Abstract
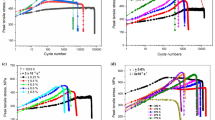
The high cycle fatigue (HCF) properties of two cast nickel base-superalloys, IN 738 LC and IN 939, were investigated using both fracture mechanics samples and smooth specimens. The crack propagation behavior was studied in terms of linear fracture mechanics at RT and at 850 °C. In addition to the influence of temperature, the influences of frequency, mean stress, and environment (vacuum, air, sulfidizing atmosphere) were studied. At 850 °C, the fatigue thresholds were found to be higher in air than in vacuum. This could be explained by crack branching. The high scatter of fatigue crack propagation rates could be related also to this phenomenon. The S/N curves at 850 °C can be predicted treating crack growth from casting pores as the predominant failure mechanism. At RT the same method is not as successful. The reason for this may be that crack growth laws measured on long, branched cracks are not applicable to short, unbranched cracks. At RT, no significant influence of frequency on S/N-curves and fatigue crack growth rates was observed for frequencies up to 20 kHz.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Müller:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, p. 649.
G. H. Gessinger:Powder Metallurgy International, 1981, vol. 2, pp. 93–101.
W. Betz and W. Track:Powder Metallurgy International, 1981, vol. 4, pp. 195–98.
M. S. Starkey and P. E. Irving: International Symposium on Low Cycle Fatigue and Life Prediction, September 23–25, 1980, Firminy (France), Conf. Proc., in press.
W. Hoffelner and E. Tschegg:Z. Werkstoffiechn., 1981, vol. 12, pp. 185–89.
P. Shahinian, H. H. Smith, and H. E. Watson:ASTM-STP 520, 1973, pp. 387-406.
T. Ohmura, R. M. Pelloux, and N. J. Grant:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1973, vol. 5, pp. 902–22.
L. A. James:Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 831–38.
M. O. Speidel:High-Temperature Materials in Gas Turbines, Elsevier Amsterdam-London-New York, 1974, pp. 207–55.
J. R. Haigh:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1975, vol. 7, pp. 271–84.
D. A. Jablonski, J. V. Carisella, and R. M. Pelloux:Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1893–1900.
K. Sadananda and P. Shahinian:Eng. Fract. M., 1979, vol. 11, pp. 73–86.
M. O. Speidel and A. Pineau:High Temperature Alloys for Gas Turbines, Appl. Sci. Publ., London, 1978, pp. 469–512.
R. B. Scarlin:ASTM STP 675, 1979, pp. 396-419.
R. B. Scarlin:International Conference on Fracture 1977, ICF 4, Conf. Proc. II, University of Waterloo Press, Waterloo, Ontario, 1977, pp. 849–58.
W. Hoffelner and M. O. Speidel:Behaviour of High Temperature Alloys in Aggressive Environments, Conf. Proc, The Metals Society, Book 266, London, 1980, pp. 993–1004.
W. Hoffelner and M. O. Speidel:Corrosion and Mechanical Stress at High Temperatures, Conf. Proc, Appl. Sci. Publ., London, 1981, pp. 275–86.
W. Hoffelner and M.O. Speidel:Advances in Fracture Research,ICF 5, Conf. Preprints, Pergamon Press, Conf. Proc. in press, 1981, vol. 5, pp. 2431-38.
R. A. Steven and P. E. J. Flewitt:J. Mat. Sci., 1978, vol. 13, pp. 367–76.
W. Hoffelner, E. Kny, and R. Stickler:Z. Werkstoffiechn., 1979, vol. 10, pp. 84–92.
C. P. Cutler and S. W. K. Shaw:lnco, Technical Publication P-BL. 378, lnco Europe Ltd., Birmingham B16 OAJ, England, 1979.
T. Geiger, R. Stickler, and G. H. White:High Temperature Alloys for Gas Turbines, Appl. Sci. Publ., London, 1978, pp. 317–33.
W. Hoffelner and M. O. Speidel:COST-50, 2nd round final report, BBC report KLR 81-48 C, Brown Boveri, CH-5401 Baden, Switzerland, 1981.
W. Hoffelner:J. Phys. E: Sci. Instr., 1980, vol. 13, pp. 617–19.
W. Hoffelner and P. Gudmundson:Eng. Fract. M., 1982, vol. 16, pp. 365–71.
F. Schmitz:COST-50, 1st round, final report TWA 62482 Kraftwerk Union, Wiesenstrasse 35, D-4330 Mulheim a.d. Ruhr, Germany, 1976.
W. Hartnagel, R. Bauer, and H. W. Griinling:Corrosion and Mechanical Stress at High Temperatures, Conf. Proc., Appl. Sci. Publ., London, 1981, pp. 255–73.
W. Griinling, B. Ilschner, S. Leistikow, A. Rahmel, and M. Schmidt:Behaviour of High Temperature Alloys in Aggressive Environments, Conf. Proc., The Metals Society, Book 266, London, 1980, pp. 869–93.
M. O. Speidel: unpublished research, 1978, BBC-Research Center, CH-5401 Baden, Switzerland; now Professor at the Swiss Institute of Technology, ETH, Zurich, Switzerland.
S. R. Holdsworth:High Temperature Alloys for Gas Turbines, Appl. Sci. Publ. London, 1978, pp. 549–72.
R. P. Skelton and J. R. Haigh:Mat. Sci. Eng., 1978, vol. 36, pp. 17–25.
R. M. N. Pelloux:Advances in Fracture Research, ICF 5, Conf. Proc., Pergamon Press, in press.
M. O. Speidel:The Theory of Stress Corrosion Cracking in Alloys, NATO Sci. Aff. Div., Brussels, 1971, pp. 345–54. 34. D. A. Woodford: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 299-308.
H. D. Solomon and L. F. Coffin:ASTM STP 520, 1973, pp. 112-22.
L. A. James:Int. J. Fract. M., 1972, vol. 8, pp. 347–49.
H. Riedel and J.R. Rice:ASTM STP 700, 1980, pp. 112-30.
C. F. Shih, M. D. German, and V. Kumar:Int. J. Pres. Ves. & Piping, 1981, vol. 9, pp. 159–96.
H. Tada, P. Paris, and G. Irwin:The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, Del Research Corp., Hellertown, PA, 1973, pp. 27.1–28.1.
K. M. Friedl, R. B. Scarlin, and V. Zelizko:Advances in Fracture Research, ICF 5, Conf. Preprints, Pergamon Press, Conf. Proc. in press, 1981, vol. 2, pp. 923-32.
H. Schmidt: unpublished research, BBC-Research Center, CH-5405 Baden, Switzerland, 1981.
H. W. Griinling, K. Schneider, and H.v. Amim:COST-50, 2nd round, final report, Brown Boveri & Cie. AG, Zentrales Labor fur Werkstofftechnik, Postfach 351, D-6800 Mannheim 1, Germany, 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffelner, W. High-cycle fatigue-life of the cast nickel base-superalloys in 738 LC and IN 939. Metall Trans A 13, 1245–1255 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02645508
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02645508