Abstract
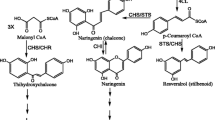
We have analysed the expression of the 8–10 members of the gene family encoding the flavonoid biosynthetic enzyme chalcone synthase (CHS) from Petunia hybrida. During normal plant development only two members of the gene family (CHS-A and CHS-J) are expressed. Their expression is restricted to floral tissues mainly. About 90% of the total CHS mRNA pool is transcribed from CHS-A, wheares CHS-J delivers about 10% in flower corolla, tube and anthers. Expression of CHS-A and CHS-J during flower development is coordinated and (red) light-dependent. In young seedlings and cell suspension cultures expression of CHS-A and CHS-J can be induced with UV light. In addition to CHS-A and CHS-J, expression of another two CHS genes (CHS-B and CHS-G) is induced in young seedlings by UV light, albeit at a low level. In contrast to CHS genes from Leguminoseae, Petunia CHS genes are not inducible by phytopathogen-derived elicitors. Expression of CHS-A and CHS-J is reduced to a similar extent in a regulatory CHS mutant, Petunia hybrida Red Star, suggesting that both genes are regulated by the same trans-acting factors. Comparison of the promoter sequences of CHS-A and CHS-J reveals some striking homologies, which might represent cis-acting regulatory sequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell JN, Ryder TB, Wingate VPM, Bailey JA, Lamb CJ: Differential accumulation of plant defense gene transcripts in a compatible and incompatible plant-pathogen interaction. Mol Cell Biol 6: 1615–1623 (1986).
Breatnach R, Chambon P: Organisation and expression of eukaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Ann Rev Biochem 50: 349–383 (1981).
Bruns B, Hahlbrock K, Schäfer E: Fluence dependence of the ultraviolet-light-induced accumulation of chalcone synthase mRNA and effects of blue and far-red light in cultured parsley cells. Planta 169: 393–398 (1986).
Chappell J, Hahlbrock K: Transcription of plant defence genes in response to UV-light or fungal elicitor. Nature 311: 76–78 (1984).
Coen ES, Carpenter R, Martin C: Transposable elements generate novel patterns of gene expression in Antirrhinum majus. Cell 47: 285–296 (1986).
Colijn CM, Jonsson LMV, Schram AW, Kool AJ: Synthesis of malvidin and petunidin in pigmented tissue cultures of Petunia hybrida. Protoplasma 107: 63–68 (1981).
Cramer CL, Ryder TB, Bell JN, Lamb CJ: Rapid switching of plant gene expression induced by fungal elicitor. Science 227: 1240–1242 (1984).
Cramer CL, Bell JN, Ryder TB, Bailey JA, Schuch W, Bollwell GP, Robbins MP, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ: Co-ordinated synthesis of phytoalexin biosynthetic enzymes in biologically stressed cells of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). EMBO J 4: 285–289 (1985).
Danglmayer B, Stotz G, Spribille R, Forkman G: Relationship between flower development, anthocyanin accumulation and activity of enzymes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis in Matthiola incana R. Br. Z Naturforsch 38c: 551–555 (1983).
Devereux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O: A comprehensive set of computer programs for the VAX. Nucl Acids Res 12: 387–395 (1984).
Dixon RA: The phytoalexin response: elicitation signalling and control of host gene expression. Biol Rev 61: 239–291 (1986).
Dixon RA, Gerrish C, Lamb CJ, Robbins MP: Elicitor mediated induction of chalcone isomerase in Phaseolus vulgaris. Planta 159: 561–569 (1983).
Douglas C, Hoffman H, Schulz W, Hahlbrock K: Structure and elicitor or UV-light stimulated expression of two 4-coumarate: CoA ligase genes in parsley. EMBO J 6: 1189–1195 (1987).
Ebel J: Phytoalexin synthesis: The biochemical analysis of the induction process. Ann Rev Phytopath 24: 235–264 (1986).
Ebel J, Schmidt WE, Loyal R: Phytoalexin synthesis in soybean cells: Elicitor induction of phenylalanine ammonia lyase and chalcone synthase mRNA and correlation with phytoalexin accumulation. Arch Biochem Biophys 232: 240–248 (1984).
