Summary
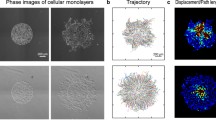
We investigated the effects of human placental scatter factor (hSF), mouse scatter factor (mSF) and recombinant human hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) on motility and morphology of individual Madin-Darby canine kidney cells using a computerized cell tracking system. All three factors increased the velocity of individual cells and the ratio of moving to stationary cells. Similarly, all three factors caused changes in morphologic features of cells, leading to increased area, flatness, and polarity. Increases in area and flatness but not polarity were slightly greater with HGF than with hSF or mSF. These results suggest that SFs and HGF have similar effects on motility and morphology of isolated epithelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhargava, M. M.; Li, Y.; Joseph, A., et al. Structure and function of scatter factor from human placenta. In: Goldberg, I. D.; Rosen, E. M., eds. Cell motility factors. Geneva: Birkhauser-Verlag; 1991:63–75.
Bottaro, D. P.; Rubin, J. S.; Faletto, D. L., et al. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science 251:802–804; 1991.
Dowrick, P. G.; Warn, R. M. In cellular response to factors which induce motility in mammalian cells. In: Goldberg, I. D.; Rosen, E. M., eds. Cell motility factors. Geneva: Birkhauser-Verlag; 1991:89–108.
Furlong, A.; Takehara, T.; Taylor, W. G., et al. Comparison of biological and immunochemical properties indicates that scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor are indistinguishable. J. Cell Sci. 100:173–177; 1991.
Gherardi, E.; Gray, J.; Stoker, M., et al. Purification of scatter factor, a fibroblast-derived basic protein that modulates epithelial interactions and movement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:5844–5848; 1989.
Gherardi, E.; Stoker M. Scatter factor and hepatocytes. Nature 346:228; 1990.
Nakamura, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Watanabe, H., et al. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature 342:440–443; 1989.
Poon, S. S. S.; Jaggi, B.; Palcie, B. Cell recognition algorithm for the cell analyzer. IEEE Proc. Eng. Med. Biol. 3:1545–1547; 1987.
Rosen, E. M.; Goldberg, I. D. Protein factors which regulate cell motility. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 25:1079–1089; 1989a.
Rosen, E. M.; Goldberg, I. D.; Kacinski, B. M., et al. Smooth muscle releases an epithelial cell scatter factor which binds to heparin. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 25:163–173; 1989b.
Rosen, E. M.; Meromsky, L.; Goldberg, I. D., et al. Studies on the mechanism of scatter factor. Effects of agents that modulate intracellular signal transduction, macromolecule synthesis and cytoskeleton assembly. J. Cell Sci. 96:639–649; 1990a.
Rosen, E. M.; Meromsky, L.; Setter, E., et al. Purified scatter factor stimulates epithelial and vascular endothelial cell migration. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 195:34–43; 1990b.
Rosen, E. M.; Meromsky, L.; Romero, R., et al. Human placenta contains an epithelial scatter protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168:1082–1088; 1990c.
Rosen, E. M.; Meromsky, L.; Setter, E., et al. Quantitation of cytokinestimulated migration of endothelium and epithelium by a new assay using microcarrier beads. Exp. Cell Res. 186:22–31; 1990d.
Schor, S. L.; Schor, A. M.; Grey, A. M., et al. Mechanism of action of the migration stimulating factor produced by fetal and cancer patient fibroblasts: effect on hyaluronic acid synthesis. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 25:737–746; 1989.
Stoker, M.; Gherardi, E.; Perryman, M., et al. Scatter factor is a fibroblastderived modulator of epithelial cell motility. Nature 327:239–242; 1987.
Stoker, M.; Gherardi, E. Regulation of cell movement: the mitogenic cytokines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1072:81–102; 1991.
Thurston, G.; Jaggi, B.; Palcic, B. Cell motility measurements with an automated microscope system. Exp. Cell Res. 165:380–390; 1986.
Thurston, G.; Jaggi, B.; Palcic, B. Measurement of cell motility and morphology with automated microscope system. Cytometry 95:411–417; 1988.
Warn, R. M.; Dowrick, P. Motility factors on the march. Nature 340:186–187; 1989.
Weidner, K. M.; Behrens, J.; Vandekerckhove, J., et al. Scatter factor: molecular characteristics and effect on the invasiveness of epithelial cells. J. Cell. Biol. 111:2097–2108; 1990.
Weidner, K. M.; Arakaki, N.; Hartmann, G., et al. Evidence for the identity of human scatter factor and human hepatocyte growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:7001–7005; 1991.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LI, Y., Joseph, A., Bhargava, M.M. et al. Effect of scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor on motility and morphology of mdck cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal 28, 364–368 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877060
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02877060