Abstract
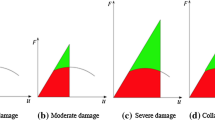
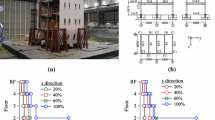
An energy-based damage model currently used for seismic analysis of structures is modified to ensure a positive value in the damage index at all levels of inelastic response. At the ultimate limit state, the modified model gives the same plastic strain energy capacity as the previous damage model. Testing of small-scale cantilever specimens showed different strength deterioration parameters for coldrolled and hot-rolled steel and composite systems of double cantilevers. The strength deterioration parameter for the composite system is smaller than that of the individual cantilevers. Various weighted-average rules for combining local member damage indices into story-level damage indices are compared with measured story-level damage indices. Based on testing of small-scale steel cantilevers, the current combination rules predict the story-level damage reasonably well near the ultimate limit state but tend to underestimate the story-level damage in the less severely damaged states. A combination rule based on best fitting of the experimental data obtained in this study is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D i orD ji :
-
damage index forith local member
- D s j , Dglobal :
-
damage index forjth story and structure, respectively
- (D s j )theo :
-
story-level damage index predicted from local member damage
- (D s j )expt :
-
measured story-level damage index
- E h or(E h ) i :
-
design plastic strain energy dissipated byith member
- E hm :
-
plastic strain energy dissipated under monotonic loading
- m :
-
exponent for combination rule
- V y :
-
lateral yield strength ofith member
- w i orw j :
-
weighting factor forith local orjth story damage index, respectively
- W i :
-
tributary gravity load resisted byith member
- (W story ) j :
-
gravity load resisted byjth story
- W total :
-
total gravity load of structure
- β* :
-
strength deterioration parameter
- Δ m :
-
maximum response displacement
- Δ um :
-
ultimate displacement under monotonic loading
References
Barenberg, M.E. andFoutch, D.A., “Evaluation of Seismic Design Procedures for Highway Bridges,”Jour. Struct. Div., ASCE,114 (7),1588–1605 (1988).
Bracci, J.M., Reinhorn, A.M., Mander, J.M., and Kunnath, S.K., “Deterministic Model for Seismic Damage Evaluation of Reinforced Concrete Structures,” technical report NCEER-89-0033, National Center for Earthquake Engineering Research, State University of New York at Buffalo, (1989).
Chai, Y.H., Romstad, K.M., andBird, S.M., “Energy-based Linear Damage Model for High-intensity Seismic Loading,”Jour. Struct. Div., ASCE,121 (5),857–864 (1995).
Park, Y.J. andAng, A.H.S., “Mechanistic Seismic Damage Model for Reinforced Concrete,”Jour. Struct. Div., ASCE,111 (4),722–739 (1985).
Park, Y.J., Ang, A.H.S., andWen, Y.K., “Seismic Damage Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Buildings,”Jour. Struct. Div., ASCE,111 (4),740–757 (1985).
Seidel, M.J., Reinhorn, A.M., andPark, Y.J., “Seismic Damageability Assessment of R/C Buildings in Eastern U.S.,”Jour. Struct. Div., ASCE,115 (9),2184–2203 (1989).
Williams, M.S. andSexsmith, R.G., “Seismic Damage Indices for Concrete Structure: A State-of-the-art Review,”Earthquake Spectra,11 (2),319–349 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, Y.H. Characterization of story-level seismic damage using an energy-based damage model. Experimental Mechanics 39, 53–61 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02329301
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02329301