Summary
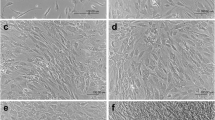
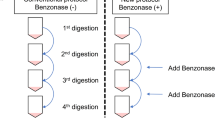
Dichloromethylenebisphosphonate (Cl2MBP), a compound structurally related to inorganic pyrophosphate but resistant to hydrolysis of endogenous phosphatase to yield inorganic phosphate, inhibits bone resorption and soft tissue mineralizationin vivo. Previously, we have shown that bone cells isolated from rat calvaria respond profoundly to the exposure of Cl2MBP. To determine whether the cellular effects evoked by Cl2MBP are confined to a particular bone cell type, calvaria from 1 day postnatal rats were subjected to a sequential time-dependent enzyme digestion, yielding five bone cell populations marked by differences in PTH response, alkaline phosphatase activity and collagen, as well as hyaluronic acid synthesis. Culturing these bone cell populations with Cl2MBP revealed that previously observed results found with mixed bone cells (inhibition of cell proliferation, diminution of hyaluronic acid synthesis, and increase in alkaline phosphatase) were limited to cell populations which, according to the isolation scheme, stem from the outer tissue layer(s) of the calvaria. Collagen synthesis, however, was found to be equally increased regardless of cell type. These present results indicate that the action of Cl2MBP on bone may be cell specific.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleisch H (1983) Bisphosphonates: mechanisms of action and clinical applications. In: Peck W. A. (ed) Bone and mineral research. Annual 1. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, Oxford, Princeton, pp 319–351
Meunier PJ, Alexandre C, Edouard C, Mathieu L, Chapuy MC, Bressot C, Vignon E, Trechsel U (1979) Effects of disodium dichloromethylenediphosphonate on Paget's disease of bone. Lancet 2:489–492
Douglas DL, Russell RGG, Preston CJ, Prenton MA, Duckworth T, Kanis JA, Preston FE, Woodhead JS (1980) Effect of dichloromethylene disphosphonate in Paget's disease of bone and in hypercalcaemia due to primary hyperparathyroidism or malignant disease. Lancet 2:1043–1047
Chapuy MC, Meunier PJ, Alexandre CM, Vignon EP (1980) Effects of disodium dichloromethylene diphosphonate on hypercalcemia produced by bone metastases. J Clin Invest 65:1243–1247
Sirs ES, Sherman WH, Baquiran DC, Schlatterer JP, Osserman EF, Canfield RE (1980) Effects of dichloromethylene diphosphonate on skeletal mobilization of calcium in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 302:310–315
Jung A, van Ouwenaller C, Chantraine A, Donath A (1981) Use of dichloromethylene diphosphonate in metastatic bone disease. N Engl J Med 305:343–344
Fast DK, Felix R, Dowse C, Neuman WF, Fleisch H (1978) The effects of diphosphonates on the growth and glycolysis of connective-tissue cells in culture. Biochem J 172:97–107
Ende JJ (1978) Some effects of EHDP and Cl2MDP on the metabolism of isolated bone cells. Proc Kon Ned Akad Wet C-81:252–264
Felix R, Fleisch H (1979) Increase in alkaline phosphatase activity in calvaria cells cultured with diphosphonates. Biochem J 183:73–81
Felix R, Fast DK, Sallis JD, Fleisch H (1980) Effect of diphosphonates on glycogen content or rabbit ear cartilage cells in culture. Calcif Tissue Int 30:163–166
Felix R, Fleisch H (1981) Increase in fatty acid oxidation in calvaria cells cultured with diphosphonates. Biochem J 196:237–245
Felix R, Fleisch H (1981) The effect of diphosphonates on periosteal bone cells in culture. Experientia 37:817–818
Guenther HL, Guenther HE, Fleisch H (1979) Effects of 1-hydroxyethane-1, 1-diphosphonate and dichloromethanediphosphonate on rabbit articular chondrocytes in culture. Biochem J 184:203–214
