Abstract
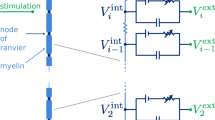
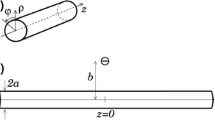
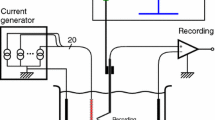
The paper extends a mathematical model for point-source electrical stimulation of a nerve. In the original model, it was assumed that all the axons in the nerve have the same diameter. In this paper the model is extended to represent a nerve with an arbitrary distribution of axon diameters. It is shown that the assumption of identical axons is justified for a typical human nerve if the ‘representative’ axon diameter is taken as the area-weighted average of the diameter distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, K. W. andPlonsey, R. (1988) Development of a model for point source electrical fibre bundle stimulation.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,26, 466–475.
Altman, K. W. andPlonsey, R. (1989a) Analysis of the longitudinal and radial resistivity measurements of the nerve trunk.Ann. Biomed. Eng.,17, 313–324.
Altman, K. W. andPlonsey, R. (1989b) Excitation in a model for time-dependent electrical nerve bundle stimulation. IEEE EMBS 11th Ann. Int. Conf., Seattle, Washington, 8th–12th Nov., 975–976.
Altman, K. W. andPlonsey, R. (1990a) Point source nerve bundle stimulation: Effects of fiber diameter and depth on simulated excitation.IEEE Trans.,BME-37, 688–698.
Altman, K. W. andPlonsey, R. (1990b) Analysis of excitable cell activation: relative effects of external electrical stimuli.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,28, 574–580.
Andrietti, F. andBernardini, G. (1984) Segmented and ‘equivalent’ representation of the cable equation.Biophys. J.,46, 615–623.
Boyd, I. A. andDavey, M. R. (1968)Composition of peripheral nerves. E. & S. Livingstone, London.
Geddes, L. A. andBaker, L. E. (1967) The specific resistance of biological material—a compendium of data for the biomedical engineer and physiologist.Med. & Biol. Eng.,5, 271–293.
McNeal, D. R. (1976) Analysis of a model for excitation of myelinated nerve.IEEE Trans.,BME-23, 329–337.
Plonsey, R., Henriquez, C. andTrayanova, N. (1987) Extracellular (volume conductor) effect on adjoining cardiac muscle electrophysiology.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,26, 126–129.
Poduslo, J. F. (1984) Glycoproteins of the peripheral nervous system. InPeripheral neuropathy, vol. 1.Dyck, P. J., Thomas, P., Lambert, E. H. andBunge, R. (Eds.), W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Rattay, F. (1986) Analysis of models for external stimulation of axons.IEEE Trans.,BME-33, 974–977.
Roth, B. J. andWikswo, J. P. Jr (1985) The electric potential and magnetic field of an axon in a nerve bundle.Math. Biosci.,76, 37–57.
Roth, B. J. andGielen, F. L. H. (1987) A comparison of two models for calculating the electrical potential in skeletal muscle.Ann. Biomed. Eng.,15, 591–602.
Rubinstein, J. T. andSpelman, F. A. (1988) Analytical theory for extracellular electrical stimulation of nerve with focal electrodes. I. Passive unmyelinated axon.Biophys. J.,54, 975–981.
Rushton, W. A. H. (1951) A theory of the effects of fibre size in medullated nerve.J. Physiol.,115, 101–122.
Schoonhoven, R., Stegeman, D. F., van Oosterom, A. andDautzenberg, G. F. M. (1988) The inverse problem in electroneurography—I: conceptual basis and mathematical formulation.IEEE Trans.,BME-35, 769–777.
Tasaki, I. (1955) New measurements of the capacity and the resistance of the myelin sheath and the nodal membrane of the isolated frog nerve fiber.Am. J. Physiol.,181, 639–650.
Thomas, P. K. andOlsson, Y. (1984) Microscopic anatomy and function of the connective tissue components of peripheral nerve. InPeripheral neuropathy, vol. 1.Dyck, P. J., Thomas, P., Lambert, E. H. andBunge, R. (Eds.), W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Tung, L. A. (1978) A bidomain model for describing ischemic myocardial d.c. potentials. Ph.D. dissertation, MIT, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Veltink, P. H., van Alsté, J. A. andBoom, H. B. K. (1988) Simulation of intrafascicular and extraneural nerve stimulation.IEEE Trans.,BME-35, 69–75.
Veltink, P. H., van Veen, B. K., Struijk, J. J., Holsheimer, J. andBoom, H. B. K. (1989) A modeling study of nerve fascicle stimulation.,BME-36, 683–692.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roth, B.J., Altman, K.W. Steady-state point-source stimulation of a nerve containing axons with an arbitrary distribution of diameters. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 30, 103–108 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446201
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446201