Abstract
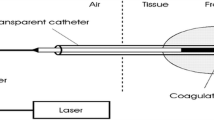
Interstitial thermal laser destruction is an attractive modality for treatment of primary and metastatic liver tumours. Using a bare fibre the volume of tissue destroyed is limited and repeated therapy is necessary. This is time consuming and it is not easy to be certain that the entire lesion is treated. We have investigated the use of a modified laser fibre. The tip of this fibre is provided with a cap made of quartz glass emitting the laser radiation laterally and circumferentially. The necrosis had an ellipsoid shape with a size amounting to 2.1±0.63 cm on 1.6±0.58 cm using 3 W power with an exposure of 600s. These lesions were much larger than the necrosis induced by bare laser fibre photocoagulation which, at most, amounts to 1.2±0.46 cm using 1.5W power for 600s. These sizes were very suitable for using the method clinically. However, the lesions were not always reproducible due to damage of the fibre during long time exposure. We conclude that further research is necessary to increase the reliability of the fibre before clinical application for therapy of liver metastasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matthewson, K, Coleridge-Smith P, Northfield TC, Bown SG. Comparison of continuous wave and pulsed excitation for interstitial Nd-YAG laser induced hyperthemia.Lasers Med Sci 1986,1:197–201
Matthewson K, Coleridge-Smith P, O'Sullivan JP. Biological effects of intrahepatic Nd-Yag laser photocoagulation in rats.Gastroenterology 1987,93:550–7
Van Eyken P, Hiele M, Fevery J et al. Comparative study of low power Neodymium-YAG laser interstitial hyperthermia versus ethanol injection for controlled hepatic tissue destruction.Lasers Med Sci 1991,6:35–42
Huang GT, Wang TH, Sheu JC et al. Low-power laserthermia for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Cancer 1991,27:1622–7
Masters A, Bown SG. Interstitial laser hyperthermia in the treatment of tumours.Lasers Med Sci 1990,5:129–36
Castro DJ, Lufkin RB, Saxton RE et al. Metastatic head and neck malignancy treated using MRI guided interstitial laser phototherapy: an initial case report.Laryngoscope 1992,102:26–32
Sugiyama K, Sakai T, Fujishima I et al. Stereotactic interstitial laser-hyperthermia using Nd-YAG laser.Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 1990,54–5:501–5
Roux FX, Merienne L, Leriche B et al. Laser interstitial thermotherapy in stereotactical neurosurgery.Lasers Med Sci 1992,7:121–6
Frank F, Hessel S. Technical prerequisites for the interstitial thermotherapy with the Nd-Yag laser.Optical Fibers in Medicine V. SPIE, 1990,1201:233–8
Van Eeden PJ, Steger AC, Bown SG. Fibre tip considerations for low power laser interstitial hyperthermia.Lasers Med Sci 1988,3:A336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiele, M., Penninckx, F., Gevers, A.M. et al. Interstitial thermotherapy for liver tumours: Studies of different fibres and radiation characteristics. Laser Med Sci 8, 121–125 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02547808
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02547808