Abstract
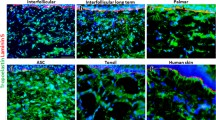
Three different, human epithelial-mesenchymal compounds (EMC) were generated in vitro for prospective grafting in epithelial defects. All compounds consisted of a fibroblast-populated collagen lattice as a mesenchymal component seeded with different types of cultured epithelial cells isolated from biopsies of healthy skin, oral mucosa and respiratory mucosa. Maturation of the epithelial cells was enabled by the presence of a high calcium concentration (1.8 mM) when cultures were lifted to the air-liquid interface. Light and electron microscopy revealed moderate differentiation of the multilayered epithelium in all compounds as well as basement membrane development at the epithelial-mesenchymal junction after 2–3 weeks. A coherent, tissue-like consistency of the collagen lattice and the presence of a basement membrane preventing detachment of the epithelium permitted easy handling and even loose suturing of the compounds produced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aihara M (1989) Ultrastructural study of grafted autologous cultured human epithelium. Br J Plast Surg 42: 35–42
Bell E, Sher S, Hull B, Merill C, Rosen S, Chamson A, Asselineau D, Dubertret L, Coulomb B, Lapiere C, Nusgens B, Neveux Y (1983) The reconstruction of living skin. J Invest Dermatol 81: 2s-10s
Billingham RE, Reynolds J (1952) Transplantation studies on sheets of pure epithelium and on epidermal cell suspensions. Br J Plast Surg 5: 25–36
Bohnert A, Hornung J, Mackenzie IC, Fusenig NE (1986) Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions control basement membrane production and differentiation in cultured and transplanted mouse keratinocytes. Cell Tissue Res 244: 413–429
De Luca M, Albanese E, Megna M, Cancedda R, Mangiante PE, Cadoni A, Franzi AT (1990) Evidence that human oral epithelium reconstituted in vitro and transplanted onto patients with defects in the oral mucosa retains properties of the original donor site. Transplantation 50: 454–459
Gallico GG, O'Connor NE, Compton CC, Kehinde O, Green H (1984) Permanent coverage of large burn wounds with autologous cultured human epithelium. N Engl J Med 311: 448–451
Gallico GG, O'Connor NE, Compton CC, Remensnyder JP, Kehinde O, Green H (1989) Cultured epithelial autografts for giant congenital naevi. Plast Reconstr Surg 84: 1–9
Hanamure Y, Deguchi K, Ohyama M (1994) Ciliogenesis and mucus synthesis in cultured human respiratory epithelial cells. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 103: 889–895
Hull BE, Finley RK, Miller SF (1990) Coverage of full-thickness burns with bilayered skin equivalents: a preliminary clinical trial. Surgery 107: 496–502
Jorissen M, Schueren B van der, Berghe H van den, Cassiman JJ (1989) The preservation and regeneration of cilia on human nasal epithelial cells cultured in vitro. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 246:308–314
Langdon JD, Leigh IM, Navsaria HA, Williams DM (1990) Autologous oral keratinocyte grafts in the mouth. Lancet 335: 1472–1473
Mol MAE, Nanninga PB, Eendenburg JP van, Westerhof W, Mekkes JR, Ginkel CJW van (1991) Grafting of venous leg ulcers. An intraindividual comparision between cultured skin equivalents and full-thickness skin punch grafts. J Am Acad Dermatol 24: 77–82
Nanchahal J, Otto WR, Dover R, Dhital SK (1989) Cultured composite skin grafts: biological skin equivalents permitting massive expansion. Lancet II: 191–193
O'Connor NE, Mulliken JB, Banks-Schlegel S, Kehinde O, Green H (1981) Grafting of burns with cultured epithelium prepared from autologous epidermal cells. Lancet I: 10: 75–78
Premachandra DJ, Woodward BM, Milton CM, Sergeant RJ, Fabre JW (1990) Treatment of postoperative otorrhoea by grafting of mastoid cavities with cultured autologous epiedermal cells. Lancet 335: 365–367
Ross UH (1992) In vitro production and subsequent transplantation of a living skin substitute in rat model. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 249: 263–267
Ueda M, Ebata K, Kaneda T (1991) In vitro fabrication of bioartificial mucosa for reconstruction of oral mucosa: basic research and clinical application. Ann Plast Surg 27: 540–549
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ross, U.H., Wittmann, G. Living epithelial-mesenchymal compounds formed in vitro suitable for autografting. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 254 (Suppl 1), S12–S17 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02439712
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02439712