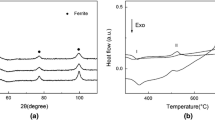
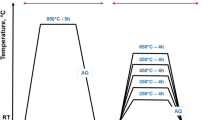
The effect of heat treatment on the microstructure, hardness and density of sintered (1129°C, 45 min) specimens of iron-base powder alloys containing 0.8 – 2.5% C, 2% Cu and additives of chromium- and molybdenum-alloyed Astaloy E iron powder is studied.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Here and below in the paper the content of elements is given in wt.%.
References
F. V. Lenel, Powder Metallurgy: Principles and Applications, Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, NJ (1980), 225 p.
R. M. German, Powder Metallurgy of Iron and Steel, Wiley, USA (1998).
M. M. A. Bepari and K. M. Shorowordi, “Effects of molybdenum and nickel additions on the structure and properties of carburized and hardened low carbon steels,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 155, 1972 – 1979 (2004).
K. Saitou, “Microwave sintering of iron, cobalt, nickel, copper and stainless steel powders,” Scr. Mater., 54(5), 875 – 879 (2006).
M Azadbeh, et al., “Modeling the response of physical and mechanical properties of Cr – Mo prealloyed sintered steels to key manufacturing parameters,” Mater. Design, 55, 633 – 643 (2014).
K. Tabeshfar and G. A. Chadwick, “Dimensional changes during liquid phase sintering of Fe – Cu compacts,” Powder Metall., 27(1), 19 – 24 (1984).
R. Oro, et al., “Liquid phase sintering: spreading, wetting and infiltration behavior in a successful reference system, Fe – C – Cu,” in: Proc. Euro PM 2011, Barcelona, Spain (2010), pp. 57 – 62.
N. Candela, et al., “Influence of microstructure on mechanical properties of molybdenum alloyed P/M steels,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 168(3), 505 – 510 (2005).
M. Zhang, et al., “Effect of heat treatment on the micro-indentation behavior of powder metallurgy nickel-based superalloy FGH96,” Mater. Design, 49, 705 – 715 (2013).
Metals, Handbook, Vol. 4. Heat Treating (1991), p. 237.
Steel Powders for Sintered Components, Iron, Höganäs AB (2002).
H. S. Shin, et al., “The liquid film migration in a sintered Fe – Cr – C base alloy,” Metall. Mater. Trans., A26(6), 1389 – 1393 (1995).
S. Berg, “P/M steel suitable for sinter hardening in respect of cost and performance,” Adv. Powder Met. Particulate Mater., 5, 5 – 8 (2001).
G. Dowson, Powder Metallurgy: The Process and Its Products, Adam Hilger, USA (1990).
V. de P. Martinez, et al., “Mechanical alloying of Cu – Mo powder mixtures and thermodynamic study of solubility,” Mater. Lett., 61(4), 929 – 933 (2007).
F. C. Campbell, Elements of Metallurgy and Engineering Alloys, ASM International (2008), p. 64.
Y. W. Rhee, Y. L. Ho, and L. K. Suk-Joong, “Diffusion induced grain-boundary migration and mechanical property improvement in Fe-doped alumina,” J. Europ. Ceram. Soc., 23(10), 1667 – 1674 (2003).
H. Danninger, et al., “Heat treatment of Cr – Mo sintered steels based on Astaloy CrM,” in: European Congress and Exhibition on Powder Metallurgy EURO PM-2001 (2001), pp. 28 – 33.
H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, “Martensite and bainite in steels: Transformation mechanism & mechanical properties,” Le Journal de Physique IV, 7, C5-367 – C5-376 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 7, pp. 51 – 54, July, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ostovan, F., Matori, K.A., Yusoff, H.M. et al. Investigation of the Structure and Hardness of Quenched Sintered Materials Produced from Iron-Base Alloyed Powders (Astaloy E). Met Sci Heat Treat 58, 431–434 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-016-0030-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-016-0030-8