Abstract
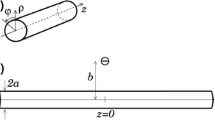
A model is presented for determining the excitation (transmembrane) potentials on nerve and muscle fibres in a cylindrical bundle from an external point source electrode at the surface and within the preparation. The fibre bundle is considered to be immersed in an infinite isotropic conductive medium and is idealised as an infinitely extending cylinder. This cylinder is initially represented as an isotropic monodomain. A subsequent degree of complexity introduces anisotropy in the monodomain, and finally the bundle is represented as an anisotropic bidomain comprised of the interstitial radial and longitudinal conductivities, the intracellular longitudinal conductivity and the fibre membrane between the two domains. In this latter model, electrical coupling from extracellular to intracellular space is included by means of the bidomain formulation. Computational aspects are discussed, and preliminary results for prescribed conditions are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, K. W. andPlonsey, R. (1986) A two-part model for determining the electromagnetic and physiologic behavior of cuff electrode nerve stimulators.IEEE Trans.,BME-33, 285–293.
Bracewell, R. N. (1986)The Fourier transform and its applications, 2nd edn., revised. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Brigham, E. O. (1974)The fast Fourier transform. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
Clark, J. W. andPlonsey, R. (1970) A mathematical study of nerve fiber interaction.Biophys. J.,10, 937–957.
Gray, A. andMathews, G. B. (1966)A treatise on Bessel functions and their applications to physics. Dover Publications, New York.
Hodgkin, A. L. andRushton, W. A. H. (1946) The electrical constants of a crustacean nerve fibre.Proc. R. Soc. B.,133, 444.
McNeal, D. (1976) Analysis of a model for excitation of myelinated nerve.IEEE Trans.,BME-23, 329–337.
Plonsey, R. andBarr, R. (1982) The four-electrode resistivity technique as applied to cardiac muscle.,BME-29, 541–546.
Plonsey, R. andBarr, R. C. (1986) A critique of impedance measurements in cardiac tissue.Ann. Biomed. Eng.,14, 307–322.
Press, W. H., Flannery, B. P., Teukolsky, S. A. andVetterling, W. T. (1986)Numerical recipes: the art of computing. Cambridge University Press, New York.
Rattay, F. (1986) Analysis of models for external stimulation of axons.IEEE Trans.,BME-33, 974–977.
Reilly, J. P., Freeman, V. T. andLarkin, W. D. (1985) Sensory effects of transient electrical stimulation—evaluation with a neuroelectric model.,BME-32, 1001–1011.
Roth, B. J. andGielen, F. L. H. (1987) A comparison of two models for calculating the electrical potential in skeletal muscle.Ann. Bioeng.,15, 591–602.
Smythe, W. R. (1968)Static and dynamic electricity. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Stegeman, D. F. andde Weerd, J. P. C. (1982) Modelling compound action potentials of peripheral nerves in situ. I. Model description; evidence for a non-linear relation between fibre diameter and velocity.EEG Clin. Neurophysiol.,54, 436–448.
Tasaki, I. (1955) New measurements of the capacity and the resistance of the myelin sheath and the nodal membrane of the isolated frog nerve fiber.Am. J. Physiol.,181, 639–650.
Tasaki, I. (1964) A new measurement of action currents developed by single nodes of Raniver.J. Neurophysiol.,27, 1199–1206.
Weidmann, S. (1952) The electrical constants of Purkinje fibres.J. Physiol.,118, 348–360.
Wilson, O. B., Clark, J. W., Ganapathy, N. andHarman, T. L. (1985) Potential field from an active nerve in an inhomogeneous, anisotropic volume conductor—the forward problem.IEEE Trans. BME-32, 1032–1041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altman, K.W., Plonsey, R. Development of a model for point source electrical fibre bundle stimulation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 26, 466–475 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441913
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441913