Guenther HL, Guenther HE, Fleisch H (1981) The effects of 1-hydroxyethane-1, 1-diphosphonate and dichloromethanediphosphonate on collagen synthesis by rabbit articular chondrocytes and rat bone cells. Biochem J 196:293–301
Guenther HL, Guenther HE, Fleisch H (1981) The influence of 1-hydroxyethane-1, 1-diphosphonate and dichloromethanediphosphonate on lysine hydroxylation and cross-link formation in rat bone, cartilage and skin collagen. Biochem J 196:303–310
Gallagher JA, Guenther HL, Fleisch H (1982) Rapid intracellular degradation of newly synthesized collagen by bone cells. Effect of dichloromethylenebisphosphonate. Biochim Biophys Acta 719:349–355
Cohn DV, Wong GL (1979) Isolated bone cells. In: Simmons DJ, Kunin AS (eds) Skeletal research: an experimental approach. Academic Press, New York, San Francisco, London, pp 3–20
Wiestner M, Krieg T, Hörlein D, Glanville R, Fietzek P, Müller P (1979) Inhibiting effect of procollagen peptides on collagen biosynthesis in fibroblast cultures. J Biol Chem 254:7016–7023
Guenther HL, Felix R, Fleisch H (1984) Comparative study of deflazacort, a new synthetic corticosteroid, and dexamethasone on the synthesis of collagen in different rat bone cell populations and rabbit articular chondrocytes. Calcif Tissue Int 36:145–152
Solursh M, Vaeerweyck A, Reiter RS (1974) Depression by hyaluronic acid of glycosaminoglycan synthesis by cultured chick embryo chondrocytes. Dev Biol 41:233–244
Engel PC, Jones JB (1978) Causes and elimination of erratic blanks in enzymatic metabolite assay involving the use of NAD+ in alkaline hydrazyne buffers: improved conditions for the assays of L-glutamate, L-lactate, and other metabolites, Anal Biochem 88:475–484
Brown BL, Albano J, Ekins R, Sgherzi A, Tampion W (1971) A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenine 3′,5′ cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J 121:561–582
Borle AB, Nichols N, Nichols G (1960) Metabolic studies of bone in vitro. I. Normal bone. J Biol Chem 235:1206–1210
Luben RA, Wong GL, (Cohn DV 1976) Biochemical characterization in the parathormone and calcitonin of isolated bone cells—provisional identification of osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Endocrinology 99:526–534
Luben RA, Wong GL, Cohn DV (1977) Parathyroid-stimulated resorption of devitalised bone by osteoclast-type bone cells. Nature 265:626–630
Wong GL, Cohn DV (1974) Separation of parathyroid hormone and calcitonin-sensitive cells from non-responsive bone cells. Nature 252:713–715
Partridge NC, Alcorn D, Michelangeli VP, Kemp BE, Ryan GB, Martin TJ (1981) Functional properties of hormonally responsive normal and malignant cultured rat osteoblastic cells. Endocrinology 108:213–219
Miller SC, Jee WSS (1977) The comparative effects of dichloromethylenediphosphonate (Cl2MDP) and ethane-1-hydroxy-1, 1-diphosphonate (EHDP) on growth and modeling of rat tibia. Calcif Tissue Int 23:207–214
Luben RA, Goggins JF, Raisz LG (1974) Stimulation by parathyroid hormone and bone hyaluronate synthesis in organ culture. Endocrinology 94:737–745
Felix R, Guenther HL, Fleisch H (1984) The subcellular distribution of14C-dichloromethylenebisphosponate and14C-hydroxyethylene-1, 1-bisphosphonate in cultured calvaria cells. Calcif Tissue Int 36:108–113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guenther, H.L., Gallagher, J.A. & Fleisch, H. Differential response of bone cells isolated by sequential digestion to dichloromethylenebisphonate in culture. Calcif Tissue Int 36, 568–575 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02405368
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02405368