Abstract
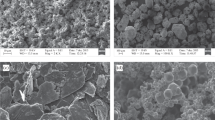
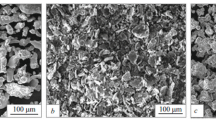
Rapidly-solidified powders of an iron-based superalloy were characterized before and after consolidation by hot isostatic pressing. Powders made by inert gas atomization were compared to powders made by centrifugal atomization. Although many of the powder characteristics were similar, the microstructures were not. The inert gas atomized powder structure is cellular while the centrifugally atomized powder structure is dendritic. In general the finer powder particles have the finer micro-structure with the effect more noticeable in centrifugally atomized powders. After consolidation, the differences in microstructure are more dependent on the consolidation temperature and post-consolidation heat treatment than in the powder type or size. Higher consolidation temperatures and/or post-consolidation heat treatment will result in transformation of the as-solidified microstructures. The transformed microstructure and the mechanical properties can in some cases be related to the as-solidified structure. Heat treatment is needed to obtain mechanical properties equivalent to those of ingot metallurgy processed material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Cohen, B.H. Kear, and R. Mehrabian: inRapid Solidification Processing, Principles and Technologies, II, M. Cohen, B. H. Kear, and R. Mehrabian, eds., Claitor’s Publishing Div., Baton Rouge, LA, 1980, p. 1.
R. Mehrabian, B. H. Kear, and M. Cohen, eds.:Rapid Solidification Processing, Principles and Technologies, Claitor’s Publishing Div., Baton Rouge, LA, 1978,e.g., pp. 78, 239, and 246.
M. Cohen, B.H. Kear, and R. Mehrabian, eds.:Rapid Solidification Processing, Principles and Technologies, II. Claitor’s Publishing Div., Baton Rouge, LA, 1980,e.g. pp. 1, 273, and 385.
J. K. Beddow:The Production of Metal Powders by Atomization, Heydon and Son, Ltd., London, 1978.
J. A. Tallmage:Powder Metallurgy Processing-New Techniques and Analysis, H.A. Kuhn and A. Lawley, eds., Academic Press, New York, NY, 1978, p. 1.
A.R. Cox, J. B. Moore, and E. C.van Reuth:Proc. Third International Symposium on Superalloys, B.H. Kear, D.R. Muzyka, J. K. Tien, and S. T. Wlodek, eds., Claitor’s Publishing Division, Baton Rouge, LA, 1976, p. 45.
P. R. Holiday, A. R. Cox, and R. J. Patterson, II: Ref. 2, p. 246.
C. J. Levi and R. Mehrabian:Metall. Trans. B, 1980, vol. 11B, p. 21.
B. H. Kear, P. R. Holiday, and A. R. Cox:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, p. 191.
R. D. Field and H. L. Fraser:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, p. 131.
J. E. Smugeresky and R. M. German:Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9A, p. 253.
S. R. Coriell and R. F. Sekerka: Ref. 3, p. 25.
M. C. Flemings:Solidification Processing, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1974, p. 58.
J. W. Cahn, S. R. Coriell, and W. J. Boettinger: “Symposium on Laser and Electron Beam Processing,” C. W. White and P. S. Pearcy, eds., Materials Research Society, Boston, MA, November 18, 1979.
A. W. Thompson and J. A. Brooks:Metall. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, p. 1431.
T. Headley, M. M. Karnowsky, and W. R. Sorenson:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, p. 345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smugeresky, J.E. Characterization of a Rapidly Solidified Iron-Based Superalloy. Metall Trans A 13, 1535–1546 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644793
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02644793