during petal development, The Plant Cell, 1992, 4: 1383–1404.
Martin, C., Gerats, T., Control of pigment biosynthesis genes during petal development, The Plant Cell, 1993, 5: 1253–1264.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed., New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
Jefferson, R. A., Kavanagh, T. A., Bevan, M. W., GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase is a sensitive and versatile fusion marker in higher plants, EMBO J., 1987, 6: 3901–3907.
Cox, K. H., Goldberg, R. B., Analysis of plant gene expression, in Plant Molecular Biology: A Practical Approach (ed. Shaw, C. H.), Oxford: IRL Press, 1988, 1–34.
Schiebel, W., Pelissier, T., Riedel, L. et al., Isolation of an RNA-directed RNA polymerase-specific cDNA clone from tomato, The Plant Cell, 1998, 10: 2087–2101.
Dalmay, T., Hamilton, A., Rudd, S. et al., An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene in Arabidopsis is required for posttranscriptional gene silencing mediated by a transgene but not by a virus, Cell, 2000, 101(5): 543–553.
Hamilton, A. J., Baulcombe, D. C., A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants, Science, 1999, 286: 950–952.
Jorgensen, R. A., Cluster, P. D., English, J. J. et al., Chalcone synthase cosuppression phenotypes in Petunia flowers: comparison of sense vs. antisense constructs and single-copy vs. complex T-DNA sequences, Plant Mol. Biol., 1996, 31: 957–973.
Voinnet, O., Baulcombe, D. C., Systemic signaling in gene silencing, Nature, 1997, 389: 553.
Voinnet, O., Lederer, C., Baulcombe, D. C., A viral movenent protein prevents spread of the gene silencing signal inNicotiana benthamiana, Cell, 2000, 103: 157–167.
Hammond, S. M., Bernstein, E., Beach, D. et al., An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells, Nature, 2000, 404: 293–296.
Zamore, P. D., Tuschl, T., Sharp, P. A. et al., RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals, Cell, 2000, 101: 25–33.
Tuschl, T., Zamore, P. D., Lehmann, R. et al., Targeted mRNA degradation by double-stranded RNAin vitro, Genes Dev., 1999, 13: 3191–3197.
Baulcombe, D. C., Mechanisms of pathogen-derived resistance to viruses on transgenic plants, The Plant Cell, 1996, 8: 1833–1844.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Xi, Y., Zhang, Z. et al. Co-suppression in transgenicPetunia hybrida expressing chalcone synthase A (chsA). Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 44, 661–668 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879361
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879361