Abstract
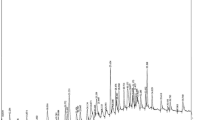
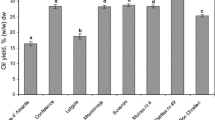
Fatty acid compositions of crude melon seed oil from two different sources were compared. Melon seeds fromCitrullus vulgaris (syn.C. lanatus) contained phosphatidylcholine (PC), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) and phosphatidylserine (PS), whereas melon seeds fromCitrullus colocynthis contained only PC and LPC, but not PS. Analysis of the total lipids revealed that the major fatty acid of the oils was 18:2n-6.Citrullus vulgaris seed oil contained 71.3% andC. colocynthis contained 63.4% of 18:2n-6. The predominant fatty acids in theC. vulgaris PC were 18:2n-6 (32.2%), 18:1n-9 (26.4%) and 16:0 (22.2%), whereas theC. colocynthis PC contained 44.6% of 18:1n-9 as the major fatty acid. The level of monoenes in theC. colocynthis variety (46.2%) was different from theC. vulgaris (27.3%). The major fatty acid in the LPC was 18:1n-9 for both varieties. Notably, theC. colocynthis variety did not contain any PS. The major fatty acids in theC. vulgaris PS were 18:1n-9 (37.9%) and 18:2n-6 (33.7%). Of all the phospholipids, LPC contained the greatest amount of monoenes, 48.6–52.4%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Girgis, P., and F. Said,J. Sci. Food Agric. 19:615 (1968).
Kamel, B.S., H. Dawson and Y. Kakuda,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 62:881 (1985).
Curtis, L.C.,Proc. Am. Hort. Sci. 52:403 (1948).
Sawaya, W.N., N.J. Daghir and P. Khan,J. Food Sci. 48:104 (1983).
Kroll, J., and F.R. Hassanien,Nahrung 27:K1 (1983).
Lazos, E.S.,J. Food Sci. 51:1382 (1986).
Scholfield, C.R., inLecithins, edited by B.F. Szuhaj and G.R. List, American Oil Chemists’ Society, Champaign, 1985, pp. 1–20.
Folch, J., M. Lees and G.H. Sloane-Stanley,J. Biol. Chem. 226:497 (1957).
Akoh, C.C., and R.S. Chapkin,Lipids 25:613 (1990).
Chapkin, R.S., S.D. Somers and K.L. Erickson, Ibid.:766 (1988).
Weber, E.J., inLecithins, edited by B.F. Szuhaj and G.R. List, American Oil Chemists’ Society, Champaign, 1985, pp. 39–55.
Cherry, J.P., Ibid.,, edited byB.F. Szuhaj andG.R. List, American Oil Chemists’ Society, Champaign, 1985, pp. 57–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Akoh, C.C., Nwosu, C.V. Fatty acid composition of melon seed oil lipids and phospholipids. J Am Oil Chem Soc 69, 314–316 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02636057
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02636057