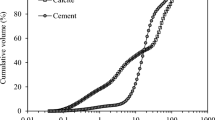
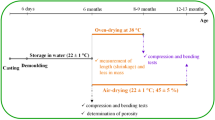
Abstract
This paper concerns the observation, interpretation and modelling of changes in mortar strength at the very beginning of its lifetime in relation to the advance of hydration, taking a special interest in the nature of the cement and that of the superplasticizer.
A set of values was defined and determined experimentally in order to quantify the following:
-
-the initial dispersion provided to the microstructure by the superplasticizer,
-
-the effectiveness of the hydrates corresponding, at a given degree of hydration, to the ratio of the infinitestimal increase in the strength to the corresponding increase in the quantity of products formed,
-
-the relative variation in effectiveness of the hydrates in the mortar depending on the influence of the dispersing agent.
During the early phase preceding traditional setting, it seems that there is a unique relation between the character of the initial dispersion and the binding efficiency. It is thought that increases in the binding efficiency of the hydrates relate only to the increase in the degree of flocculation and the initial characteristics of the mortar without additive.
Résumé
Cet article concerne l’observation, I’interprétation et la modélisation de l’évolution des résistances du mortier au tout début de son existence en fonction de l’avancement de l’hydratation, en s’intéressant particulièrement à l’influence de la nature du ciment et de celle du superplastifiant.
Il y est défini et déterminé expérimentalement un ensemble de grandeurs visant à quantifier:
-
-Ia dispersion initiale apportée à la microstructure par le fluidifiant,
-
-le rendement des hydrates correspondant, à un degré d’hydratation donné, au rapport de l’augmentation infinitésimale des résistances par l’augmentation correspondante de la quantité des produits formés,
-
-la variation relative du rendement des hydrates dans le mortier traduisant l’influence du fluidifiant sur le rendement.
Pendant la phase précédant la prise traditionnelle, il semble qu’il y ait une relation unique entre les grandeurs adimensionnelles traduisant la dispersion initiale et la variation relative du rendement, ce qui tendrait à montrer que l’accroissement du rendement des hydrates ne serait donc fonction que de l’accroissement du degré de floculation et des caractéristiques initiales du mortier non adjuvanté.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Legrand, C. and Wirquin, E., ‘Study of the strengths of very young concrete as a function of the amount of formed hydrates-Influence of superplasticizers’,Mater. Struct. 166 (27) (1994) 106–109.
Mutin, J.C., Nonat, A. and Eddajibi, A.H., ‘Hydration et prise’ in ‘Connaissance générale du béton’ (École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, Paris, 1989).
Powers, T.C., ‘The Properties of Fresh Concrete’ (John Wiley, New York, 1968).
Jiang, S.P., Mutin, J.C. and Nonat, A., ‘Analysis of the hydrationsetting relation: towards a comprehensive approach of the cement setting’, Proceedings of the 9th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement, 1992 (New Delhi) Volume IV, 17–23.
Legrand, C. and Wirquin, E., ‘Influence of superplasticizers dosage on the quantity of hydrates needed to obtain a given strength for very young concrete’,Mater. Struct. 167 (27) (1994) 135–137.
Legrand, C. and Wirquin, E., ‘First development of the strength in a microconcrete’ in ‘Hydration and Setting of Cements’ Proceedings of an International Workshop, July 1991 (RILEM, Dijon, 1992) 299–306.
Kouakou, A., Legrand, C. and Wirquin, E., ‘Mesure de l’énergie d’activation apparente des ciments dans les mortiers à l’aide du calorimètre semi-adiabatique de Langavant’,Mater. Struct. 191 (29) (1996) 444–447.
Legrand, C., ‘Le comportement rhéologique des suspensions de ciment’ in ‘Le Béton Hydraulique’ (École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, Paris, 1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editorial note Prof. Claude Legrand is a RILEM Senior Member. He participates in the work of RILEM TCs 145-WSM (Workability of Special Concrete Mixes) and 150-ECM (Efficiency of Concrete Mixers).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kouakou, A., Legrand, C. Influence of initial microstructuring of the cement paste in fresh mortar on early hydration-strength binding. Mat. Struct. 31, 225–229 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480419
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480419