Summary
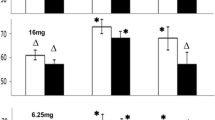
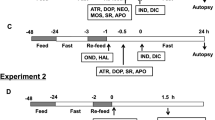
Combined administration of reserpine and Iproniazid to the cat has produced gastric and duodenal ulcers. Change in the time interval of administration of these drugs gave rise to variations in the site of gastric and duodenal lesions. When the animals were pre-treated with Iproniazid, duodenal ulcer occurred mainly with the most severe histopathological change when the two drugs (Reserpine and Iproniazid) were given at a 30 minute interval. Posttreatment with Iproniazid resulted mainly in gastric ulcers and the most severe changes were seen when the drugs were administered at 2 hour intervals. Consequently, it is suggested that gastric ulcer is produced at low intracellular amine levels while duodenal ulcer is produced at high level in addition to mutual imbalance of amines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashizawa, S. (1965) Gastric ulcer. Naika, 16: 208–211.
Brodie, B. B., Olin, J. S. and Shore, P. A. (1957) Possible inter-relationship between release of brain norepinephrine and serotonin by reserpine. Science, 125: 1293–294.
Brodie, B. B. and Shore, P. A. (1957) A concept for a role of serotonin and noradrenaline as chemical mediators in the brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 66: 631–642.
Brodie, D. A. (1962) Ulceration of the stomach produced by restraint in rats. Gastroenterology, 43: 107–109.
Dragstedt, L. R., Woodward, E. R. Linares, C. A. and De La Rosa, C. (1964) The pathogenesis of gastric ulcer. Ann. Surg., 160: 497–511.
Emas, S. and Grossman, M. I. (1967) Production of duodenal ulcers in cat by infusion of porcine gastrin. Gastroenterology, 52: 959–965.
Ivy, A.C., Grossman, M.I. and Bachrach, W.H. (1950) Peptic ulcer. Blakiston, Philadelphia.
Kim, K. S. and Shore, P. A. (1963) Mechanism of action of reserpine and insuline on gastric amines and gastric acid secretion, and the effect of monoamine oxidase inhibition. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther., 141: 321–325.
Kirsner, J. B. (1957) Drug-induced peptic ulcer. Ann. Intern. Med., 47: 666–699.
Mann, F. C. and Williamson, C. S. (1923) The experimental production of peptic ulcer. Ann. Surg., 77: 409–422.
Mann, P. J. G. and Questel, J. H. (1940) Benzedrine (B-phenyl-isopropyramine) and brain metabolism. Biochem. J., 34: 414–431.
Menguy, R. (1964) Current concepts of the etiology of the duodenal ulcer. Amer. J. Dig. Dis., 9: 199–211.
Nishizaki, H. and Murakami, T. (1966) Experimental peptic ulcer; the study of ulcerogenic properties of experimental peptic ulcer in animals. The proceedings of the Third World Congress of Gastroenterology, (Vol. 2) 115–117.
Nishizaki, H. and Sakai, Y. (1967) The influence of several monoamine oxidase inhibitors on the peripheral organs-especially the response of the stomach and duodenum. The autonomic nervous system, 4: 63–64.
Sakai, Y., Chio, H., Nitanai, S., Ishii, N, Mugikura, M. and Ashizawa, S. (1968) Study on the experimental peptic ulcer; First report, Search into the production of duodenal ulcer. Jap. J. Gastroenterol., 65: 1222–1223.
Sakai, Y. and Ashizawa, S. (1968) Studies on experimental peptic ulcer; Second report, Search into the production of gastric ulcer. The proceedings of the Third Asian-Pacific Congress of Gastroenterology, (Vol. 1) 225–239.
Shay, H., Komarov, S. A., Felo, S. S., Merenze, D., Gruenstein, M. and Siplet, H. (1945) A simple method for the uniform production of gastric ulceration in the rat. Gastroenterology, 5: 43–61.
Shimamoto, K., Yamamoto, I., Orita, M. and Takagi, H. (1964) Pharmacology, Igaku Shoin, Tokyo.
Shore, P. A., Mead, J. A. R., Kuntzman, R. G., Spector, S., and Brodie, B. B. (1957) On the physiologic significance of monoamine oxidase in brain. Science, 126: 1063–1064.
Shore, P. A., Pletcher, A., Tomich, E. G., Carlsson, A., Kuntzman, R. and Brodie, B. B. (1957) Role of brain serotonin in reserpine action. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 66: 609–615.
Zeller, E. A. and Bursky, J. (1952) In vivo inhibition of liver and brain monoamine oxidase by l-Isonicotinyl-2-isopropyl hydrazine. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 81: 459–461.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, Y. Experimental peptic ulcer induced by combined administration of reserpine and iproniazid. Gastroenterol Jpn 5, 110–116 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02775233
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02775233