Ebel J, Hahlbrock K: Biosynthesis. In: Harborne JB, Mabry TJ (eds) The Flavonoids, pp. 641–680. Chapman and Hall, London/New York (1982).
Edwards K, Cramer CL, Bolwell GP, Dixon RA, Schuch W, Lamb CJ: Rapid transient induction of phenylalanine ammonia lyase mRNA in elicitor treated bean cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 6731–6735 (1985).
Fluhr R, Chua NH: Developmental regulation of two genes encoding ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit in pea and transgenic petunia plants: Phytochrome response and blue light induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2358–2362 (1986).
Gardiner SE, Schroeder J, Matern U, Hammer D, Hahlbrock K: mRNA dependent regulation of UDP-apiose synthase activity in irradiated plant cells. J Biol Chem 255: 10752–10757 (1980).
Gerats AGM, Wallroth M, Donker-Koopman W, Groot SPC, Schram AW: The genetic control of the enzyme UDP-glucose: 3-O-glucosyltransferase in flowers of Petunia hybrida. Theor Appl Genet 65: 349–352 (1983).
Green PJ, Kay SA, Chua NH: Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light responsive elements upstream of the rbcs-3A gene. EMBO J 6: 2543–2549 (1987).
Harborne JB: Nature, function, distribution. In: Cody V, Middleton E, Harborne JB (eds) Flavonoids: Plant Flavonoids in Biology and Medicine, pp. 15–24. Alan R. Liss, New York (1986).
Heller W, Hahlbrock K: Highly purified “flavanone synthase” from parsley catalyzes the formation of naringenin chalcone. Arch Biochem Biophys 200: 617–619 (1980).
Henikoff S: Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted break points for DNA sequencing. Gene 28: 351 (1984).
Hermann A, Schulz W, Hahlbrock K: Two alleles of the single copy chalcone synthase gene in parsley differ by a transposon-like element. Mol Gen Genet 212: 93–98 (1988).
Hrazdina G: Anthocyanins. In: Harborne JB, Mabry TJ (eds) The Flavonoids, pp. 135–186. Chapman and Hall, London/New York (1982).
Kaulen H, Schell J, Kreuzaler F: Light induced expression of the chimeric chalcone synthase NPT-II gene in tobacco cells. EMBO J 5: 1–8 (1986).
Koes RE, Spelt CE, Reif HJ, van denElzen PJM, Veltkamp E, Mol JNM: Floral tissue of Petunia hybrida (V30) expresses only one member of the chalcone synthase multigene family. Nucl Acids Res 14: 5229–5239 (1986).
Koes RE, Spelt CE, Mol JNM, Gerats AGM: The chalcone synthase multigene family of Petunia hybrida: sequence homology, chromosomal localization and evolutionary aspects. Plant Mol Biol 10: 159–169 (1987).
Kuc J: Phytoalexins from the Solanaceae. In: Bailey JA, Mansfield JW (eds) Phytoalexins, pp. 80–105 Blackie, Glasgow (1982).
Kuhn D, Chapell J, Boudet A, Hahlbrock K: Induction of phenylalanine ammonia lyase and 4-coumarate: CoA ligase mRNAs in cultured plant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 1102–1106 (1984).
Lawton MA, Dixon RA, Hahlbrock K, Lamb CJ: Rapid induction of the synthesis of phenylalanine ammonia lyase and chalcone synthase in elicitor treated bean cells. Eur J Biochem 129: 593–601 (1983).
Lawton MA, Lamb CJ: Transcriptional activation of plant defense genes by fungal elicitors, wounding and infection. Mol Cell Biol 7: 335–341 (1987).
Maier UG, Brown JWS, Toloczyki C, Feix G: Binding of a nuclear factor to a consensus sequence in the 5′ flanking region of zein genes from maize. EMBO J 6: 17–22 (1987).
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1982).
Medhy MC, Lamb CJ: Chalcone isomerase cDNA cloning and mRNA induction by fungal elicitor, wounding and infection. EMBO J 6: 1527–1533 (1987).
Mol JNM, Schram AW, deVlaming P, Gerats AGM, Kreuzaler F, Hahlbrock K, Reif HJ, Veltkamp E: Regulation of flavonoid gene expression in Petunia hybrida: Description and partial characterization of a conditional mutant in chalcone synthase gene expression. Mol Gen Genet 192: 424–429 (1983).
Mol JNM, Robbins MP, Dixon RA, Veltkamp E: Spontaneous and enzymic rearrangement of naringenin chalcone to flavanone. Phytochemistry 24: 2267–2269 (1985).
Peters NK, Frost JW, Long SR: A plant flavone, luteolin induces expression in Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science 233: 977–980 (1986).
Ragg H, Kuhn D, Hahlbrock K: Coordinated regulation of 4-coumarate: CoA ligase and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in cultured plant cells. J Biol Chem 256: 10061–10065 (1981).
Rall S, Hemleben V: Characterization and expression of chalcone synthase in different genotypes of Mathiola incana R. Br. during flower development. Plant Mol Biol 3: 137–145 (1984).
Redmond JW, Batley M, Djordjevic MA, Innes RW, Kuempel PL, Rolfe BG: Flavones induce expression of the nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Nature 323: 632–635 (1986).
Reif HJ, Niesbach U, Deumling B, Saedler H: Cloning and analysis of two genes for chalcone synthase from Petunia hybrida. Mol Gen Genet 199: 208–215 (1985).
Ryder TB, Cramer CL, Bell JN, Robbins MP, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ: Elicitor rapidly induces chalcone synthase mRNA in Phaseolus vulgaris cells at the onset of phytoalexin defense response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 5724–5728 (1984).
Ryder TB, Hedrick SA, Bell JN, Liang X, Clouse SD, Lamb CJ: Organization and differential activation of a gene family encoding the plant defense enzyme chalcone synthase in Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol Gen Genet 210: 219–233 (1987).
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467 (1977).
Sommer H, Saedler H: Structure of the chalcone synthase gene of Antirrhinum majus. Mol Gen Genet 202: 429–434 (1986).
Sommer H, Bonas U, Saedler H: Transposon induced alterations in the promoter region affect transcription of the chalcone synthase gene in Antirrhinum majus. Mol Gen Genet 211: 49–55 (1988).
Schäfer E, Haupt W: Blue light effects in phytochrome mediated responses. Encycl Plant Phys, New Ser 16A: 289–311 (1983).
Shirley BW, Berry Lowe SL, Rogers SG, Flick JS, Horsch R, Fraley RT, Meagher RB: 5′ proximal sequences of a soybean ribulose1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit gene direct light and phytochrome controlled transcription. Nucl Acids Res 15: 6501–6514 (1987).
Tietjen KG, Matern U: Differential response of cultured parsley cells to elicitors from two non-pathogenic strains of fungi. 1. Identification of induced products as coumarin derivatives. Eur J Biochem 131: 409–413 (1983).
Tobin EM, Silverthorne J: Light regulation of gene expression in higher plants. Ann Rev Plant Phys 36: 569–593 (1985).
Tunen AJ van, Koes RE, Spelt CE, van der Krol AR, Stuitje AR, Mol JNM: Cloning of the two chalcone flavanone isomerase genes from Petunia hybrida: coordinate, light regulated and differential expression of flavonoid genes. EMBO J 7: 1257–1263 (1988).
Vlaming P de, Cornu A, Farcy E, Gerats AGM, Maizonier D, Wiering H, Wijsman HJW. Petunia hybrida: A short description of the action of 91 genes, their origin and their map location. Plant Mol Biol Rep 2: 21–41 (1984).
Weiher JC, Konig M, Gruss P: Multiple point mutations affecting the Simian Virus 40 enhancer. Science 219: 626–631 (1983).
Wienand U, Weydemann U, Niesbach-Klösgen U, Peterson PA, Saedler H: Molecular cloning of the c2 locus of Zea mays the gene coding for chalcone synthase. Mol Gen Genet 203: 202–207 (1987).
Wiering H, de Vlaming P: Genetics of flower and pollen colours. In: Sink KC (ed) Monographs on Theoretical and Applied Genetics: Petunia, pp. 49–75. Springer-VerlagBerlin (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koes, R.E., Spelt, C.E. & Mol, J.N.M. The chalcone synthase multigene family of Petunia hybrida (V30): differential, light-regulated expression during flower development and UV light induction. Plant Mol Biol 12, 213–225 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020506
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020506